| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2218091
![]()
METHOD OF SELECTION OF OBSTETRIC TACTICS
The name of the inventor: Orlov, AV; Gilyanovskiy M.Yu .; Zamanskaya TA; Orlov V.I.
The name of the patent holder: Rostov Research Institute of Obstetrics and Pediatrics
Address for correspondence: 344012, Rostov-on-Don, st. Mechnikova, 43, RNII Obstetrics and Pediatrics, Patent Department
The effective date of the patent: 2002.01.24
(EN) The invention relates to the field of medicine, namely obstetrics, and can be used in solving the issue of the method of delivery of pregnant women. The dopplerometric examination is performed and the indices of the resistance of the blood flow velocity curves (CSC) in the middle cerebral artery (CMA) of the fetus are determined before and after the functional test with interrupted respiration. With a decrease in the resistance indices, the KSK CMA of the fetus is given birth through the natural birth canal, and with an increase in the resistance indices of the CSK CMA of the fetus, or in the absence of changes, the delivery by cesarean section is chosen. The method allows to increase the accuracy in the choice of tactics of delivery and to shorten the study period.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely obstetrics, and will find use when deciding on the method of delivery of pregnant women.
In recent decades, the worldwide increase in the frequency of abdominal delivery has been combined with a real decrease in perinatal mortality, while in Russia the incidence of cesarean section has increased by an average of 3 times and amounted to about 12% [Strizhakov AN Et al., 2000]. One of the most important factors for increasing the number of cesarean sections is fetal indications, which determine almost 80% of operative delivery [Strizhakov AN et al., 1999]. A certain increase in the number of pregnant women with extragenital pathology and a complicated course of pregnancy caused an increase in perinatal morbidity and mortality. Improving the outcome of labor for this contingent of pregnant women is possible with the improvement of diagnosis and selection of the optimal type of delivery.
In the scientific medical and patent literature there is a sufficient number of methods for determining the tactics of labor, allowing for each pregnant individual to identify and select the tactics of delivery: in an operative or natural way.
A method is known for predicting the course of labor by measuring intrauterine pressure with two sensors simultaneously in the region of the bottom and the lower segment of the uterus, and if the pressure in the region of the lower segment exceeds the pressure in the region of the uterine fundus, the normal course of labor is predicted, and if the pressure in the region of the uterus Predict the pathological course of childbirth (Authorship 827022, 1981).
The disadvantage of the method is the lack of evaluation of the functional state of the fetus, as well as its compensatory-adaptive capabilities.
A method is known for diagnosing a condition requiring surgical delivery in pregnant women with heart disease by determining the volume of circulating blood, cardiac and shock index after physical exertion, and determining the minute and shock volume of blood, total peripheral resistance, pulmonary perfusion, Q interval, and diastolic amplitude ratio Waves to systolic rheopulmonograms and on the basis of changes in these indicators diagnose the need for operative delivery (author's comment 1209150, 1986).
The disadvantage of this method is its applicability only in pregnant women with heart defects, and the lack of evaluation of the functional state of the fetus.
A method for determining indications for a caesarean section in a pregnant woman with a transversal pelvis by X-ray and pellvimetry is known, with an index calculation of the ratio of the entrance area to the fetal mass and the determination of the direct diameter of the wide part of the cavity and the interosseous diameter. When the diameter of the wide part of the cavity is shorter than 12.5 cm in combination with the entry index less than 39.0 and when the interosseous diameter is less than 10.0 cm in combination with the entry index less than 39.0, the need for cesarean section (auth. 1627116, 1991).
The disadvantage of the method is the use of such a complex and unsafe method for the health of the mother and fetus, such as X-ray neoplasmometry. And there is no evaluation of the functional state of the fetus and its compensatory-adaptive capabilities.
