| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2149277
![]()
WIND MOTOR
The name of the inventor: Anatoly Filippovich Tupikov; Tupikov Kirill Alexandrovich; Tupikova Ekaterina Aleksandrovna; Tupikova Galina Anatolevna; Tupikov Alexander Anatolievich
The name of the patent holder: Anatoly Filippovich Tupikov; Tupikov Kirill Alexandrovich; Tupikova Ekaterina Aleksandrovna; Tupikova Galina Anatolevna; Tupikov Alexander Anatolievich
Address for correspondence: 129226, Moscow, 1st Agricultural avenue 5, apt.71, Tupikova GA
Date of commencement of the patent: 1995.12.28
The invention relates to wind turbines and can be used to generate torque and transmit it to a power take-off consumer.
The technical result of increasing the torque is achieved due to the fact that in a windmill containing an aerodynamic pipe and a turbine formed in the turbine and kinematically connected to the power take-off device, the turbine is made in the form of a truncated cone formed by a smaller solid and large annular Bases bound together by blades, one of the longitudinal edges of which is located along the conditional surface of the cone, while the conicity is directed towards the flow of air.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to wind turbines and can be used to generate torque and transmit it to a power take-off consumer.
A windmill is known , containing a wind- wheel of different diameter fixed on the shaft, whose blades are directed radially [1].
The disadvantage of this windmill is that the front wind wheel of a smaller size cuts off the air streams, which reduces the efficiency of the subsequent windwheels.
A windmill is also known , containing a turbine fixed on a vertical shaft, formed by blades, the longitudinal edges of which are located along a conditionally cylindrical surface [2].
The disadvantage of this windmill is that not all the blades are simultaneously involved in the creation of torque, which reduces the efficiency.
The closest solution to the technical essence and the result achieved is a windmill containing an aerodynamic tube and a turbine formed in it, which is bladed and kinematically connected to a power take-off device [3].
The disadvantage of this windmill is that the turbine blades are located radially and along the length are limited by the diameter of the pipe, as a result of which the design radius of the blade torque is limited by the diameter of the wind tunnel.
The purpose of the invention is to increase the torque.
The goal is achieved by the fact that in a windmill containing an aerodynamic pipe and a turbine formed in it and which is kinematically connected to a power take-off device, the turbine is made in the form of a truncated cone formed by a smaller solid and large annular base, fastened together by blades, one of The longitudinal edges of which are located along the conditional surface of the cone, while the conicity is directed towards the flow of air, as a result of which the radius of the torque and the area of the blades are increased, which increases the efficiency.
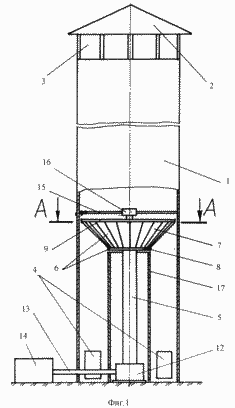
The invention is explained by the drawings, in which: FIG. 1 shows the general view of the windmill; In Fig. 2 - section AA.
 |
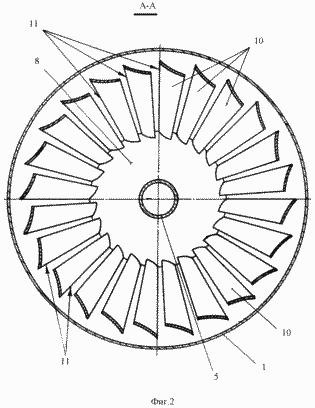 |
The wind turbine consists of a wind tunnel mounted on the base of the wind tunnel 1, above which there is a probe 2 and there are windows 3 for the airflow outlet, and windows 4 for supplying air flow are provided in the lower part. In the wind tunnel 1, a shaft 5 is rotatably mounted on which is fixed a turbine 6 made in the form of a truncated cone 7 formed by a smaller solid base 8 and a large annular base 9. The bases 8 and 9 are fastened together by blades 10, one longitudinal edge 11 of each Of which is located along the conditional surface of the cone 7.
The shaft 5 is connected to a power take-off device, for example, with a current generator 14, by means of a reducer 12 and a shaft 13, and the upper end of the shaft is provided with length-adjustable spokes 15 fixed at their ends on the wall of the wind tunnel 1 and others on the bearing 16 of the shaft 5. Under the smaller base 8 of the cone 7 and coaxial with the turbine 6, an airflow regulator 17 is installed. Streams of high-temperature air or a gas-air mixture can be supplied from kilns for the burning of ceramic products and materials, blast furnaces, steelworks and other industries where high fluxes of high-temperature gas-air mixtures are emitted into the atmosphere.
High-temperature air or a gas-air mixture is supplied to the windows 4. Due to the potential difference between the environment and high-temperature air, the latter starts to rise up in the wind tunnel 1. The stabilizer 17 ensures the straightness of the ascending air flow, which ensures the maximum air flow rate. The upward flow of air acts on the blades 10 of the turbine 6. As a result, the latter starts to rotate and through the shaft 5 the reduction gear 12 and the shaft 13 transmit the torque to the current generator 14 which generates electric power.
The position of the shaft 5 with the turbine 6 relative to the cylindrical wall of the turbine 1 is provided by adjusting the length of the spokes 15. Thus, increasing the length of the blades due to their arrangement along the conditional surface of the cone provides maximum torque.
INFORMATION SOURCES
- Author. Svid. USSR N 1076618, 1984.
- German Patent No. 729533.
- Science and Life, No. 1, 1981. "Sow the wind to shake the electricity." - (prototype).
CLAIM
- A wind turbine comprising an aerodynamic tube and a turbine formed therein, and which is kinematically connected to a power take-off device, characterized in that the turbine is made in the form of a truncated cone formed by a smaller solid and large annular base, joined together by blades, one of the longitudinal edges of which Located on the conditional surface of the cone, while the conicity is directed towards the flow of air.
- A wind turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that it is provided with a flow stabilizer located under the smaller base of the turbine cone and coaxial therewith.
- A turbine according to claim 1, characterized in that the turbine shaft is provided with adjustable spokes fixed at one end on the wall of the wind tunnel.
print version
Date of publication 11/14/2006




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.