| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2212723
![]()
electromotive DEVICE
Name of the inventor: Bryantsev Alexander
The name of the patentee: Bryantsev Alexander
Address for correspondence: 140105, Moscow region, Ramenskoye, st.. Chugunov, 38, kv.10, A.M.Bryantsevu
Starting date of the patent: 2001.06.29
The invention relates to electrical engineering and can be used in controlled reactors for reactive power compensation or a capacitive ground fault current in electrical networks. The technical result is to reduce the consumption of materials. The apparatus comprises a magnet system with two middle and two lateral rods and yokes. On average rods arranged winding sections connected to its middle point control transmitter. Average rods are made with a reduced from two times to three-section with respect to the total cross section of the lateral rods and yokes, and at the same height rods up to 5% is the product of the effective cross section of the winding at a constant ratio to the nominal magnetic conduction device.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to electrical engineering and can be used for controlled magnetization reactors installed in the mains for reactive power compensation or a capacitive ground fault current.
The electromotive device is known [1], comprising a magnetic system made of two cores with cores and yokes. To ensure sinusoidal current consumption in nominal operation and, consequently, reduce distortion throughout the range of adjustment rods which are placed on a partitioned winding provided with portions of reduced cross section. A disadvantage of [1] is enlarged relative to sections of reduced cross section rods and yoke cores, resulting in increased material consumption and losses in the device.
Partially disadvantages [1] eliminated in a known electromotive device [2], which is closest to the technical nature of the present invention. Unlike the analogue [1] the magnetic system of the prototype device is formed as a unitary structure composed of two and four rods yoke - the two middle and two side. The two middle portions of the rod provided with a reduced cross-section and are arranged alternately winding sections combined-DC. Execution of the magnetic system in a single design allowed us to separate AC and DC magnetic flux path and reduce their closures, ensuring reduction in material consumption on the yoke and loss in them. However, as in the analogue [1], the rods, which are located on the winding section are formed with portions of reduced cross section. As a result, enlarged with respect to these rods sectional areas leads to increased consumption of materials as rods themselves and to the coil, which is located on them.
The aim of the invention is to reduce the consumption of materials and losses due to changes in the design and introduction of new connections (relationships) between its elements.
This object is achieved in that the electromotive device comprising a magnetic system with two yokes, two middle and two side bars, medium rods on which there are sections of the winding are made continuous, and the sum of their cross-section from two to three times smaller than the cross section amounts yoke and the lateral rods and the height of the rods to within 5% is the product of the effective winding section at a constant ratio to the nominal magnetic permeance device.
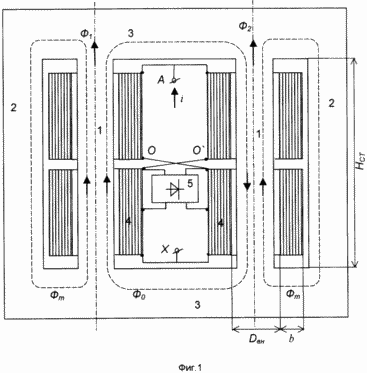 |
New in the present invention is a modified construction and new connections between the elements. Average rods are made solid, its cross section corresponds to the sum of a certain way yoke sections and the lateral rods and the height - with an effective cross section of the winding device and the nominal magnetic conductivity. The device is illustrated by drawings. 1 shows a construction of the magnetic system, the order of placement of coils and their electrical connection diagram indicating characteristic geometric dimensions. The magnetic system comprises two secondary shaft 1, two side rod 2 and two yoke 3. In medium rods 1 arranged windings changeable DC 4 to the middle point and the branch manager of the winding 4 connected inverter 5. Figure 2. shows waveforms of consumed electric current of the network unit 6 7 mains voltage, the control voltage converter 8 and the magnetic flux in secondary magnetic cores system 9, 10. |
Elektoroinduktsionnoe device in accordance with the formula of the present invention operates as follows. When connecting winding terminals 4 to the AC mains (A-A) in the idle control inverter 5 in the middle rods 1 having the same magnitude and direction of the flow variables with amplitude P m, is closed through the side bars of the magnetic system 2. The amplitude of the flow F m approximately is the saturation flux medium rods F S, and the permanent magnetic flux F 0 is absent. In none of the sections of the yoke magnetic flux flows do not exceed the saturation S and O device current is practically zero. This mode is also called idle mode. Diagram of electric current 6, voltage 7, 8, magnetic fluxes 9, 10 for this case is shown in FIG. 2 in the time interval t 0 -t 1.
