Modern operating systems are fairly resistant to crashes and, as a rule, the higher the stability of the system, the smaller the changes introduced into the system during operation. However, still have to make changes to the operating system configuration (installing new software, system updates or drivers, changing system settings and components), as a result, Windows may respond inappropriately. Therefore, it is important to do regular backups, which can be useful when restoring the system. This article looks at what features a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 to recover from various failures.
Usually, the process of loading the operating system is divided into several parts:
initialization, the boot loader, kernel loading, registration. Accordingly, if problems arise on any of these phases, the operating system can not perform a successful upload.
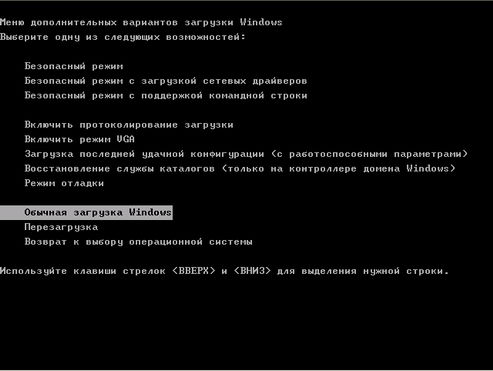
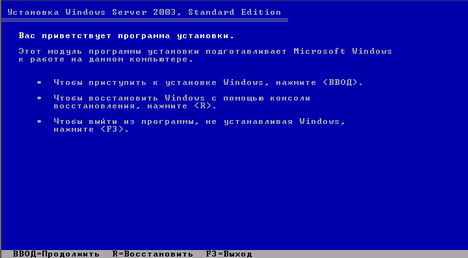
In Windows there are various recovery tools that you can use to repair Windows performance. This Safe Mode (Safe Mode), Recovery Console (Recovery Console) and the ERD (Automatic System Recovery). To select these modes, you must enter the Startup menu, for that press F8 at boot time. (Screen 1)
Using the Last Known Good Configuration (Last Known Good Configuration)
If the problem occurred immediately after the change of system settings (usually after you install a new driver), you should use the Windows boot to the Last Known Good Configuration (Last Known Good Configuration).
This mode restores the registry information and driver settings that were used when the system last successfully loaded.
At the same time, recovering only registry branch HKLM \ System \ CurrentControlSet, and therefore do not solve the problems caused by damage to or loss of the system partition or files.
If you are unable to boot Windows in the Last Known Good Configuration, the last change that was made in the system, and were likely factor hindering starting correctly. Remove or upgrade malfunctioning software or drivers, then boot normally.
Boot the system in Safe Mode (Safe Mode)
When booting in Safe Mode (Safe Mode) Windows loads only the drivers and services that are needed for the job. You must use this mode to solve the problems caused by bugs in the drivers, bad programs or services that start automatically. Booting in this mode, disable or remove misbehaving component that prevents booting Windows.
If the computer is unable to boot into safe mode, use the Recovery Console (Recovery Console). If the Recovery Console and does not help, it is likely a hardware problem. Remove the new hardware and try to start your computer in normal mode.
In the case in Safe Mode loading was completed successfully, it is necessary to determine the cause of the possible failure during the boot process. The operating system provides several tools that can help.
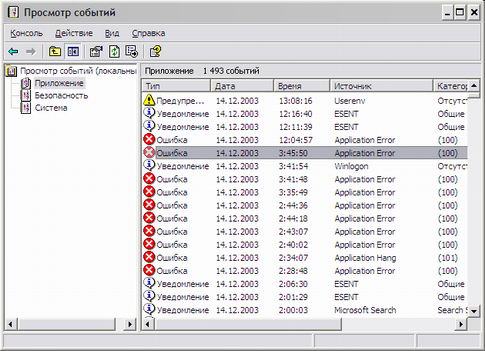
Log on as a user with system administrator privileges, and view event logs (eventvwr. Msc). It is necessary to carry out an analysis of the system log and the Application log for warnings and error messages (screen 2). Pay attention to the event sources.
