A shortage of just 4 products provokes a headache
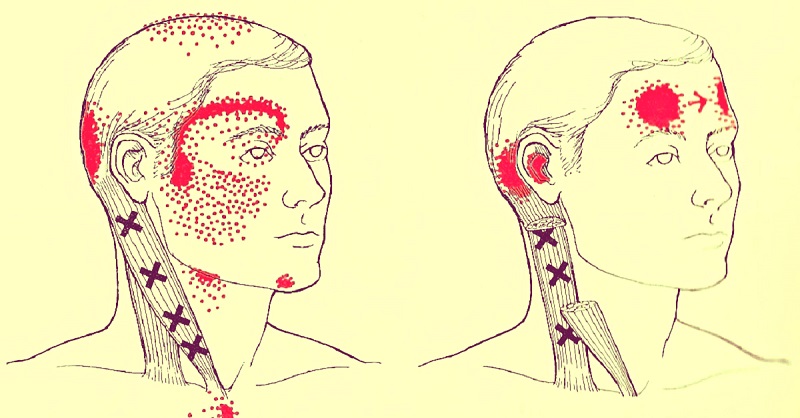
Headache (cephalalgia, from Greek to brain + pain) is one of the most common nonspecific symptoms of various diseases and pathological conditions, which is pain in the head or neck area. Most often, the cause of the headache is vascular disorders associated with the expansion or spasm of the vessels inside or outside the cranium. This general clinical symptom should be distinguished from migraine, which is its particular case.
Headache is not a pain sensation of the nervous tissue of the brain, since there are no pain receptors in it. It arises due to the effect on the areas located in the head or neck 9, sensitive to pain: the skull (periosteum), muscles, nerves, arteries and veins, subcutaneous tissue, eyes, nasal sinuses and mucous membrane. The method of treating a headache depends on the identified disease or the cause of the onset of the symptom, in most cases, analgesics are prescribed.
Migraine (french migraine from other Greek or hematrania hemicrania - hemicrania or "half of the head") is a neurological disease whose most common and characteristic symptom is episodic or regular severe and painful headache attacks in one (rarely in both) Half of the head. In this case, there are no serious head injuries, stroke, brain tumors, and the intensity and pulsating nature of the pains are associated with a vascular headache, and not with a headache from tension. Headache with migraine is not associated with an increase or a sharp decrease in blood pressure, a bout of glaucoma or an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP).
Headaches are the companions of many diseases. But there is one kind of headache, unbearable and exhausting. It's a migraine. It is familiar to every 6th inhabitant of the planet. As a rule, pain with migraine is localized in one hemisphere of the brain. More often migraine is observed in emotional people, with reduced resistance to stress.
Historical reference
Individual mentions of periodic headaches, reminiscent of the description of the clinic migraine, appeared more than 5000 years ago. In the XIX-XVI centuries BC in Babylonian literature, descriptions of attacks of headache were also found, which was compared with a flash of lightning. For the first time gemikraniya, which is accompanied by vomiting and poor health in general, was described in the papyrus of Ebers as a "half headache". In the book "Tzizhuang" of 581 BC it was stated that Chinese doctors tried to treat the symptom with the "chen-chiu therapy" method (acupuncture and cauterization). Herodotus wrote that in Ancient Egypt among the priests involved in healing, there were those who specialized only in the treatment of headaches. Hippocrates in his work "Aphorisms" described various types of cephalgia and first identified it as a disease, and he first described the symptoms of migraine. Aretei Cappadocia in the book "On acute and chronic diseases" described 3 types of headache: cephalgia - a moderate, episodic, lasting from 1-3 hours to several days and resembling a tension headache; Cephalea - lasting longer, more intense, difficult to treat and, most likely, due to organic pathology; Heterocranium - similar in the clinic with migraine. The term "hemicrania", from which the term "migraine" originated, was introduced by Galen. He used the works of Aretei of Cappadocia, but the described symptoms gave an explanation. The Roman physician explained hemicranic pain with anatomical features of the structure of the skull, believing that the sickle-shaped septum explains the pain in only one half of the skull. The first classification of headaches called "De Cephalalgia" was developed by Thomas Willis in 1672. In 1787, Christian Baur divided all the headaches into idiopathic (primary) and symptomatic (secondary), and also identified 84 categories of headaches. At the end of the XIX century, in the book "On migraine headaches and other similar diseases" by Edward Leving, the differential difference between migraine and other headaches similar in clinical practice was demonstrated. The clinical symptoms of cluster headache were described by Harris in 1926, but the priority of the description of the disease belongs to Reader (1924). In 1939, Horton also described the clinic for clustered cephalalgia, but unlike Harris, he regarded it as erythromelalgia, and then as histamine cephalgia. Later, this condition was referred to as Horton's syndrome. For the first time the similarity of these states was indicated by Ekb in 1947, and since 1952, at the suggestion of Kunkel, the disease is called "cluster cephalgia." In 1962, at the National Institute of Diseases of the Nervous System, the Headache Committee introduces a new definition of headache in practice, and also develops a classification of cephalgia and prosopalgia that lasted 26 years. In 1988, the International Classification Committee for Headache introduces a new classification of headaches and facial pains, which is still used today.
Causes of headache
Predisposition to migraine is due to heredity, gender (women are more exposed to it), an incorrect way of life, a psycho-emotional background. Age is also important: doctors observe migraines more often in young people, beginning with adolescence, and the disease fades to old age.
Nutrition plays a huge role in the occurrence of migraine attacks. It is proved that the deficiency of a number of elements in the body is capable of provoking severe headaches 4 times more often. We identified 4 groups of products, the lack of which contributes to the onset of migraine.
Deficiency of these substances leads to a headache
Predisposition to migraine is due to heredity, gender (women are more exposed to it), an incorrect way of life, a psycho-emotional background. Age is also important: doctors observe migraines more often in young people, beginning with adolescence, and the disease fades to old age.
Nutrition plays a huge role in the occurrence of migraine attacks. It is proved that the deficiency of a number of elements in the body is capable of provoking severe headaches 4 times more often. We identified 4 groups of products, the lack of which contributes to the onset of migraine.
1 Folic acid and vitamin B12
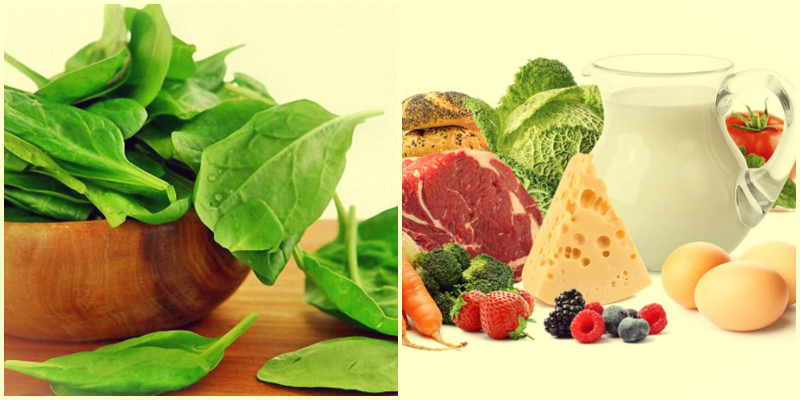

