The history of the first battery
The first experiments showed the ability to accumulate, ie congest electrical energy were produced shortly after the opening of the Italian scientist Volta phenomena of galvanic electricity.
In 1801, French physicist Hauterivian, skipping across the water through platinum electrodes current, found that after the current through the water is interrupted, it is possible by connecting the electrodes to each other, get a short-term electric current.
Scientist Ritter was doing then the same experience, to use instead of platinum elekrodov of gold electrodes, silver, copper and so on. D., And separating them from each other with pieces of cloth soaked in salt solutions, he received the first secondary, t. E. Capable of donating stored in therein the electric power element.
The first attempts to create a theory of such an element were made Volta, Marianini and Becquerel, who argued that the battery depends on the action of the expansion of electric shock salts solutions on the acid and alkali, and that the latter then combine to produce an electric current again.
This theory was defeated in 1926 by experiments Deryariva who first applied in the battery acidified water.
Acidified water when the current is decaying, obviously, into oxygen and hydrogen, and the decomposition of the element and is obliged by the subsequent action. This provision has proved brilliantly Grove, built his famous gas battery, consisting of plates, descended into acidified water and surrounded at the top: one - hydrogen and the other - oxygen. However, the battery in this way was very impractical, because a very large amount of gas required to file for storing large amounts of electricity, which occupied a large amount.
 Great practical improvement in the development of the battery was made in 1859 by Gaston Plante, who as a result of a long series of experiments came to the battery type, consisting of lead plates with a large surface, which lead oxide coated with a charged current, and. separating oxygen and liquid gave an electric current.
Great practical improvement in the development of the battery was made in 1859 by Gaston Plante, who as a result of a long series of experiments came to the battery type, consisting of lead plates with a large surface, which lead oxide coated with a charged current, and. separating oxygen and liquid gave an electric current.
Plante took two strips of sheet lead, paving between the cloth strip and the strip folded around a circular stick. Then, the resulting bundle, he pulled together by rubber rings and placed in a container with acidified water. Repeated loading and unloading of the battery, on the surface of the plates formed the active layer of the current, which is involved in the process and gave a large capacity element. However, the need for a very large number of charges and discharges the battery Plante to give it some capacity, greatly increases the cost of the battery cost and hampered his production.

Battery Plante
The next improvement, the battery led to its modern usage, it was used in 1880 by Camille Faure lattice lead plates, grids cells which were filled with a specially prepared mass for preparation of a pre. This process greatly simplify and cheapen the production of batteries, reducing battery forming a very short process.

Further improvements in the history of lead-acid batteries were already on the way to improve applied Faure method for filling and forming grid plate without making drastic changes in battery design. In parallel with the development of lead-acid batteries have a number of major and fatal drawbacks such as high weight per unit of capacity, failure to maintain without damage in a discharged state, and so on. G., Was the development of application for the manufacture of batteries and other metals, except lead.
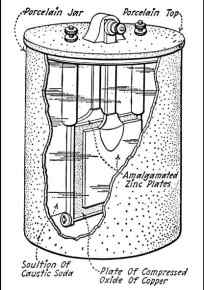
 The simplest of these batteries, but also has a number of shortcomings, is a member Lalavda. When passing through the exhaust member Lalande normal current in the reverse direction to restore the copper oxide is converted into copper recovers its liquid properties and is deposited on the zinc electrode of the zinc in the form of loose mass or powder. The latter circumstance, and hinders the application element Lalande as a battery, as deposited zinc electrode rests on very fragile, easily separated from it and does not give a good contact. The big advantage of this element is its low weight per unit of capacity, compared with lead-acid batteries.
The simplest of these batteries, but also has a number of shortcomings, is a member Lalavda. When passing through the exhaust member Lalande normal current in the reverse direction to restore the copper oxide is converted into copper recovers its liquid properties and is deposited on the zinc electrode of the zinc in the form of loose mass or powder. The latter circumstance, and hinders the application element Lalande as a battery, as deposited zinc electrode rests on very fragile, easily separated from it and does not give a good contact. The big advantage of this element is its low weight per unit of capacity, compared with lead-acid batteries.
Work on the improvement of the battery was carried out by many scientists as Rainier, Somelinom, Darius and others, and in 1901 a new type of battery was patented nesvintsovogo both Edison and Yungnerom.
This battery system comprises two plates, one containing iron oxide and another oxide black Nikkel, descended in 20% caustic solution, usually potassium hydroxide, with addition of 0.5 - 1% of lithium hydroxide.

Thomas Edison about electric - 1912 Year
Edison Yungnera elements and are widely used in cases where low weight is required and simplicity for charging batteries, since they may be any length of time in a discharged state. they displace lead-acid batteries, however, could not like because of their high price and because of the low impact and low voltage given by them. Thus, aside zhelezonikkelevym batteries, a large space for all portable and mobile units, while for lead batteries has a wide field of application in stationary installations.
Yemtsov G. Electric accumulators

You can also support shram.kiev.ua, click:
Do not be amiss to your friends and find out this information, share with them the article!

Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.