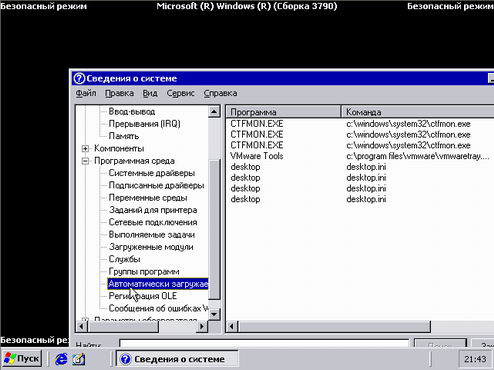
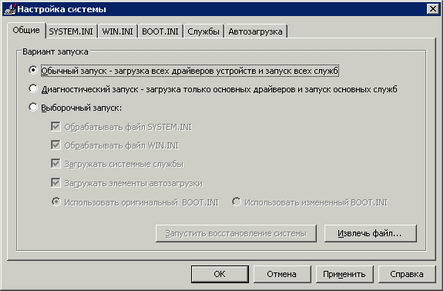
No information about the System Viewer (msinfo32. Exe) displays various information about the hardware, system components, and software environment. To get started, use this tool to determine the failed devices, and possible conflicts between them. In the console tree, select the component and then Problem Devices. Also check for conflicts under Hardware Resources. If the problematic device is detected, disable, reconfigure, or try update the driver used by them. To disable the device drivers and use the Device Manager snap-in from Administrative Tools \ Computer Management. If hardware conflicts were found, please see Software Environment - Startup Programs (screen 3). Try to disable programs that are downloaded automatically, and then restart the computer. To set a ban, use the System Configuration Utility (Msconfig.exe), if after loading the ban goes well, allow for a startup program. If this does not work, use the Diagnostic Startup mode that can be set in the System Configuration Utility (Screen 4).
Look at the boot log file -% Systemroot% \ Ntbtlog. txt and mark those device drivers and services that were not loaded in Safe Mode. This may help to identify the problem component.
Using Microsoft Windows Recovery Console (Recovery Console)
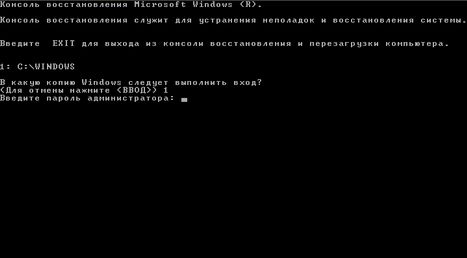
Recovery Console is a set of command line tools that can help to restore Windows in case the computer is unable to boot. Access to the console can be run in two ways: from a bootable CD Windows Server 2003 (Screen 5) or if the Recovery Console was pre-installed on the computer. The console must be run in the event that either the Last Known Good Configuration, or run in recovery mode the positive effect was not given.
What you can do in this mode:
- access to local drives;
- to enable or disable device drivers or services;
- Copy the files from the installation disk or removable media (reverse copying is prohibited);
- create a new boot sector and a new master boot record (MBR) . This may be necessary if the load fails with the existing boot sector.
Recovery Console prevents unauthorized access to the sections requiring a password to enter the local system administrator (screen 6). For domain controllers, this password is set on the stage of the master works DCPROMO or use the ntdsutil command. exe with a further mode selection «Set DSRM Password».
In order to display all available commands Recovery Console, type help at the command prompt (or help <command> to get help on a specific command).
Before you start working with teams check the status of your hard drive. To do this, use chkdskF / R command. In that case if chkdsk can not gain access to your disk, do check all cable connections and switches on your disk.
If chkdsk can not fix a problem with the hard drive, your file system or MBR may have been tampered with. Try using Fixmbr team and Fixboot to recover, otherwise you have to re-create partitions and reformat your hard disk or to apply to companies that are engaged in the restoration of hard disk drives.
