§ 8 The constant of the counter.
In the passports for electric meters, a parameter such as the counter constant is indicated. This section tells what it is and what it is for.
It was said above that the torque of the counter disk rotation is proportional to the load, i.e.,
![]() ,
,
And the counteracting moment is proportional to the disk rotation frequency, i.e.,
![]()
If the disk rotates during t units of time, then, at equilibrium (that is, at a steady-state rotation frequency), we have.
![]() And since Pt = A and nt = N , then
And since Pt = A and nt = N , then
![]() Where N is the number of revolutions of the disk corresponding to the energy A;
C is the counter constant.
Where N is the number of revolutions of the disk corresponding to the energy A;
C is the counter constant.
The last expression shows that the amount of energy measured by the counter is proportional to the number of revolutions of the disk.
The disc is connected with a counting mechanism by means of a worm pair, by which the amount of electric power is determined.
Unlike the pointing devices, in which the measured value is determined by the arrow, when measuring the energy by the counter, it is necessary to make two readings: A1 at time t1 and A2 at time t2.
Then the measured amount of energy A with the time interval t = t2-t1 is determined as the difference of two readings, i.e.
A = A2-A1
The counter constant is determined from expression
C = A / N.
The constant shows the number of units of electricity per revolution of the disk.
It should be borne in mind that the nominal constant of the counter C nom is determined by the counting mechanism in one revolution of the disk and is unchanged.
The actual counter constant C is determined by the actual amount of energy counted by the counter per revolution of the disk.
Then the error of the counter can be expressed:
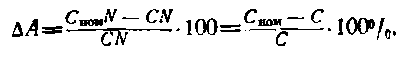
The number of revolutions of the disk, during which the counting mechanism changes by one unit of the measured value, for example by 1 kWh, is called the gear ratio of the counter.
This counter parameter is also unchanged purely mechanical value and is associated with the gear ratio of the counting mechanism.
The counter constant and the gear ratio of the counter are interrelated.
It is customary to determine the counter constant as the number of watt-seconds per revolution of the disk.
If the gear ratio is N A r / kWh, then
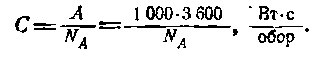
The gear ratio of the meter is usually indicated on the meter: 1 kW * h = N A of revolutions of the disk.
For example, if the shield indicates 1 kW * h = 1250 revolutions of the disk, the counter's constant will be:
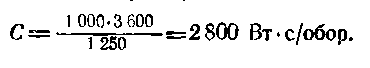
At nominal load, the disk rotates at a certain frequency, called the nominal speed.
This parameter is sometimes indicated in the technical specification of the counter (rounded rpm).
Nominal speed of rotation indirectly characterizes the wear resistance of the meter disk supports: the smaller it is, the more durable the supports.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.