| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2127939
![]()
ELECTRIC FIXTURE KIT ELECTRIC GENERATOR
The name of the inventor: Maneev MN; Medvedev M.M.
The name of the patent holder: Enterprise "Technocrat"
Address for correspondence: 123310, Moscow, Pyatnitskoe Sh., 37-308, Maneev M.N.
Date of commencement of the patent: 1997.08.19
The invention relates to the field of electrical engineering and can be used in small and alternative electric power engineering. The proposed electric face-to-face set-up generator consists of a casing in which a stator and a rotor are placed, consisting of disks arranged on a common axis in an alternating order. The disks contain a certain even number of coils arranged sectorially with magnetic axes parallel to the axis of rotation of the rotor. The coils are wound on cores of magnetic material with high induction and close to a rectangular hysteresis loop and are connected so that their magnetic poles in the disk plane alternate. The stator disks are rigidly connected to the casing, and the rotor discs are fixed to the hollow shaft and rotate relative to the stator shafts. The windings of the stator disks are independent, and the rotor ones are connected in series and output into the cavity of the shaft. In this case, according to the invention, the end stator disks are closed from the outside by the contactors of the generator magnetic circuits made in the form of solid rings of the same material as the stator and rotor cores, while the coils of both the stator and the rotor are wound so that their magnetic poles in the plane Disks alternate. The invention is aimed at increasing the generator efficiency, which is the technical result.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of electrical engineering and is a constructively new alternating current electric generator.
A generator of the end type with two fixed discs with windings constituting the stator is known (UK patent GB 2118376 A) , between which are disposed rotor disks of a rotor with permanent magnets in its sectors being inductors. This generator has significant drawbacks: low magnetic induction from permanent magnets; Significant additional magnetic resistance due to losses in the material of magnets; And, finally, the inability to regulate the output voltage with a change in the rotor speed.
The proposed generator is devoid of these drawbacks.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
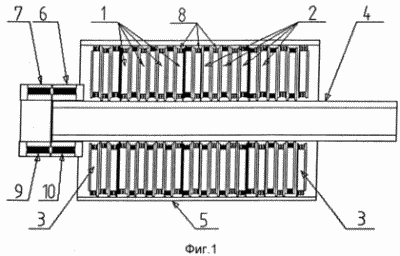
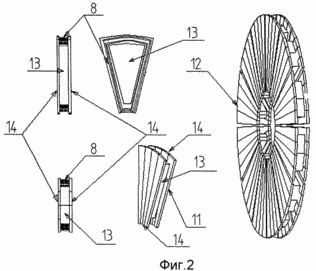
A schematic (in section) of the construction of the generator is shown in FIG. 1. The generator consists of rotor 1 and stator 2 disks arranged in alternating order. Internal 2 and end stator disks 3 are structurally different. The generator is enclosed in a casing 5, to which stator disks are rigidly attached. The rotor disks 1 are rigidly fixed to the hollow shaft 4 and rotate together with it. Windings of 8 stator and rotor disks (and are shown in section). On the shaft 4, one half of the 6 rotating transformer with the secondary winding 10 is fixed. Another fixed half of it is fixed to the generator housing. The internal cavity of the shaft 4 is intended to accommodate the electric power elements of the rotor. Both the stator and rotor disks represent some construction of a non-conductive and non-magnetic material into which the placed sectorically-electric coils 8 are embedded, wound on special shaped cores 13, the shape of which is shown in FIG. 2. Magnetic cores of internal disks, both rotating and stationary, consist of a core 13 and pole plates 14 made of a material with a high magnetic induction, close to a rectangular hysteresis loop. The magnetic circuits of the inner disk assembly (without a containment, supporting structure) are shown in FIG. 2 at number 12. The pair of the stator and rotor disks constitute a generator section, the form of which is represented (and without a containment structure, but with a portion of the casing 5) in FIG. 3 and 4, and in FIG. 3 shows the internal, and in FIG. 4 - end section. The end section differs from the internal one in that the outer pole plates of the stator disk are replaced by a solid ring made of the same material as the pole plates and cores. They are the closures of the magnetic circuits of the generator. The coils on both the stator and rotor disks are wound so that their magnetic axes are parallel to the axis of rotation of the rotor. The windings of all the coils on each disk are connected in series and electrically commutated so that when the current flows through them, the magnetic poles alternate on the disk planes. Therefore, the number of coils on each disk is necessarily the same and even. The electrical connections of the stator disks are independent, and the rotor ones are connected in series and so that the magnetic polarity of all the coils located on the same line parallel to the axis of rotation on all the disks is the same. The conclusions of the rotor disks are withdrawn into the cavity of the shaft. The rotary transformer assembly consists of two independent windings 9 and 10, each placed in its half 7 and 6 respectively, of an armored core made of the same material as the cores. In Fig. 5, numbers 6 and 7 show the profile of the half of the core of the rotating transformer (general view and section). The conclusions of the secondary winding of the transformer are output to the shaft cavity.
The generator works in the usual way: when the excitation current flows in the rotor coils and the rotor rotates, the magnetic field of the rotor coils induces electromagnetic EMF in the stator coils and the load current when the stator coils are connected to the load.
The described generator is intended for use in small and alternative power engineering, characteristic small and variable speeds of rotation and magnitudes of the mechanical moment of a mechanical drive. Therefore, its control circuitry shown in FIG. 6, contains a number of special electrical devices to ensure the operation of the generator under these conditions. This is a rectifier-commutator 19 of stator disc windings, a buffer battery 20, an inverter 22 and a transformer 21 for matching with an electrical network. The excitation power - the rotor - is provided by an alternating current flowing to the primary winding 9 of the rotating transformer. The current from the secondary winding of this transformer is rectified by the rectifier 16 and stabilized in magnitude by the current stabilizer 17. Thus, a constant current flows both in magnitude and direction in the rotor coils. This is achieved by parrying the secondary (parasitic) EMF induced by the load current flowing in the stator coils. Ultimately, this leads to an increase in the efficiency of the generator.
CLAIM
- An electric end set generator consisting of a stator and a rotor made in the form of disks arranged in a casing along a common axis in an alternating order, the stator disks being rigidly connected to the casing and the rotor disks being fixed to the shaft, characterized in that the stator and rotor discs are made of Nonmagnetic material with high electrical resistance and contain a certain even number of coils with magnetic axes parallel to the axis of rotation of the rotor wound on cores of high-inductance magnetic material close to a rectangular hysteresis loop and closed at the poles with plates of the same material as And the end stator disks are closed from the outside by the contactors of the generator magnetic circuits made in the form of solid rings of the same material as the cores of the stator and rotor coils, while the coils of both the stator and the rotor are wound so that their magnetic poles in the plane of the discs Alternate.
- Generator according to claim 1, characterized in that the rotor shaft is hollow, and the winding leads of the rotor disks are driven into the shaft cavity.
- Generator according to claim 2, characterized in that it comprises a transformer wound in an armored core, one half of which contains a primary winding and is rigidly attached to the shroud, and the other is mounted on a shaft and comprises a secondary winding, the terminals of which are withdrawn into the shaft cavity.
- The generator according to claim 3, characterized in that the supply of windings of the rotor disks is provided by a constant current stabilized in magnitude coming in the form of an alternating current from the secondary winding of the transformer, followed by rectification and stabilization.
- The generator according to claim 1, characterized in that it comprises an electronic output voltage regulator when the rotor speed changes, consisting of a rectifier-commutator of stator disk windings, a buffer battery, an inverter and a matching transformer.
print version
Date of publication 10.12.2006гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.