People who lack these substances are prone to excessive irritability and absent-mindedness. They are also more prone to stress. Interestingly, we often try to relieve the headache with drugs that contain aspirin. And this substance just reduces the content of folic acid and vitamin B12 in the body.
Spinach is the champion in the maintenance of folic acid, it is also rich in broccoli, asparagus, avocado, beetroot, carrot, pumpkin. Vitamin B12 is abundant in chicken eggs.
2 Copper and iron
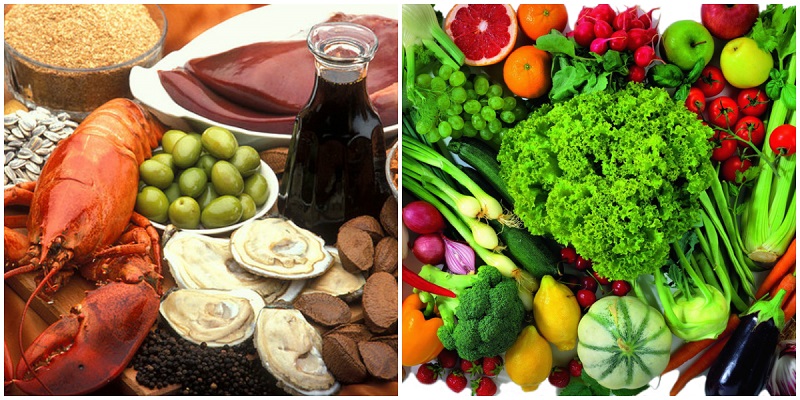