In addition, the inability to use Safe Mode to boot the system can be caused by damage to the Windows registry or boot files. The boot files (Ntldr, Ntdetect.com, Boot.ini, Ntbootdd.sys - for SCSI controllers, bootfont.bin - for localized versions of Windows), located in the root of the system partition can be restored from the i386 directory on the installation of Windows Server 2003 distribution. system registry files every time you create a copy of the state of the system are copied to the system partition to the directory% Systemroot% \ Repair. Using the Recovery Console, you can restore damaged registry files from this directory to the source -% Systemroot% \ system32 \ config. Do not forget to save your current files to another directory before performing this restore process. After that, the Windows registry will contain information that has been on since the last system state backup. Changes in the system, starting from this moment will be lost after the recovery. If the backup was never produced, the catalog Repair will contain a copy of the data made after directly after the installation of Windows.
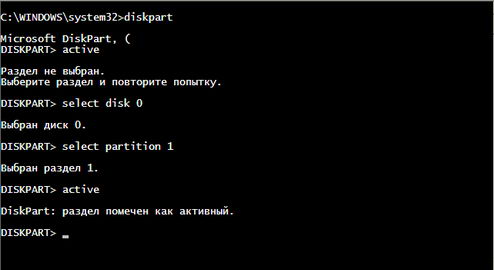
However, not all the problems blame the operating system and sometimes fails to load occurs before the download itself. For example, if any other partition you mark on the error as "active", will not contain the operating system startup files (and most likely it will be so), the computer will not start. In this case, using the Recovery Console, you must return to mark the active partition the system partition. To do this, use the diskpart command. You must first select your system partition to run files (settings select disk <n> and select partition <m> - wherein n, m numbers that satisfy the naming conventions ARC), and then use the option active A, to mark it as an active (screen 7 )..
If problems occur after the selection of the operating system to be loaded, then it indicates a loss of operating system files.
Use Automated System Recovery
Whatever it was, it is likely a server failure. Server load modes, such as Safe Mode and Last Known Good Configuration can help to restore the system. However, backup disaster recovery (FAA) should be included in the regular maintenance plan for your server as the last chance to restore Windows.
ABC performs recovery of the system partition and the state of the system needed to start and run the Windows Server 2003 component.
How to restore the system from a set of ABC?
To be able to recover from system crashes, using disaster recovery, follow these steps.
- Before starting the recovery process, you should have:
- ABC diskette created in advance;
- created in advance with media archive system partition;
- CD with the distribution;
- if the system uses a disk array controller or drive, you must have a driver for it on a separate diskette.
- Boot from the CD with the Windows Server 2003 CD- ROM or DVD- ROM.
- If there is an additional driver mentioned in the first step, press the F6 key to use it during the installation process.
- Press the F2 key when the setting mode will offer to do it at the bottom of the screen.
Insert the floppy disk into the drive of ABC, you should have created earlier (screen 7). Then follow the instructions on the screen.
It is important to understand that a set of ABC will not restore your data files. This backup set restores only Windows components and programs that have been installed in the system catalogs. It is also desirable to have restored server equipment and the same drive configuration as that of the source server.
Using the Recover your Windows installation
In that case, if you have not created a pre-set ABC, then use it for recovery is not possible. The negative result of the launch of the system through the Last Known Good Configuration or in Safe mode may be due to the loss of any Windows system files. Then you should try to repair your damaged installation of Windows Server 2003 running Windows installation from the CD. To do this, proceed as follows.
- Boot from the CD with the Windows Server 2003 CD- ROM or DVD- ROM.
- If there is an additional driver for the disk drive, press the F6 key to use it during the installation process.
- After starting the installation process by clicking on "Proceed to install Windows» (Start Windows Setup), and press ENTER to continue. No need to choose the Recovery Console usage mode. And confirm the acceptance of the license agreement.
Then, the installation process will begin to search for installed versions of Windows on your local drives. If a previous installation of Windows has not been found, you may have a problem directly with a physical disk. If the previous installation was defined, the process of installing Windows will try to recover it. From the options, select your installation of Windows Server 2003 and press R (to continue without repairing, press ESC). To restore the system, simply follow the instructions on the screen. In many cases, rehabilitation of existing Windows installation can help restore your server performance. After recovery it is imperative to perform the Event Viewer logs and determine what components or access to which resources were not restored.
Restore from Backup
The latest option is to restore from a backup, you must have been done regularly on a running system. To use it, you must install a new copy of Windows. If the local disk is workable, then delete the existing system partition and create a new one (the new partition size should be no less than the former). Install a new copy of Windows Server 2003 on the same partition where Windows was placed earlier. Then you can begin to restore from a backup.