The method of choosing the optimal obstetric tactics using dopplerometry is described, which allows to identify and assess the degree of severity of hemodynamic disorders of uteroplacental and fetoplacental blood flow (Strizhakov AN et al., 1991, Obstetrics and Gynecology, 8, pp. 3-5, Savchenko I.Yu., ibid., Pp. 8-11).
The disadvantage of the method is the lack of evaluation of the compensatory-adaptive capacity of the fetus.
A method for determining the management of births by determining the ratio of the size of the true pelvic conjugate and the biparietal size of the fetal head according to the formula K = T / A, and the frequency of high-amplitude contractions of the uterus, the absence of growth of which at a value of "K" is less than 1.14 determines the choice of operational tactics (Patent of the Russian Federation 2012218, 1994).
The disadvantage of the method is the lack of evaluation of the functional state of the fetus, as well as its compensatory-adaptive capabilities.
There is a known method of conducting labor in women with operated uterus by echographic measurement of the thickness of the lower segment of the uterus in the peak of the contract and during its relaxation into the active phase of labor and opening the uterine throat more than 3 cm. With an increase in the thickness of the lower segment in the fray by 0.2 cm and more Births continue to lead through the natural birth canal, in the absence of this change, the uterine scar is considered functionally insolvent and produces a cesarean section (patent RF 2069992, 1996).
The shortcomings of this method can be attributed, in addition to specificity, the impossibility of a preliminary (planned) definition of the tactics of labor; Adjustments to tactics are made already in the process of childbirth.
A method of conducting labor in rheumatic heart diseases is known by determining the presence of cardiac rhythm disturbances, enlargement of the heart chambers, activity of the rheumatic process and changes in blood circulation. Each of the diagnostic features is assigned a certain number of points from 1 to 26 and with the number of points from 1 to 13 births go through the natural birth canal without turning off attempts, from 18 to 27 points - give birth by cesarean section (RF patent 2151543, 2000).
The disadvantage of this method is its applicability only in pregnant women with rheumatic heart defects.
A method for determining the tactics of conducting labor during gestosis by a complex study of the structure of the placenta using ultrasound complex scanning and biosynthetic function of the placenta using the radioimmunoassay method is described. With relative fetoplacental insufficiency (FPN) and the effectiveness of gestosis therapy, births through natural birth canals are possible, with absolute FPN in conditions of chronic fetal hypoxia and ineffectiveness of the current therapy, a caesarean section operation is chosen (Kustov SM, diss. , 2000, Novosibirsk, page 23).
The disadvantage of the method is the lack of evaluation of the compensatory-adaptive capacity of the fetus.
The prototype of the claimed method is a method for determining the indications for delivery by cesarean section in FPN, and the syndrome of fetal development retardation during pregnancy for more than 32 weeks. (Strizhakov AN et al., Obstetrics and Gynecology 5, 2000, page 16.). Indications for delivery by cesarean section in the planned order are:
- retardation of fetal development or appearance of dopplerometric signs of centralization of its blood circulation when pregnancy is overdone (SDO in fetal aorta> 8.0, SDO in middle cerebral artery (SMA) of fetus <2.8);
- pelvic presentation or transverse position of the fetus;
- a combination of hemodynamic disorders 1B - II degree in the mother-placenta-fetus system, initial signs of fetal hypoxia with another obstetric pathology (large fetus, the age of the pervious older than 30, burdened obstetric history, etc.);
- progression of the initial signs of FPN (worsening of CTG indices, growth of SDS or appearance of signs of centralization of blood circulation in Doppler study), despite the ongoing treatment.
The disadvantage of the prototype is its polyinformativity and multifactority of the studied indicators using several instrumental methods of research, which significantly complicates its practical use.
The analysis of the revealed methods of choosing the optimal obstetric tactics testifies to the lack of a simple, universal and accurate method that would allow screening of pregnant women to determine the planned tactics of labor management.
The claimed invention makes it possible to solve this problem.
The aim of the invention is to develop an accurate screening method for selecting obstetric tactics.
