Swine flu | Swine flu (A / H1N1, A / H1N2, A / H3N1, A / H3N2 and A / H2N3)

Symptoms - The main symptoms coincide with the usual symptoms of influenza - headache, fever, cough, vomiting, diarrhea, runny nose.
Prevention - For the primary prevention of persons at risk in the Russian Federation and abroad, an accelerated development of a vaccine for the prevention of influenza on the basis of a specific strain of the pathogen is carried out. The WHO memo on highly pathogenic influenza indicates the need to exclude close contact with people who "seem unwell, have high body temperature and cough." It is recommended that your hands and soap are washed thoroughly and often enough. "Stick to a healthy lifestyle, including full sleep, eating healthy food, physical activity." With proper heat treatment, the virus dies.
At the University of Southampton, the bactericidal role of surfaces of copper and copper alloys against the A / H1N1 virus was established. So, if for about 24 hours on the surface of stainless steel there were about 500,000 units of the virus, then after 1 hour 75% of the total number of virus units were inactivated on the copper surface, and after 6 hours only 500 units remained active (0.075% of the original quantity ). In Germany and Great Britain, the production of domestic and water fittings made of bactericidal copper alloys has already begun.
Treatment - A person can be vaccinated (through vaccinations) and congenital immunity.
Treatment of diseases caused by most strains of "swine flu" is carried out with drugs Amantadine, Zanamivir, Oseltamivir and Rimantadine, which, however, have limited effectiveness.
Most known antiviral agents are ineffective in a disease caused by a mutated "Mexican" strain of A / H1N1. At the moment there is no full-blown drug against this strain of A / H1N1 - existing drugs can only alleviate the course of the disease, especially in its early stages (in cases when the patient seeks medical help within 48 hours after the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease).
Do not use products containing aspirin, due to the risk of developing Ray's syndrome.
Epidemics caused by the H1N1 influenza virus
Memo on the prevention of influenza and other acute respiratory infections (ARI) - ARI is a large group of acute viral diseases that are characterized by airborne transmission and primary injury of the upper respiratory tract. Influenza is the most common acute respiratory viral disease, a feature of which is extremely rapid spread and severe intoxication. The mechanism of transmission of the influenza virus is airborne. Influenza can lead to serious complications from the pulmonary, cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine systems. Prevention of diseases. Preventive measures are directed primarily to increase the body's resistance to the action of pathogens of influenza, as well as other ARI and ARI.
Experts, especially during the period of increasing morbidity, note the following methods of prevention:
- Full nutrition with the inclusion of vitamins in their natural form;
- Hardening and frequent ventilation of premises;
- The use of restorative and toning-immunomodulating drugs and preparations of targeted immunostimulating action.
Highly effective are recommendations of general sanitary and hygienic direction, in particular: - Frequently wash hands with soap, especially after a visit;
- Cover your nose and mouth with a handkerchief (or disposable napkins), especially when you cough and sneeze;
- Widely use the means of alternative medicine (folk), homeopathic preparations, oxolin ointment.
What you need to pay attention to:
- There are some features of the clinical course of influenza in different age groups. In young children, symptoms of neurotoxicosis (vomiting, convulsions), even in the presence of subfebrile body temperature, may appear first of all. In elderly people against the background of acute respiratory infections, cardiovascular diseases worsen, chronic foci of infection are activated, which significantly influences the clinical manifestations of influenza.
- Disease mainly begins acutely, from manifestations of general intoxication (chills, a feeling of heat, severe headache, pain in the eyes). The patient is disturbed by general weakness, aches in the back, sacrum, joints, muscle pains, sleep is disturbed. Attention is drawn to the face of the patient: hyperemia, puffiness, shining eyes - it all looks like the face of a tear-stained child. The incubation period for influenza varies from several hours to 3 days.
- Basically, on the second day of the disease, a dry cough appears, and begins to disturb the pain in the chest. On 3-5 days cough becomes softer, there is an insignificant quantity of slimy sputum. Nasal breathing is disrupted through the mucosal edema.
