| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2154333
![]()
Reactive power compensators
Name of the inventor: Klimash VS .; Simonenko IG
The name of the patentee: Klimash Vladimir Stepanovich; Simonenko Irina G.; Komsomolsk-on-Amur State Technical University
Address for correspondence: 681013, Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Lenin Avenue 27, Technical University.
Starting date of the patent: 1997.01.24
The invention is intended for high-speed network reactive power compensation and stabilize the load voltage when operating in soft rezkoperemennoy networks and industrial loads. The compensator comprises a sensor network reactive power load sensor deflection voltage transformer, two inverters with a total for their filter and reversible rectifier. The inverters are controlled by a control system that ensures the regulation of the phase angles respectively ![]() +
+ ![]() and
and ![]() -
- ![]() +
+ ![]() with respect to the mains voltage. Regulation
with respect to the mains voltage. Regulation ![]() produced reactive power in the network function, and regulation
produced reactive power in the network function, and regulation ![]() in deviation of the load voltage function. The technical result - improved weight and size and increasing performance.
in deviation of the load voltage function. The technical result - improved weight and size and increasing performance.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to power electronics and more particularly to devices to improve the quality and energy efficiency, and can be used in the industrial power systems.
Known reactive power compensator (Patent RF N 1793514 from 15.11.93, cl. Of H 02 J 3/18), which is taken as a prototype. It comprises two three-phase transformer with primary windings coupled in series included in the load circuit, and two three-phase inverter, which inputs are combined via a three-phase rectifier connected to the network, the network load or more. The outputs of the first and second inverters respectively connected to the primary windings of the first and second three-phase transformers. phase control of the output voltage of one inverter is made as a function of input reactive power deviation from zero and the phase of the other inverter control - as a function of output voltage deviation from the target, such as nominal level.
The disadvantages of the device is necessary to carry a lot of weight and the dimensions of the transformer equipment and relatively low speed. They are caused by the fact that the two transformers in the device and two additional summation voltage formed inverters produced after transformation.
The object of the invention is to improve the weight and size and increasing performance.
As a result, the solution of the problem reduced the phase control range of the transformer secondary circuit, and therefore, the magnetizing effect on the magnetic circuit of inverters. It is possible to increase the rate of phase variation and speed of the device, and instead of two and three-phase transformers to apply one.
The solution of this problem is achieved by the fact that some of the conclusions of the secondary winding of the three-phase transformer connected to the output of the second three-phase inverter, and other findings of its primary winding connected to the network, and the three-phase rectifier is configured to power two-way exchange between its output and the combined inputs of inverters included inductive - capacitive filter, and introduced to a common inverter control system, through which the input clock phase adjusting unit ![]() clock connected to the network and its first and second outputs respectively connected to first and second three-phase inverters, providing regulation of the output voltage of the first phase of the three-phase inverter at an angle
clock connected to the network and its first and second outputs respectively connected to first and second three-phase inverters, providing regulation of the output voltage of the first phase of the three-phase inverter at an angle ![]() +
+ ![]() And at the second angle
And at the second angle ![]() -
- ![]() +
+ ![]() when it changes
when it changes ![]() on
on ![]() and change
and change ![]() relative voltage in a range from 0 to
relative voltage in a range from 0 to ![]() happy with the control input of the control inverters connected to the output of reactive power sensor network systems, and control input sync phase control unit is connected to the sensor, the deviation of the load voltage.
happy with the control input of the control inverters connected to the output of reactive power sensor network systems, and control input sync phase control unit is connected to the sensor, the deviation of the load voltage.
 |
 |
 | |
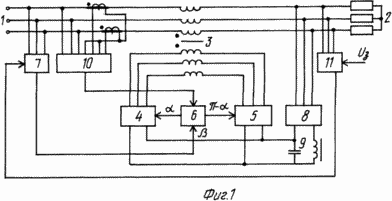
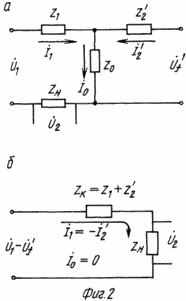
1 is a block diagram of an apparatus, Figure 2 - the equivalent circuit, and Fig. 3 - timing charts for explaining an action of reactive power compensator.