The problem is solved by determining the indices of the resistance of the blood flow velocity curves in the middle cerebral artery (CMA) of the fetus before and after the functional test with interrupted breathing and with the decrease of the resistance indices of the KSK CMA of the fetus by the dopplerometric measurement, the births are carried out through the natural birth canals, And if the indices of KSK CMA resistance of the fetus increase or if there are no changes, the delivery by cesarean section is chosen.
The claimed method has the following advantageous differences from the prototype:
1. In the prototype we are talking about the state of the hemodynamics of the fetus, ascertainable only in a state of rest; On the evaluation of its functional state, which does not allow to assess the state of compensatory-adaptive capabilities of the intrauterine fetus. In the method we propose, creating an artificial hypoxemia of the fetus with a delay in the breathing of the mother, we simulate a situation in which the fetus is inevitable with an increase in the intensity of labor. As a result of this initiated hypoxemia, the fetus undergoes temporary adaptive hemodynamic restructuring, which makes it possible to judge the adaptive-compensatory reserves of the intrauterine fetus necessary to counteract the birth stress.
2. The claimed method does not require a long examination of the pregnant woman, there is no need to use CTG, to evaluate the biophysical profile of the fetus, oxytocin test, and so on. It can be used as a screening method.
By creating artificial hypoxemia in the interruption of breathing, we bring the pregnant woman closer to the "natural" conditions in which the fetus is located during each contraction in the intranatal period. As a result of this provocative hypoxemia, the fetus undergoes temporary adaptive hemodynamic restructuring, very close to the one that occurs in childbirth. In this case, the type of reaction of the fetal cerebral vessels is due to a change in the blood gas (oxygen and carbon dioxide) voltage in the mother and in the fetus when the respiration is delayed.
Expansion of cerebral vessels of the fetus (decrease in the indices of resistance of KSK CMA fetus) in response to temporary hypoxemia with interruption of respiration is a physiological response. This reaction makes it possible to protect the fetal CNS during temporary hypoxemia. This makes it possible to ensure a normal blood supply to the fetal brain in the conditions of labor (optimum oxygen supply). This mechanism of centralization of fetal circulation is the response physiological response of adaptive-compensatory mechanisms of the fetus to hypoxemia and indicates the possibility of delivery in a natural way.
The spasm of the fetal cerebral vessels (an increase in the indices of resistance of the KSK SMA fetus) in response to a temporary hypoxemia in the interruption of breathing, as well as the absence of any reaction, in our opinion, is not physiological, as there is no compensatory enhancement of cerebral blood flow in the fetus Response to hypoxemia. Spasm of the fetal brain vessels in this case is due to a violation in the functioning of the adaptive-compensatory mechanisms of the fetus during hypoxemia. This disorder is due to the long-term chronic fetal hypoxia. The lack of response of the cerebral vessels of the fetus is explained by the so-called loss of vasoreactivity, which is also one of the manifestations of chronic hypoxia. In these cases (in the presence of spasm or absence of the reaction of cerebral vessels in response to a functional test with discontinuous breathing), it is inappropriate to put the fruit into a powerful hypoxemic effect that occurs during fights and attempts, as the probability of weighting the existing hypoxia and the onset of cerebral edema is high Disadaptation of the mechanisms of the regulation of fetal blood flow, in this case it follows the tactic of choice to perform a caesarean section operation.
Functional test with interrupted breathing has long been used in cardiology with functional diagnostics to detect hidden changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, which are best manifested during stress tests. In obstetrics, for the diagnosis of hypoxia of the fetus during the recording of CTG, samples are taken with a delay in breathing during inspiration and exhalation (Eilamazyan EK Obstetrics, St. Petersburg, 2000). However, this type of sample is different from the sample with interrupted breathing and is not used to select the tactics of delivery.