When you turn to the work of the control converter 5 between the midpoints of 0, 0 'winding 4 appears controlled in magnitude and sign of the rectified voltage 8, which in turn leads to the emergence and rise of in the magnetic flux bias F 0, is closed through the middle pins 1 and yoke 3 . as a result, the variable component of flows F 1 and F 2 medium rods 1 begins to move in the area of technical saturation magnetization curve and as a result, this leads to the saturation of the secondary rods 1 and the current ascending 6 in the winding 4. With increasing flow bias F 0 time saturated state averages rods and increases (see FIG. 2, the time interval t 1 -t 2).
In nominal mode, in addition to variable flow F m, in the middle bars are closed steady stream of F it, and equal in magnitude to the flow medium rods F S saturation. As a result, during a busy state of each of the bars is equal to exactly half of the period. Moreover, due to the different areas of variables F m and a constant stream # 0 in the secondary terminals 1, one half of the period of one rod is saturated, and the other - the other (see Figure 2, the time interval t 2 -t 3.).
With further increase in flow bias F 0 6 AC devices continues to increase (see. FIG. 2, t 3 -t 4 interval) until the complete saturation medium rods (see FIG. 2, the time interval t 4 -t 5). The flux bias F 0max thus becomes equal to twice the value of saturation flux medium rods F S.
The principal feature of the device is that in the rated operation, as a prototype, it consumes a sinusoidal current. Consequently, this provides a significant reduction of harmonic currents and throughout the range of adjustment of idling and up to complete saturation secondary rods. This is due to the equality within the manufacturing tolerances of the rod height product of the effective coil cross-section on the attitude of constant magnetic device to the nominal conductivity: 
g n - nominal magnetic conductivity of the device;
D ext - the inner diameter of the winding;
b - radial dimension of the winding;
to don = ± 0,05 - tolerance for deviation parameters in the design and manufacture.
When the ratio of (1) the magnetic conductivity of the device in the nominal mode remains unchanged. The device is kept in a state where one of the secondary cores is saturated and the other is not. Consequently, the consumption of current network 6 has a strictly sinusoidal.
Unlike the prototype of the proposed device does not require a reduced section in the middle sections of the rods to ensure sinusoidal current at rated speed. When the relation (1) is achieved at a constant height over the entire cross section of the rods. Lack proposed device in the expanded portion of the cross section of middle rod insatiable to 1.5-2.0 times reduces material costs as rods themselves and to the winding-variable and DC losses in them.
Another important feature of the proposed device is that the yoke 3 and the side bars 2 in all modes of operation the device must not saturate. Otherwise it leads to distortion and an increase in current 6 losses in the device due to buckling of the field outside the magnet system. On the other hand, increasing the degree of lateral sections and yoke cores should not exceed the appropriate values, otherwise it leads to a product overrun materials.
 |
To implement conditions of unsaturated yoke 3 and the side bars 2 and the possible consumption of materials minimizing their total cross section as many times should exceed the total cross-section of middle rod, how many times the value of the sum of a constant stream of 0 and the amplitude of the alternating flux F m is greater than the flow medium rods F S saturation. If the mode change range is in the range from idle to rated (see. Fig. 2, t 2 -t 1 interval), the total cross section of the lateral rods and yoke should exceed the sum of the cross sections of rods medium twice (2, 2 interval t -t 3). In the limiting case corresponding to complete saturation medium rods (Fig. 2, the interval t 4 -t 5), this ratio should be increased to three. It is this range of the ratio of sections stipulated in the present invention. |
The efficiency of the proposed electromotive device and its high technical and economic indicators are confirmed by simulations and calculations. Compared to analogue and prototype, the invention has the main advantage - a decrease in the consumption of materials and waste. As an added benefit, you can consider simplifying the structure of the magnetic medium rod system (excluded areas of reduced cross-section).
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. The electromotive device. No. 1164795 H 01 F 27/34; H 01 F 29/1. Bulletin of Inventions 24, 1985
2. USSR Author's Certificate 1706322, H 01 F 29/14, 1985 For internal use only.
CLAIM
Electromotive device comprising a magnetic system with two yokes, two side and two middle rods at medium rods arranged windings, to the middle point is connected to the control converter, providing the appearance of in the middle bar is closed through the side bars of the same magnitude and direction of the variable magnetic flux and multidirectional steerable constant value of magnetic flux, characterized in that the average amount of cross-sections of rods 2-3 times less than the sum of the cross sections of the side yoke and cores, and the height of rods with an accuracy of 5% equal to the product of the effective cross section of the windings at a constant ratio of the magnetic nominal magnetic conduction device.
print version
Publication date 15.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.