Stereo pictures (> 127 pieces)
Stereo image is a picture or video sequence that uses two separate images to achieve a stereo effect. To create a stereo image in the 3D modeling program, you must make a double rendering of the scene - from two cameras corresponding to the eyes of the observer.
How to watch stereo pictures

Various devices and methods are used to create and view stereo images. To look is simple, it is more difficult to learn. And on the monitor will be no worse than on paper! But when printing with poor quality or large magnification, you can see the printer's errors. The picture is not visible ...
- Approaching almost in a dense to the monitor (~ 5 cm to the screen).
- We relax our eyes and do not try to focus.
- We take the head backwards (~ 15-20 cm from the screen).
- If you "caught" the focus during the "departure", then we return to step 1.
- If you feel that soon 21 cm "departure" is delayed in this position.
- The main thing is not to "catch" the focus, meaning - the image should remain as it were outside the picture.
All the stereo images were successfully tested by me! They work! If you can not "see", try another one!
Not everything is easy to see, for some it takes a lot of strength and patience ...  And I do not advise to get involved!
Nothing happens when overexertion.
And I do not advise to get involved!
Nothing happens when overexertion.
PS At the bottom of the page you can download all images in one archive.
"True" stereoscopy
- The parallel look method allows you to see a full-color stereo picture without having any equipment, the stereo effect is achieved by bringing the eyes beyond the image plane. The method is suitable only for viewing relatively small images in the size of 60-70 mm each, which is due to the interpupillary distance of the person. "Liberty" with the scaling of the image way also does not allow.
- The method of cross-eye is similar to the previous one, but the eyes are reduced before the image ("on the bridge of the nose"). The previous method, in which the eyes look as if beyond the image, is preferable, since it causes less eye strain. On the one hand, the cross-pair can be of arbitrary size and arbitrarily scaled when viewed; on the other hand, the imaginary image arises between the screen and the observer, which limits the size of the displayed object or turns it into a "puppet copy."
- The method of mirror separation of images (mirror split) allows you to dispense with the strain of view by applying a mirror to separate the fields of the view. The stereo picture for this method, as well as for the previous one, is the left and right frames, only one of them is inverted. The mirror is placed perpendicular to the face, close to the bridge of the nose, and perpendicular to the same picture, to the place of separation of the left and right frames. Usually the left frame is mirrored with respect to the true position of the object. In this case, you need to look with both eyes to the right: the right eye looks at the right image, the left through the mirror - to the left. Smoothly adjusting the mirror, you need to combine the images so that a stereo effect appears. The advantage of this method is that using only improvised materials, you can get a full-color stereo image. The disadvantage is that you have to place the face close to the screen or use a very long mirror. For large images, you need wide mirrors, which in combination can create a rather cumbersome design.
- Anaglyph-glasses are colored glasses, instead of lenses, which have color filters CMY. A cheap but effective method, physically it does not provide the correct transmission of a color stereo image, however the nervous system interprets it quite well. The adaptation time is about 30 seconds, after long use for a proportional period, color perception is violated.
- Shutter glasses. On the screen, the picture is projected for the left eye, then for the right eye. Accordingly, the glasses open the view to the left eye, then to the right eye. Used in 3D cinema format XpanD. Occasionally used in computer games, as they allow you to use a conventional CRT monitor (but with a powerful video card - the load on it is doubled). LCD monitor is not suitable for everyone - the true refresh rate for most of them does not exceed 30..75 Hz (referring to the actual time for the reconstruction of LCD chains, and not the frequency of scanning). An example of such technology is nVIDIA 3D Vision. To use 3D Vision, you need an LCD, plasma or OLED monitor with a scan rate of 100 Hz or higher, a video card from nVIDIA with 3D Vision and special glasses. Beginning in 2009-2010, the world began mass production of TVs working on this principle. In April 2010, Russia started the production of 3D TV-sets Samsung in the Kaluga region. The viewer wears LCD glasses, which alternately (at a frequency of 60 Hz) obscure the left and right eyes of the person, the TV at the same time shows 120 images per second.
- Polarized stereo glasses.