- Already in the first hours the body temperature can reach 39-40 ° C, keep at this level for 2-3 days. However, if further fever continues or develops its second wave (the whole lasts longer than 5-7 days), this indicates the development of bacterial complications.
- Treatment of ARVI and influenza is a complex problem, so it should be determined by a doctor. It's not necessary to self-medicate, it's dangerous! With timely and correct treatment, the illness ends with complete recovery.
Memo for influenza A / H1N1
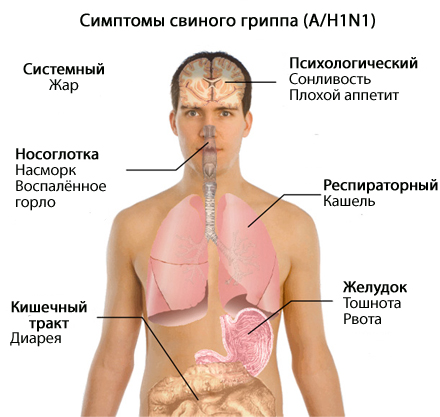
Clinical signs of influenza type A / H1N1 :
headache,
muscle pain,
a sore throat,
Increased body temperature,
cough,
Runny nose, nasal congestion,
In some cases - vomiting and diarrhea.
How can you get an A / H1N1 influenza virus?
From another sick person airborne, airborne (virus particles are transported by air from a sick person to a healthy one during a conversation, coughing, sneezing), with close contact (finding at a distance of about 2 meters)
How long is an infectious influenza A / H1N1?
The infectious period (the period when the patient is dangerous to others) with influenza type A / H1N1 may be within 7 days of the onset of the disease, but if the clinical symptoms of the disease persist - then until they disappear
How to prevent infection with influenza A / H1N1?
- avoid contact with people who have manifestations of influenza infection;
- limit visits to places of large concentrations of people;
- often ventilate the premises;
- wash hands frequently with soap and water;
- Try not to touch the eyes, nose or mouth with unwashed hands;
- avoid hugs, kisses and handshakes;
- Cover your nose and mouth with a sneeze or cough with a disposable nasal towel, which should be discarded immediately after use;
- if a person has flu symptoms, then it is necessary to stay away from it at a distance of at least two meters
How to prevent the spread of influenza in children's institutions?
- during the epidemic rise in the incidence of influenza, new children are not admitted to pre-school institutions;
- the transfer of children from the group to the group is excluded;
- to stop visiting of a children's institution by unauthorized persons;
- in the preschool institutions, a daily inspection of children is of great importance when they arrive at it in the morning, and at the slightest signs of the disease children are not accepted into the collective;
- the room in which the children are located should be well ventilated, they must be ventilated several times a day;
- Wet cleaning of premises is necessary not less than two times a day;
- it is necessary for children to observe the rules of personal hygiene (frequent washing of hands during the day);
- for the time of the epidemic (pandemic) the staff of the institution should wear gauze clothes;
- staff of the institution should be vaccinated against seasonal or influenza A H1N1 (if vaccine is available);
- Persons who have been in contact with a child who has confirmed the diagnosis of influenza A H1N1, it is necessary to conduct a course of chemoprevention of oseltamivir
- for the time of the epidemic (pandemic), children's institutions are closed.
What should parents know to prevent infecting children with the flu?
- teach children to wash their hands often with soap for 20 seconds;
- Parents should also perform this procedure, which serves as a good example for children;
- teach children to cough and sneeze into a napkin or hand;
- Parents should also perform this procedure, which serves as a good example for children;
- to teach children not to approach the patients closer than one and a half to two meters;
- sick children should stay at home (do not attend pre-school and school);
- Refrain children and parents from visiting places of congestion.
What should I do if a child gets sick with the flu?