The claimed method is carried out as follows. A pregnant ultrasound dopplerometric study using an ultrasound device Alloka 1400, a and Toshiba (ECCOCEE) SSA-340A with color Doppler mapping is performed at 39-40 weeks. A convection electron sensor with a frequency range of 3.5 MHz is used. The functional test with interrupted breathing is carried out according to the following procedure. First determine the baseline level of cerebral blood flow of the fetus. To do this, examine the blood flow in the middle cerebral arteries of the fetus in the B-mode of scanning, obtaining the average axial section of the fetal head at the level of the legs of the brain with the removal of the bone boundary of the anterior and middle cranial fossa, which is the anatomical projection of the location of the middle cerebral artery of the fetus in the region of the sylvian furrow. The control volume is set in the projection of the middle cerebral artery of the fetus located closer to the sensor and a measurement is made. Sometimes, with difficult visualization of the middle cerebral arteries of the fetus, the regime of color Doppler mapping (on the Toshiba SSA-340A) was used, which made it possible to clearly determine the localization of the middle cerebral arteries of the fetus (Ageeva MI, 2000). After that, the woman is asked to stop breathing for the maximum possible time for her. And immediately after the apnea with the beginning of inspiration, an evaluation of the blood flow in the middle cerebral artery of the fetus is again performed. With a decrease in the resistance indices, the KSK CMA of the fetus is given birth through the natural birth canal, and with an increase in the resistance indices of the CSK CMA of the fetus, or in the absence of changes, the delivery by cesarean section is chosen.
The working capacity of the method is confirmed by the following examples.
Example 1
Patient M-t, 21, the history of the disease 819, first-pregnancy primigravid, gestation period 40-41 week.
General diseases: myopia of weak degree of both eyes.
There are no gynecological diseases.
Obstetrical pathology: generally uniformly dense pelvis of the 1st degree.
The course of this pregnancy was complicated:
- in the period of 5-6 weeks. Early toxicosis of mild degree,
- in the period of 36 weeks. The threat of premature birth,
- in the period of 38 weeks. Late gestosis (E),
- in the period of 40 weeks. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia (according to CTG, fetal status index 2.3).
At a period of 40 weeks, dopplerometry was performed with a functional test (interrupted breathing):
SDO CSC of MCA fetus to sample 3.03.
SDO CSC of MCA fetus after sample 3.66.
Because There was an increase in the indices of resistance of KSK SMA fetus, then it was decided to select an operative method of delivery.
Extraction of the child occurred at 5 minutes from the start of the operation.
A boy was born, weighing 3600 g, 51 cm long.
His state on the Apgar scale is 6-7 points.
The acid-base condition of arterial and venous blood taken for analysis from the umbilical cord to the child's first inspiration is shown in Table 1.
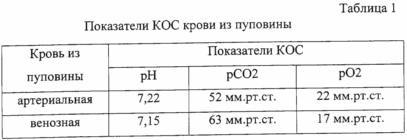
During the first five days of life, the child showed uncharacteristic signs of a central nervous system disorder that are characteristic of ischemic-hypoxic brain damage. Under the influence of ongoing drug therapy, the state of the child has improved significantly.
Thus, the method of delivery chosen by us on the basis of a sample with interrupted breathing performed during dopplerometry was optimal. The decrease in the adaptive-reserve capabilities available in a child in the antenatal period, which the child had against hypoxic disorders, could lead to an unfavorable perinatal outcome when attempting to deliver through the natural birth canal.
Example 2
Patient B-24, disease history 800, pregnancy 3, childbirth 2, gestational age 40-41 week.
General diseases: myopia of weak degree of both eyes.
Gynecological diseases chronic adnexitis since 2000.
Obstetrical pathology: late gestosis (E), anemia of pregnant women.
The course of this pregnancy was complicated:
- in the period of 4-5 weeks. Exacerbation of chronic adnexitis,
- in the period of 6-8 weeks. Early toxicosis of mild degree and threat of termination of pregnancy,
- from 32 weeks. Anemia of pregnant women,
- from 36 weeks. Late gestosis (E).
