| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2184416
![]()
METHOD OF OBTAINING ELECTRIC ENERGY BY WAY OF TRANSFORMATION
ENERGIES OF MOVING MASS
The name of the inventor: Frolov Vitaly Petrovich
The name of the patent holder: Frolov Vitaly Petrovich
Address for correspondence: 109017, Moscow, Pyzhevsky per., 7, Soil Institute. VVDokuchaev RAAS, V.P. Frolov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2000.06.22
The invention relates to methods for obtaining electrical energy. The method for obtaining electric energy by separating electric charges in a moving ion stream is that a flow of water containing ions is used as a moving ion stream, which is passed between plates of an electrically conductive material whose surface is isolated from water by a nonpolar dielectric that creates an electric field in a moving Water flow, provided that the time of passage of the field of flow by the water flow exceeds the time of passage of the gap between the plates by the ions. Then the water flow is mechanically divided into two differently charged jets, for this purpose a wedge-shaped partition of the non-polar dielectric is placed at the outlet of the field into the water stream, with the point of the partition entering the field by 0.1-100.0 mm and directing each jet to a separate collector- Accumulator of ions from electrically conductive material, where the neutralization of ions and the removal of electrical energy are performed. The technical result is the creation of a simpler method for obtaining electrical energy.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of electricity, namely to methods for obtaining electric energy by converting the energy of a moving mass containing charged particles, in particular the energy of falling water, and can be used to obtain a direct current by means of dams and dams on rivers and streams.
Modern methods for converting the potential energy of raised water into electrical energy contain, as intermediate stages, the conversion of this energy into the kinetic energy of the falling water, which is then, with greater or lesser efficiency, perceived by hydroturbines rotating electric generators in which the electrically conductive material moves relative to the magnetic field, Lorentz electrons are driven by a conductor.
A magnetohydrodynamic method of obtaining direct current electric energy is known (1), taken from our prototype. In this method, a hot gas (fuel combustion product) containing ions (the amount of ions is increased by injecting alkali metal salts) is run at high speed through a magnetic field, whereby the ions are pushed out of the flow by special Lorentz forces to special collector electrodes, from which the electric energy.
However, the existing magnetodynamic method (1) for obtaining electric energy uses expensive equipment including superconducting electromagnets operating in contact with hot gas. The material of the collector electrodes is rapidly worn out by the combination of high temperature and chemical activity of the ions. In addition, the electric potential that appears on the electrodes-collectors reduces the efficiency of the method, repelling part of the ions from its surface. The implementation of the method requires the constant presence of highly qualified personnel.
It is an object of the present invention to provide a simpler method for producing electric energy by separating electric charges in a moving ion stream in which a flow of water containing ions is used as the moving ion stream, which is passed between plates of an electrically conductive material whose surface on the water side is covered with an electrically insulating material , Creating an electric field in a moving water stream, provided that the time of passage of the electric field by the water flow exceeds the time of passage by the ions of the width of the gap between the plates, then the water flow is mechanically divided into two charges of charge differentiated by sign, for which, at the exit from the field into the water The flow is placed a wedge-shaped partition of the non-polar dielectric (the tip of the wedge-shaped partition sets in the field by 0.01-100.0 mm) and directs each jet to a separate collector-accumulator of ions from the electrically conductive material, where ions are neutralized and electric energy is removed.
To create an electric field, any voltage source is suitable from an element such as Leclanche or Weston to an electric machine that, in case of reliable electrical insulation from water, can work simultaneously on thousands of plates. The plates are made of an electrically conductive material and covered with a non-polar dielectric. The word "plate" here does not necessarily mean their flat form. They can be bent in various ways, like the lining of an electric capacitor.
Complete separation of ions under the action of the field in a moving water stream (under the condition of its laminarity) is achieved when the condition that the time of passage of the field of water by the flow of water exceeds the time of passage of ions by the ions of the width of the gap between the plates (ion drift to plate surfaces perpendicular to the direction of flow). The time for the flow of the field region by the water flow is determined by the length of the plates and the flow velocity, and the drift time ( ![]() ) Of charged ions is equal to the product of ion mobility (
) Of charged ions is equal to the product of ion mobility ( ![]() - the tabulated value, is determined by the nature of the ion) by the electric field strength H divided by the width of the gap between the plates ( l ):
- the tabulated value, is determined by the nature of the ion) by the electric field strength H divided by the width of the gap between the plates ( l ):
![]()
Ions, separated in space, are entrained with water along different tubes of non-conductive material into two groups of collectors made of electrically conductive material, intended for collecting ions of the same sign.
In the collectors, the incoming ions form high electrical potentials, taken from their bodies to capacitor banks and simultaneously to electricity consumers.
An additional advantage of the proposed method for generating electricity is the formation of an alkali solution in collector reservoirs of cations, and in the storage tanks of anions, an acid solution that can be disposed of.
EXAMPLE OF CONCRETE EXECUTION
In the drawing, the layout of the plant for implementing the proposed method is shown.
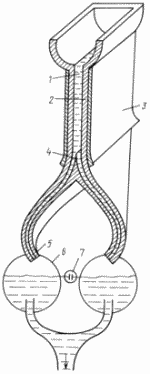 |
Water under pressure passes into the working air gap (1), which is under the influence of an electric field created by electric charges on the plates (3). Water under pressure from above slips downward, and the ions in it are separated by an electric field along the charge sign and approach the plates (3) covered with a nonpolar dielectric (2) in accordance with the charge sign. The partition (4) located in the lower part of the water stream creates two jets of water, each of which contains ions of the same sign. Water jets are guided along drain pipes (5) from non-conductive material to storage collectors from electrically conductive material (6), whose bodies are connected to the consumer and to a battery of electric capacitors (7) designed to smooth the unevenness of the energy consumption by the consumer. |
With a content of about 50 mg / l calcium salts in water (as, for example, in the natural waters of the Moscow Region) with complete separation of the ions only due to calcium salts, the proposed method makes it possible to obtain an electric current of 300-400 A when 1 liter of water is passed through the working gap In c, and the magnitude of the resulting electric voltage depends on the difference in height between the place of water extraction and the place of separation of its ions.
LITERATURE
Physical encyclopedia. M. 1984, p. 379.
CLAIM
A method for producing electric energy by separating electric charges in a moving ion stream, characterized in that a flow of water containing ions is used as a moving ion stream, which is passed between plates of an electrically conductive material whose surface is isolated from water by a nonpolar dielectric that creates an electric field in a moving Water flow, provided that the time of passage of the field of water by the flow exceeds the time of passage of ions by the ions of the gap between the plates, then the water flow is mechanically divided into two differently charged jets, for which a wedge-shaped partition of the nonpolar dielectric is placed at the outlet of the field, The wedge-shaped partition enters the field by 0.1-100.0 mm and directs each jet to a separate collector-accumulator of ions from the electrically conductive material, where the neutralization of ions and the removal of electrical energy are performed.
print version
Date of publication 09.11.2006гг




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.