Keep in mind that when you are installing Windows Server 2003, you will not be asked to change the default installation directory. The default location is \ WINDOWS. This constraint costs in the following cases: if a directory \ Winnt already exists, if you do the automatic installation with an indication of the parameter "TargetPath = ..." in the answer file or by selecting a new directory in the Advanced options when you run winnt32 program. exe from an installed copy of the operating system.
Use the following options to install Windows to an alternative system directory% SystemRoot%:
Perform automatic installation with an answer file. Automatic installation allows you to specify the installation directory, by using the parameter "TargetPath = NAMEWINDIR". This method may be used even when the CD-ROM and Windows Server 2003. Using Notepad, create a file Winnt. sif, containing the following parameters, and save it to a floppy disk. Make sure that the file is called Winnt. sif and has no additional expansion. txt.
-------
[Unattended]
UnattendMode = GuiAttended
OemPreinstall = No
TargetPath = WINNT
; where WINNT - is the name of your old directory
[Data]
unattendedinstall = yes
msdosinitiated = 0
------
Boot from the CD-ROM, a floppy disk at the same time with an answer file must be in the drive. The program will use the Windows installation answer file settings and create a system catalog name specified in the parameter "TargetPath" directory instead of \ WINDOWS.Or you can use a boot disk Windows 95 or Windows 98 to create a FAT or FAT32 partition on the new system / boot partition, and then create the directory \ WINNT. Boot from the CD-ROM Windows Server 2003. When the installation program detects the directory \ WINNT and asks you to overwrite it or press ESC to enter another name. Do not forget to convert FAT to NTFS.
Inability to specify the installation directory from the command line installation procedure usually does not matter, as long as there was a problem with the system partition, or until you reformat the original partition and reinstall Windows. In order to be able to restore your system from a backup you must install the Windows Server 2003 system directory with the same name, which he had in the original system, and only then to recover over the new copy of Windows.
Why is this important for us? Backup utility (ntbackup. Exe) can restore data from a backup to an alternate location, but it does not apply to restore the system state, namely it will help to return the operation of the system. In addition, if your system directory is not wearing a name \ WINDOWS, then it will be impossible to perform a full recovery without having to reinstall Windows Server 2003, the directory with the original name. For example, this situation usually occurs if a previous copy of Windows 2000 Server was in a different directory (\ WINNT) before its update to Windows Server 2003, with the result that the old name of the directory has been saved.
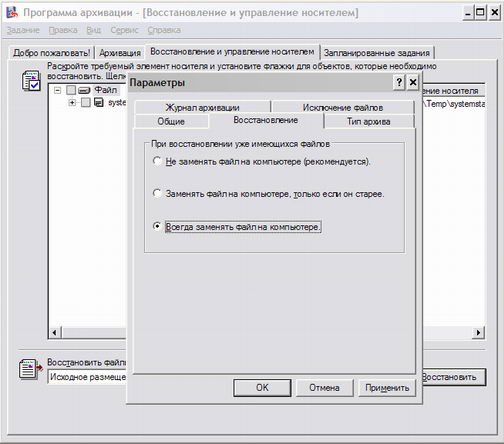
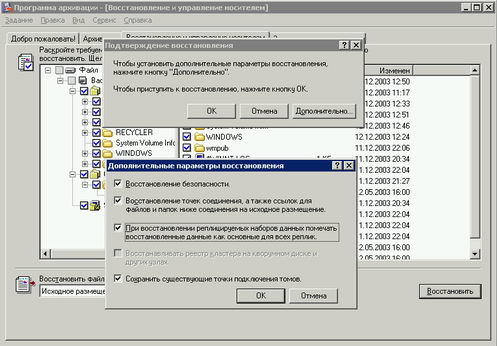
After successful installation of Windows Server 2003, the directory with the old name, use the Archiving Program (ntbackup. Exe) to perform a full system recovery (including system status) since the last backup. Necessarily need to use additional parameters and specify the "Replace existing data" mode to recover files that are already on your computer. This will ensure the recovery of all files from your backup, otherwise with the same name of the new archive copies of files and system files - files from the archive will be restored (screen 9).