The glasses themselves are somewhat more expensive than anaglyph glasses and require precise special equipment, in addition the movie screen should be aluminized so that there is no depolarization of light. However (except for a decrease in brightness and high cost), there are no obvious shortcomings. Usually used in stereo cinema theaters. Having two similar projectors, a screen and some amount of polarized film from a faulty LCD monitor, you can reproduce yourself to a greater or lesser extent such a stereo effect.
- - Based on linear polarization (cheaper, but with the head tilted, the stereo effect is lost). Used in 3D cinema format IMAX 3D.
- - Based on circular polarization (more expensive). Used in 3D cinema format RealD Cinema.
- Stereo glasses with multiband filters - provide a stereo effect due to the fact that the lenses allow only narrow bands of red, green and blue. The projection equipment is relatively cheap, but the stereo glasses themselves are expensive. Used in 3D cinema format Dolby 3D.
- Stereoscope - an optical device with two eyepieces; It is usually used to view stereo slides, but it's not difficult to put a PDA or communicator with an elongated high-resolution screen (for example, Nokia E90).
- Stereo display is an optical instrument by means of which two planar images are combined in such a way that the observer gets the impression of a relief object.
- Virtual Helmet (VR HMD) is a helmet that shows individual images for each eye. This results in a stereo effect.
To view 3D data on a computer in stereo mode, you need to use a stereo driver. The largest list of supported 3D-programs, games and stereo equipment is the stereo drivers from NVidia. Currently, an alternative to stereophotography is a 3D photo, which allows you to get a truly voluminous image of the subject.
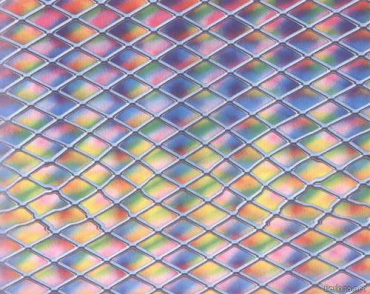
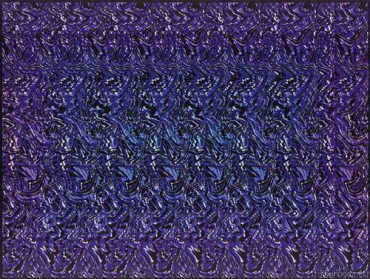
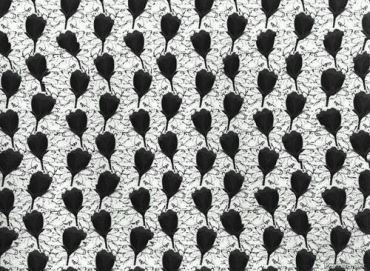
Autostereogram
- The autostereogram is perceived by the observer without any external separating devices. The stereopair is contained in a flat image in the form of alternating narrow vertical strips of conjugated images. When examining autostereograms, one should look through the image so that the left and right eyes look at the strips intended for them.
- The hologram is the wrong household name of the image covered with a grill made of microprisms on top, thanks to which there is a purely mechanical separation of the image - the left eye sees one half simply because it looks to the left, the right one is similar. Large (and, accordingly, viewed from a significant distance) images in this way can not be obtained due to a decrease in such parallax.
"Pseudosteroscopy"
The perception of volume can be obtained not only by simultaneous viewing of an object or image with two eyes simultaneously, but also by quickly changing images in one image channel (with monocular vision). So, the technology of GIF-animation allows you to create pseudo-stereoscopic 3D images (see photo at the beginning of the article).
A similar method is proposed for "pseudosteathotelivision" - by creating an anaglyph image for moving, dynamic objects. Instead of simultaneously viewing the image, the video signal is split into two color channels (usually red and blue, using the appropriate glasses). A dynamic flat color monocular image is processed in such a way that an unchanging video signal is fed to one eye (for example, a red channel) and a signal with a small time delay, from a changed dynamic scene, is fed to the second (blue channel). Due to the movement of objects in the scene, the human brain receives a "3D image" (but only if the foreground objects are either displaced or rotated). The disadvantage of this method is the limitation of the type of scenes in which a stereo effect may appear, as well as a noticeable loss of the quality of the color picture (each eye receives an almost monochromatic color image).
Another method of obtaining a pseudo-stereographic image is the use of nerve delays in the visual apparatus. A dark image is perceived by the eye a little slower than a light one. If you squint one eye (or look through the dark glass) - "lagging" the previous image of the video sequence will overlap the current image, perceived by the other eye. If the camera moves parallel to the plane of the frame ("shooting from the train window") - the "darkened" eye will perceive the video from its angle, and the second - from a close point, which gives rise to an unexpectedly strong stereo effect. Practical application does not have because of the limitations of possible angles, but it is easy in experimental reception - just a mobile phone with a camera, an electric train and a squinted eye.





































































































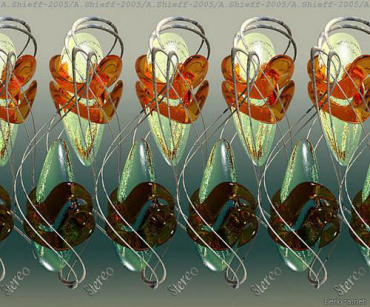





 Download archive [
Download archive [ 

Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.