- at the first signs of the disease the child must be put in bed and call a doctor;
- leave the sick child at home, except when she needs urgent medical help. Do not send the child to school or to a preschool;
- patients with influenza are dangerous to others and should be immediately isolated. Inadmissible their appearance in public transport, children's collectives and other places of mass stay of people.
- the patient should be placed in a separate room or fenced with a screen, allocate him individual dishes, towels, personal hygiene items;
- do not allow patient contact with healthy family members, except those who care for him;
- The person who cares for the patient should wear a two-layer gauze dressing or a one-time mask, which must be changed every 4 hours. After each contact with the patient, you should thoroughly wash your hands with soap;
- the mask should be either disposable, which after the change is thrown into the basket, or multiple, which after washing should be thoroughly ironed with a hot iron;
- to carry out ventilation of the premises several times a day;
- daily do wet cleaning of the premises of the house;
- air in the premises should be of sufficient humidity;
- to have disposable nasal tissues and a basket for used napkins within the reach of the patient;
- create a comfortable baby for the sick child. Very important is rest, bed rest;
- If the child has a fever, then it must give antipyretics (paracetamol or ibuprofen drugs), then call a doctor;
- Before the doctor comes to give the child to drink a lot of liquid (juice, water, fruit juice, compote, etc.);
- Do not self-medicate. Corresponding medical treatment to the patient is prescribed only by a doctor!
What signs of the disease should a child immediately seek medical help?
- Accelerated or shortness of breath
- Cyanosis around the mouth, other skin
- Appearance of hemorrhages (even very small ones), nosebleeds
- High body temperature
- Refusal of the child from drinking
- Impossibility to awaken a child or lack of her reaction to treatment
- Excessive excitation of the child or appearance of seizures
- Occurrence of vomiting, frequent loose stools
- Child's complaints of severe headache.
- Absence of urination or tears during crying.
Memo to prevent the spread of influenza type A H1 N1 in closed children's institutions
I. Organizational activities:- during the epidemic rise in the incidence of influenza, new children are not accepted for children's institutions;
- the transfer of children from the group to the group (from class to class;
- access to a children's institution of unauthorized persons is terminated
II. Sanitary and hygienic requirements for premises during the rise in the incidence of influenza:
- the premises in which the children are located must be well ventilated,
They must be ventilated several times throughout the day;
- air in the premises should be of sufficient humidity;
- it is necessary to clean the rooms at least twice a day;
- door handles, faucets in washstands, toilet surfaces should be treated several times a day with disinfectant solutions.
III. How to prevent infection with influenza A H1 N1?
- all staff of the institution should wash their hands often with soap;
- for the time of the epidemic (pandemic), the staff of the institution should wear gauze bandages;
- Outside the children's facility, staff should avoid being in crowded places, contacting people with flu;
- older children should be taught how often to wash their hands with soap;
- older children need to be taught to cough and sneeze into a napkin or arm. After that, you must throw the napkin into the basket and wash your hands with soap.
V. Personnel actions when finding a sick child:
- at the first signs of the disease the child must be isolated, then immediately hospitalized;
- before the child is hospitalized, do not allow contact with her other children, personnel other than those who take care of;
- a person who cares for a sick child should wear a respirator, or a two-layer gauze dressing or a one-time mask. Masks need to be changed every 4 hours. Mask, respirator should fit tightly to the face. After each contact with the patient, replacing the mask should be thoroughly washed with soap and hands;
- a sick child should have a separate dish, toys, pot
V. Actions of staff in the outbreak after isolation of the patient:
- after hospitalization of the child his dishes, toys, the pot must be washed with the use of detergents, disinfectants;
- After hospitalization of the child, his bedding can not be carried in an armful, after contact with the patient's linen, you should thoroughly wash your hands with soap.
- prevent persons with signs of influenza from working;
- staff of the institution should be vaccinated against seasonal or influenza A H1N1 (if vaccine is available);
- Persons who have been in contact with a child who has confirmed the diagnosis of influenza A H1N1, it is necessary to conduct a course of chemoprophylaxis of oseltamivir


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.