Deficiency of copper and iron is more characteristic of women and leads directly to anemia, hypotension, migraine and depression. Copper beans, nuts, goat cheese, avocados are rich in honey ... And regularly eating greens, lettuce, sunflower seeds, sesame, liver and sea cabbage, you will fill up the iron reserves.
3 Vitamin B6
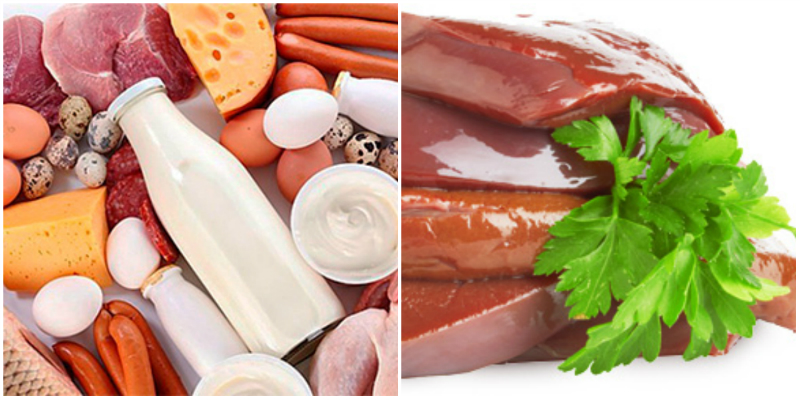

Deficiency of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) - one of the main factors of the occurrence of vascular diseases. Its a lot in beans, liver, fresh vegetables, as well as cereals. Lie on these products, if you want to preserve the health of the brain, nerves, heart and blood vessels.
4 Vitamin D
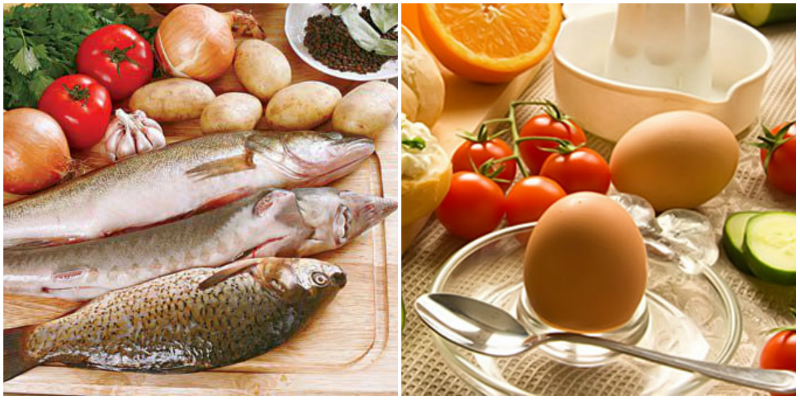

Vitamin D is naturally produced in our body under the sun's rays. And in the winter time it can be obtained from food. Eggs, beans, liver, seafood, dairy products abound in this important element of metabolism.
Full nutrition, exercise, outdoor walks can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of migraine headaches. And to relieve stress and calm down will help aromatherapy .
We hope this article will help you and your friends to forget about migraines! Be healthy!
Via takprosto.cc


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.