At the term of 39 weeks, dopplerometry with functional breakdown (interruption by breathing) was performed:
SDS KSK SMA fetus to sample 3.47
SDO CSC of MCA fetus after sample 2.94
Since there was a decrease in the indices of KSK CMA resistance of the fetus in response to a delay in breathing, it was decided to lead the birth through natural birth canals.
The first period of labor was 5:25
The second period is 0:20
The third period is 0:10
The anhydrous period is 5:10
A girl was born, with a mass of 3600 g, 51 cm long.
His state on the Apgar scale is 8-9 points.
The acid-base state of arterial and venous blood taken for analysis from the umbilical cord to the child's first inspiration is shown in Table 2.
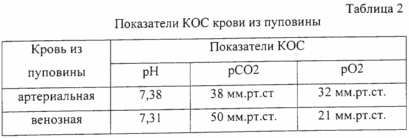
During the whole neonatal period, the child did not have any pathological changes.
Thus, the method of delivery chosen by us on the basis of a sample with respiratory delay during dopplerometry was optimal.
The claimed method examined 85 pregnant women in a period of 39-40 weeks. In 30 (35.3%) of them, the values of the resistance indices of the KSK CMA of the fetus decreased after the functional test with interrupted respiration (group 1). In 39 (47.9%) - increased (2 group), and in 16 (18.8%) - remained unchanged (group 3). These data are presented in Table 3.
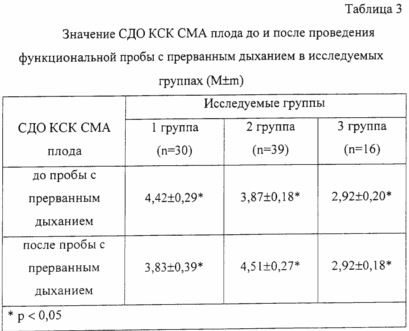
Pregnant women from group 1 were given birth through natural birth canals, pregnant women of 2 and 3 groups - by cesarean section. The state of children at birth on the Apgar scale, and the peculiarities of the functioning of the central nervous system in them on day 5 of the early neonatal period are presented in Table 4.
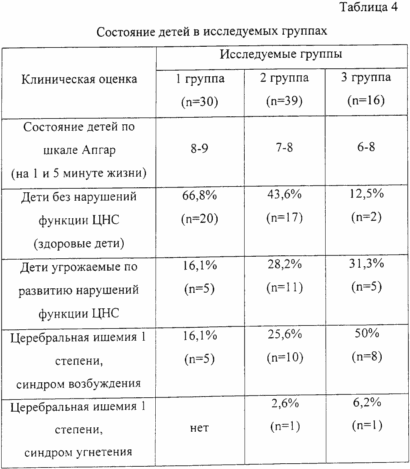
The advantages of this method are that it allows:
1. It's fast enough to choose the tactics of delivery.
2. It gives an opportunity to evaluate not only the functional state of the fetus, but also its compensatory-adaptive capabilities.
3. Significantly reduces the amount and time of research.
4. Does not require complicated computer and mathematical processing.
5. Reduces economic costs.
6. It is possible to use as a scoring method.
The proposed method of choosing the tactics of delivery is tested on sufficient clinical material and can be widely used in obstetric practice.
CLAIM
The method of selecting obstetric tactics by dopplerometric determination of resistance indexes of blood flow velocity curves in the median cerebral artery (CMA) of the fetus, characterized in that the measurements are carried out before and after the functional test with interrupted respiration and with the reduction of the resistance index of the KSK CMA fetus, Natural birth canal, and with an increase in the indices of KSK CMA resistance of the fetus or in the absence of changes, the delivery by cesarean section is chosen.
print version
Date of publication 27.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.