The main types of RAM (RAM)
RAM (RAM) is a device for temporary storage of information (only in the process of computer operation), provides quick access of the processor to the program and the data being processed.
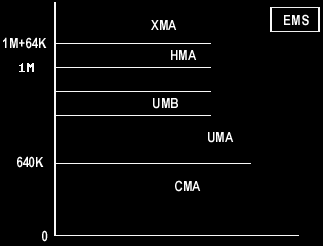
1. CMA is the main memory (Conventional Memory Area). (Area 0 - 640K).
2. UMA - Upper Memory Area. (Area 640K - 1M).
3. UMB - Upper Memory Block.
4. HMA - High Memory (High Memory Area). (Area 1M + 64K).
5. XMA - Extended Memory Area. (Area, above> 1M + 64K).
6. EMS - additional memory (Expanded Memory). (Located on a separate board).
640 KB problem
The IBM PC with the processor 8088 and 8086 RAM, available for DOS and applications, is no more than 640 KB. This was a step forward for the early 80's, compared with 64 KB for other computers. However, with the advent of the processors 80286, 80386 and older, and also modern programs, for example Windows, the limitation of 640 KB has turned into a problem that has been successfully solved with the advent of additional memory and especially extended memory. Extended Memory is a memory higher than 1M + 64K. With the advent of extended memory, the 80286, 80386SX and 80486SX processors can directly access 16 MB of memory, and the 80386DX, 80486DX and older processors can access 4 GB.
Expanded Memory is not currently applied.
Access to extended memory in MS-DOS and Windows is provided by the himem.sys driver and the extended memory manager emm386.exe, which are loaded using the config.sys file. The main memory also remains the same as before, equal to 640 KB, but try to maximally free it for application programs, downloading keyboard, mouse, etc. drivers. In the upper memory (UMA and UMB) using the autoexec.bat file. IBM RAM standard RAM: 1 MB; 2 MB; 4 MB; 8 MB; 16 MB; 32 MB; 64 MB, etc.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.