Apparatus (Fig. 1) comprises a three-phase three-phase power supply 1 and the load 2. The three-phase transformer 3, the two three-phase inverter 4 and 5 with their common control 6 and 7, the phase adjusting unit clock system, three-phase rectifier 8 with two-way exchange of energy, inductive-capacitive filter 9, the sensor network reactive power deviation of 10 and the load voltage sensor 11.
ELEMENTS circuit is connected FOLLOWS
Three-phase transformer primary winding 3 is connected between the network 1 and the load 2 and its secondary winding 4 between the outputs of the first and second three-phase inverter 5, whose inputs are combined through the filter 9 and the three-phase rectifier 8 are connected to the load (or another three-phase voltage source). Clock input 6, the inverter control system 4 and 5 via the block 7 clock phase adjustment is connected to the network and its control input - to the output of the sensor 10 network reactive power 1, while the control input of the phase adjusting unit 7 clock is connected to the sensor 11, the voltage deviation load 2.
The control system 6 performs the function of phase shift control pulses to the first and second outlets respectively at its corners ![]() and
and ![]() -
- ![]() relative to the initial phase
relative to the initial phase ![]() Regulated with respect to the mains voltage by means of the block 7.
Regulated with respect to the mains voltage by means of the block 7.
Reactive power compensator operates as follows.
The first and second three-phase inverters 4 and 5 convert the rectified voltage into two variable voltage. Vectors of the first harmonics of these stresses are shifted with respect to the mains voltage for the total initial phase ![]() About which one of these vectors to adjustable phase angle
About which one of these vectors to adjustable phase angle ![]() And the other at an angle
And the other at an angle ![]() -
- ![]()

Because the inverters 4 and 5 are connected to the secondary windings of the transformer 3 on both sides, it is applied to the inverter output voltage difference ![]()
or the amount of the complex-conjugate vectors with phase ![]() Depicted on the complex plane rotated relative to the angle of the line voltage
Depicted on the complex plane rotated relative to the angle of the line voltage ![]()

where k t - the transformation ratio.
Further reduction of all parameters of the secondary circuit to the primary (by analogy with the double-braked car power to the load circuit in the stator [4]), allow to create a reactive power compensator equivalent circuit (Fig. 2a), and neglecting the magnetizing current ![]() its simplified version (Fig. 2b), in which with sufficient accuracy to determine the voltage across the load 2
its simplified version (Fig. 2b), in which with sufficient accuracy to determine the voltage across the load 2 
From the last expression and vector diagram (Fig. 3) shows that the amplitude and phase of the vector ![]() It can be adjusted to changes
It can be adjusted to changes ![]() and
and ![]() . In particular, only control of the amplitude
. In particular, only control of the amplitude ![]() up and down relative
up and down relative ![]() by changing
by changing ![]() from 0 to
from 0 to ![]() glad and
glad and ![]() Is 0 or
Is 0 or ![]() rad, and the phases and changes in regulation
rad, and the phases and changes in regulation ![]() But at a value
But at a value ![]() Approximately equal to
Approximately equal to ![]() / 2 rad, and the anticipatory regulation
/ 2 rad, and the anticipatory regulation ![]() on
on ![]() by changing
by changing ![]() from 0 to
from 0 to ![]() / 2 rad, and lags behind
/ 2 rad, and lags behind ![]() / 2 to
/ 2 to ![]() glad. In the disclosed device change
glad. In the disclosed device change ![]() produced in the deflection function of zero reactive power network 1, a change
produced in the deflection function of zero reactive power network 1, a change ![]() in deviation from the specified function of the load voltage level 2.
in deviation from the specified function of the load voltage level 2.
