| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2169423
![]()
MAGNETIC GENERATOR
The name of the inventor: Dusaev Mirgasim Rashitovich
The name of the patent holder: Dusaev Mirgasim Rashitovich
Address for correspondence: 423250, Tatarstan, Yutazinsky rn, pos. Urusu, st. Tatarstan, 82, M.R. Dusayev
Date of commencement of the patent: 2000.01.18
Use: production of electrical energy .
The technical result consists in creating a magnetic generator with high efficiency by using the energy of permanent magnets.
The magnetic generator contains the stator windings uniformly distributed along the circumference and stator windings fixed in the casing. Their cores consist of a magnetic core and a permanent magnet with a pronounced magnetic field. Between the magnet and the magnetic circuit, forming a closed magnetic flux, there is a gap for the possibility of moving screens in it. The screens are fixed on the ends of the permanent magnets of the rotor, made of non-magnetic material. The number of rotor magnets differs from stator magnets by one unit, and the magnetic field is oriented in different directions
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the production of electrical energy.
A magnetic generator is known that contains a body, a ferromagnetic stator in the form of a disk on which the first group of armature coils with a core is fastened, a rotor with a shaft, a ring magnetic core with teeth and a permanent magnet with axial magnetization, holes are made in the magnetic circuit, With cores, the ends of the windings of which, like the ends of the windings of the coils of the first group, are outputted to the terminals fixed on the shoe housings in whose bearings the rotor shaft is fixed ( Application No. 95103846 A1, IPC 6 H 02 K 21/14, 1996 ).
A magnetoelectric generator is also known , comprising an inductor arranged in a rotatable body in the form of an axially magnetized magnet with pole-pole tips, and a working winding located on the stator magnetic circuits. The stator magnetic conductors are made of U-shaped, uniformly distributed around the circumference with the correspondence of the poles to the opposite pole-pole tips of the inductor, the number of magnetic conductors is equal to twice the number of poles of the pole pole of the inductor, and the adjacent windings are connected in series and in reverse in the case of providing an alternating voltage or, in the case of providing a unipolar pulsating voltage Patent of Russia No. RU 2053591 C1, IPC 6 H 02 K 21/12, 1991 ).
The disadvantage of these generators is the low efficiency (EFFICIENCY). The closest analogue is a magnetoelectric generator ( Patent of Russia No. RU 2053591 C1, IPC 6 H 02 K 21/12, 19991 ).
The object of the invention is to achieve a high efficiency by using the energy of permanent magnets.
The problem is solved by the fact that the magnetic generator comprises a body made of a non-magnetic material on which the cores and working windings of the stator are fixedly and uniformly distributed around the circumference, at least one core of the working winding of the stator consists of a magnetic circuit and a two-pole permanent magnet, and between a two-pole constant Magnet and magnetic circuit there is a gap for the possibility of moving in it magnetic screens fixed on the ends of bipolar permanent magnets mounted on the rotor made of non-magnetic material, while on the rotor, unlike the stator, the number of bipolar permanent magnets is less or more by one unit Whose poles are oriented to the poles of the bipolar permanent magnets of the stator.
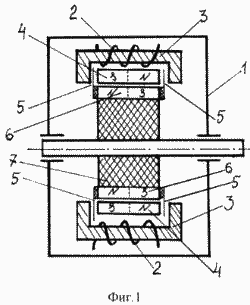
In Fig. 1 shows a magnetic generator, longitudinal section. (Conditionally).
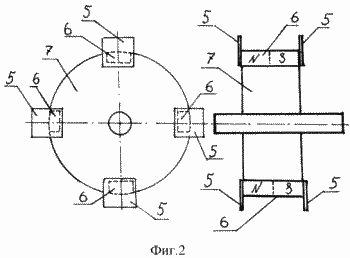
In Fig. 2 schematically shows a rotor, a front view and a side view.
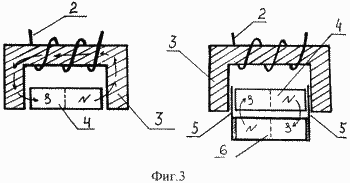
In Fig. 3 schematically shows the moment of the closed magnetic flux through the magnetic circuit
The core of the working winding and the instant of closed magnetic flux between two bipolar permanent magnets.