When you restore the state of a domain controller system, which is unique in the domain, you must be sure to install the optional parameter "When restoring replicated data sets, mark the restored data as the primary for all replicas" (Screen 10). In this mode, a new database for the File Replication Service will be built (ntfrs) of data located in the SYSVOL directory only this domain controller. If you are restoring one of several DC, the said parameter point is not necessary.
If the problem persists ...
In the event that none of the above steps did not solve the problem, use sites Microsoft Product Support Services to find a solution.
- The Knowledge Base Searchable ( http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?pr=kbinfo& ) - Search technical support articles. Refine your search criteria describing your problem or error number in the system logs.
- Asked Questions Frequently ( http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=fh;rid;faqs ) - View of typical questions about the products.
- The Product How it works Support the Newsgroups Microsoft ( http://communities.microsoft.com/newsgroups/default.asp?icp=GSS&slcid=us ) - Newsgroup used to exchange experience between users of Microsoft products and professionals (Most Valuable Professionals - MVPs).
- The Updates and Software ( http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/search.asp ) - Find software and updates to the Microsoft Download Center.
- The Event ID messages the Search ( http://eventid.net/search ) - Search error descriptions and reporting systems and recommendations to address the problems.
- Experience exchange forums ( http://forum.oszone.net/ ) - Russian-speaking Conference on operating systems.
Preparing the system for recovery
Now, knowing the modes and methods of recovery, it is necessary to do everything possible to restore passed with ease. For failures in the system should be treated as a necessary and "expect" them. To be fully prepared. So, as the troubles waiting for us in case of failure or damage to equipment components.
The important point is to provide a fault-tolerant configuration from the outset. Increase resistance to system failures:
- use RAID arrays for storing system data, this will protect them from hard disk failures. It is possible to implement a RAID arrays programmatically, without using expensive hardware controllers. For more information, refer to the built-in Windows Help:
- Use uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) allows the server to properly complete the work during a power failure:
- keep in reserve all the equipment that may fail (even power supply units):
- Use clusters provide redundancy and fault tolerance even in the event of failure of one of the nodes. However, all this is achieved due to the high cost.
Back up
Regular backup of your Windows and system status is a good foundation for recovery. In that case, if you do not use a RAID array, and your system disk has failed, then Windows can be restored from a backup. You will need to first install a new copy of Windows Server 2003 before you restore from a backup. Create a scheduled task to backup the system state and the system partition on a tape or a network share folder. In addition, it is desirable to maintain a copy of all local directories available in Sharing (distributions can be excluded from the backup job). This is to ensure that after recovery from a full backup of all public folders were still available for server customers. To compare local folders with shared folders from the command line, use the net share command.
Create a Disaster Recovery System Kits
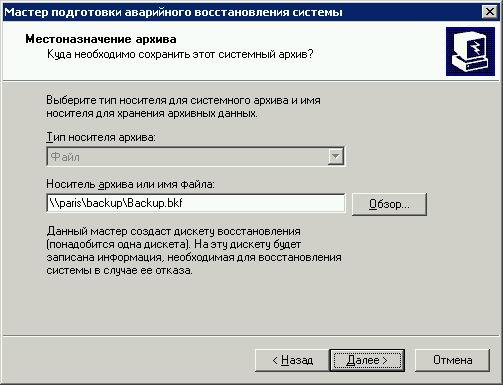
While Microsoft Windows NT and Windows 2000 use a floppy disk to save the disaster recovery system in the event of failure, Windows Server 2003 creates this Automated System Recovery set (ABC). To do this, run the Wizard to create an Automated System Recovery (screen 11) of the backup program (ntbackup. Exe). Take a blank 1.44 MB floppy disk, which will be kept information about the archive, the configuration disk (basic or dynamic), and data necessary to carry out the recovery process, as well as a backup storage medium (tape disks, ZIP disks, etc. ). (screen 12).