When active-inductive load and consumption (generation) of reactive power compensator signal from the reactive power output of the sensor 10, the network 1 is supplied to the control input 6 inverter control systems 4 and 5 and reducing (increasing) control angle ![]() relative to the initial phase
relative to the initial phase ![]() , Carries an increase (decrease) in the effective value of the additional voltage
, Carries an increase (decrease) in the effective value of the additional voltage ![]() and, accordingly, increase (decrease) in the phase of the output voltage vector
and, accordingly, increase (decrease) in the phase of the output voltage vector ![]() , Advanced vector network voltage
, Advanced vector network voltage ![]() . When this deflection sensor 11 and load voltage signals on the control input of the phase sync control unit 7 that by changing the angle with respect to the mains voltage
. When this deflection sensor 11 and load voltage signals on the control input of the phase sync control unit 7 that by changing the angle with respect to the mains voltage ![]() , Regulates the additional stress phase
, Regulates the additional stress phase ![]() current and output voltage values
current and output voltage values ![]() . As a result of the amplitude-phase output voltages of the impact on the first and second three-phase inverters 4 and 5 the additional voltage vector
. As a result of the amplitude-phase output voltages of the impact on the first and second three-phase inverters 4 and 5 the additional voltage vector ![]() so forming a module and the argument that the vector load voltage 2
so forming a module and the argument that the vector load voltage 2 ![]() It is the radius of the given circle.
It is the radius of the given circle.
When active-capacitive load compensator works similarly, but with the formation of the device output voltage is carried out in the gap with respect to the mains voltage.
In the course of the output voltage stabilization at a reduced (increased) the value of the supply voltage with respect to a predetermined, for example, the nominal value, the rectifier 8 with a two-way exchange of energy operates in the rectifier (inverter) mode, providing the transformer 3 and the entire operation of the device in the voltage boost mode (voltovycheta) to consumption additional energy from the network (with energy recovery in the network).
During the transition phase rectifier 8 from the rectifier mode to the inverter mode and vice versa the energy supplied to the DC link voltage (or current) accumulated in a filter 9 and then to the voltage boost mode discharges through inverters 4 and 5 and the transformer and the load 2, and in voltovycheta mode through the rectifier 8 is returned to the network.
Use of the compensator permits full compensation of reactive power in an AC various systems with a certain stability of the current value of the output voltage regardless of the external characteristics of the network rigidity and also on the size and nature of the load.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. German Patent N 2531518, cl. H 02 J 3/18, 1974 - analogue.
2. Application of Japan N 62-184512, cl. H 02 J 3/12. 1987 - analog.
3. The Russian Federation patent N 1793514, cl. H 02 J 3/18. 1993 - the prototype.
4. Klimash BC booster transformers with thyristor controlled like a machine dual power. The Intercollege. Sat. papers "Theory and Design of el. equipment", Khabarovsk. HPI, 1987, p. p.114-118.
CLAIM
Var compensator comprising three-phase transformer with primary and secondary windings, three-phase rectifier, the input of which is connected to the load or other three-phase voltage source and the two-phase inverter with combined inputs and and a sensor network reactive power and sensor deflection load voltage, with some primary leads phase transformer connected to a load, and the other terminals of its secondary winding connected to the output of the first three-phase inverter, characterized in that one terminals of the secondary windings of a three phase transformer connected to the output of the second three-phase inverter and the other terminals of its primary winding connected to the network, wherein three-phase rectifier is made with a two-way exchange of energy between its output and the combined inputs of three-phase inverters included inductive-capacitive filter, and put the total for the three-phase inverter control system, a clock input which through phase control unit clock is connected to the first and second of its outputs, respectively, connected to first and second three-phase inverters, providing regulation of the output voltage of the first phase of the three-phase inverter at an angle ![]() +
+ ![]() And at the second angle
And at the second angle ![]() -
- ![]() +
+ ![]() when it changes
when it changes ![]() and
and ![]() in the range from 0 to
in the range from 0 to ![]() rad., where
rad., where ![]() - Pulse phase control with respect to clock and
- Pulse phase control with respect to clock and ![]() - Phase of the clock with respect to the supply voltage, and the control input of the three-phase inverter control system is connected to the network reactive power sensor and the control input clock phase control unit connected to the output load voltage deviation sensor.
- Phase of the clock with respect to the supply voltage, and the control input of the three-phase inverter control system is connected to the network reactive power sensor and the control input clock phase control unit connected to the output load voltage deviation sensor.
print version
Publication date 15.02.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.