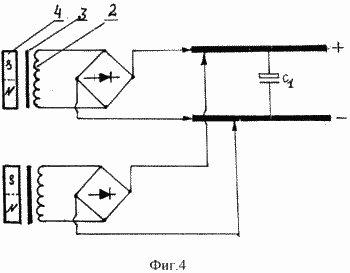
In Fig. 4 shows the connection of the stator windings through the rectifier,
Consisting of four diodes, to the common bus of the electrical circuit.
The magnetic generator comprises a body 1 made of a non-magnetic material on which the cores and working windings 2 of the stator are fixedly and uniformly distributed around the circumference, at least one core of the working winding 2 of the stator consists of a magnetic circuit 3 and a bipolar permanent magnet 4, A magnet 4 and a magnetic circuit 3 there is a gap for the possibility of moving therein magnetic screens 5 fixed to the ends of the two-pole permanent magnets 6 mounted on the rotor 7 made of non-magnetic material, while on the rotor 7, in contrast to the stator, the number of bipolar magnets 6 is less Or more by one unit, the poles of which are oriented to the poles of the bipolar magnets 4 of the stator in opposite directions.
MAGNETIC GENERATOR WORKS AS FOLLOWING
When the rotor 7 rotates, at the moment of maximum approach, at least one bipolar permanent magnet 6 mounted on the rotor 7 with one bipolar permanent magnet 4 of the core of the working winding of the stator interacts the opposite poles with each other. In this case, a closed magnetic flux from the poles N to the poles S forms between the two bipolar permanent magnets 4,6.
At this point, the magnetic flux is absent on the magnetic core 3, which is an integral part of the core of the working winding of the stator, and therefore there is no EMF on the working winding 2 of the stator.
Further, at the time of the greatest removal of the bipolar permanent magnet 6 mounted on the rotor 7 from the bipolar permanent magnet 4 of the core of the working winding of the stator, the magnetic fluxes existing between these bipolar permanent magnets are broken.
The magnetic flux from the pole N of the bipolar permanent magnet 4 of the core of the working winding of the stator rushes to its pole S through the magnetic core 3, which is an integral part of the core of the working winding of the stator. In this case, in the working winding 2 of the stator, under the influence of a time-varying magnetic flux, an induction emf occurs. With the approach of a bipolar permanent magnet 6 mounted on the rotor 7 to the two-pole permanent magnet 4, which is an integral part of the core of the working winding 2 of the stator, the cycle is repeated. The magnetic shields 5 fixed to the ends of the bipolar permanent magnets 6 mounted on the rotor 7 perform an auxiliary function: being in the gap between the bipolar permanent magnet 4 and the magnetic core 3 of the working core of the stator, these magnetic shields 5 screen residual magnetic fluxes.
The main requirement for magnetic shields is 5:
They should be made of soft magnetic material.
The hysteresis loop must be narrow. The number of working windings of the 2 stators in the magnetic generator is determined by the calculated technical parameters.
On the rotor 7, in contrast to the stator, the number of bipolar permanent magnets 6 is smaller or larger by one, thus forming the interaction of the magnetic fields of the bipolar permanent magnets 4,6 which helps to reduce the mechanical energy required to create a rotating torque on the rotor 7 , Which significantly affects the efficiency of the magnetic generator .
The received electric current through the rectifying diode bridge is supplied to the consumer. The capacitor in the circuit serves to smooth the pulsations.
CLAIM
A magnetic generator comprising working windings and stator cores fixedly installed in the housing and uniformly distributed around the circumference, a rotor with a shaft, characterized in that the cores of the working winding of the stator consist of a magnetic circuit and a permanent magnet forming a closed magnetic flux and a gap for moving shields therein Fixed to the ends of the permanent magnet made of non-magnetic material of the rotor, the screens provide an intensifying effect of switching the magnetic flux of the permanent magnets of the stator to the permanent magnets of the rotor, while the permanent magnets of the rotor and the stator are oriented with a polar angle across the magnetic field, and differ by one in number.
print version
Date of publication 04.11.2006gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.