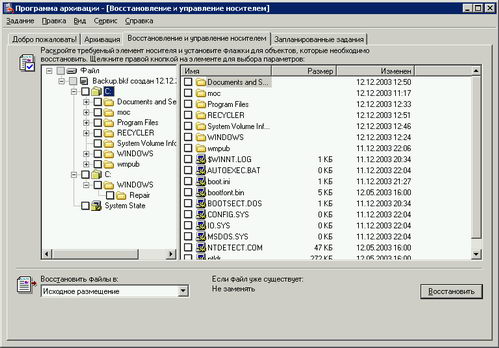
The kit will include System Status, system services, and files associated with the operating system components (or rather the system partition is full) (Screen 13). Therefore, I recommend not to create a system partition on any directory that they own, it is advisable to place them in separate sections. Data from the other sections should be included in the daily and weekly backup task server (just turn on System Status in your copy). The backup file size is usually at least 1.4 GB. After creating a set of ABC, you should keep the floppy disk with the FAA and the media as to be able to take advantage of backup media you will need is this diskette. ABC diskette is not bootable, it must only be used to restore a set of associations with the main carrier.
Sets the Emergency Repair Program Archiving executed only interactively. You can not create scheduled tasks to create them. It is recommended to create a set of ABC immediately after installation and the initial Windows setup and store it (no overwriting). This will ensure that the initial recovery point in the future. In addition, an archive made with the help of the Master System Recovery can be used to manually restore after installing a new copy of Windows.
Install the Recovery Console
Recovery Console can be used to restore the ability to boot Windows. Although you can run the Recovery Console by booting directly from the installation CD of Windows Server 2003 is much more convenient to install the Console on Windows boot options menu. To install the Recovery Console, click the "Start" menu - "Run" and type d: \ i386 \ winnt32. exe / cmdcons, where d - the drive letter of your CD- ROM. (Screen 14)
Create a floppy disk to start Windows
The boot disk may help if the Windows startup files are lost. It is not some universal launch vehicle for each machine Windows Server 2003. However, if you have a standard configuration of multiple computers, this floppy will work for all machines with the same partitioning and disk controllers from the Windows boot disk. To create a floppy disk to be copied onto a blank and formatted floppy disk the following files: Ntdetect. com, Ntldr, boot. ini (and bootfont.bin file systems for localized and Ntbootdd.sys for SCSI controllers). These files are located in the system / boot partition root (by default, they have a "hidden" attribute).
Naming conventions for ARC
Understand as hard drives and partitions are named for your system, unfortunately, is not an easy task. To ensure universal naming convention across multiple platforms, Microsoft uses specific designations for all the drives and partitions. These symbols are called ARC (short for Advanced RISC Computing) - is the primary naming convention which is used and on the Intel platform and RISC systems.
The agreement describes the adapter type and number, disc number, rdisk number and a partition number:
<Adaptertype> (x) disk (y) rdisk (z) partition (n)
<Adaptertype> - can be SCSI, multi controller or signature. Use multi for all non-SCSI controllers and SCSI controllers that use BIOS - most controllers on Intel processors.
(X) - is the controller number, starting with zero. If <adaptertype> is a signature, then (x) is an 8-character code disc.
(Y) - SCSI device number for the drives on the SCSI controller. In the case of multi this value will always be zero.
(Z) - for SCSI devices will always be zero, or a serial number for the drive on the controller of multi, numbering also starts at zero.
(N) - the partition number on the destination disk. The countdown begins with one and zero is reserved for the unused space.
Summing up
Failure will happen, so be prepared for it accordingly. Prepare procedure (scheme) recovery of your system and make a description of the major components of the server and its settings (partition sizes, file systems, server role, the administrator passwords and recovery mode, installed software, etc.). When the thunder will strike and bustle begins, as it usually happens during crashes, people often forget important steps and make wrong decisions. Standard procedures provide the sequence of actions without the need to take decisions on the spot.
partition boot sector - part of the hard disk partition that contains information about the file system disk and a short program in machine language, designed for loading the operating system.
Master Boot Record - first sector on the hard drive from which the computer boot process begins. The MBR contains the partition table for the disk and a small executable code called the primary boot code
RAID arrays - a technique standardization and classification of fault-tolerant disk systems. There are different RAID levels with different combinations of performance, reliability and cost.
28.06.2004


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.