| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2108750
![]()
METHOD OF DIAGNOSIS OF CHRONIC ENDOMETRITIS
The name of the inventor: Posiseeva LV; Boyko E.L .; Borzova N.Yu .; Malyshkina AI; Shekhlova N.V.
The name of the patent holder: Ivanovo Research Institute of Maternity and Childhood of the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation
Address for correspondence:
The effective date of the patent: 1995.09.25
The invention is intended for the diagnosis of chronic endometritis. In the menstrual blood, the level of soluble antigen of leukocytes-2 (PAL-2) is determined. At the level of RAL-2, equal to or above 640 μg / ml, chronic endometritis is diagnosed. The method allows to diagnose with a high accuracy chronic endometritis, is simple and accessible in execution.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely to obstetrics and gynecology, can be used to diagnose chronic endometritis by the content of certain soluble proteins in menstrual blood.
Inflammatory diseases of internal genitalia occur more often at a young age and in 65-77.8% of patients take a heavy, protracted course, which leads to loss of women's ability to work and infertility [1 and 2].
The frequency of chronic endometritis (CE), according to various authors, varies widely - from 0.2 to 66.3%, averaging 14% [3 and 4]. Apparently, such a wide range of CHE frequency can be explained by the use of different morphological criteria in setting the range. In recent years, there has been a tendency to increase the frequency of CHE, which is associated with a wide use of intrauterine contraception, an increase in the number of abortions and various intra-uterine manipulations, including endoscopic research methods.
As a prototype, a method of histological examination of scraping of the endometrium was chosen. Endometrial scraping is advisable at the end of the secretion phase (on days 5-6 of basal temperature rise). The resulting material is fixed in a 15% formalin solution, stained with hematoxylin-zosin. Chronic endometritis is detected on the basis of the presence of plasma cells and a tendency to predominantly focal congestion of the small-cell infiltrate [5 and 6].
The disadvantages of the prototype method are:
1. The main condition of the method is the implementation of a total scrap of the endometrium (the accuracy of the method in this case is 90.1 to 95%), with biopsy (local fence) of the endometrium, the accuracy of the method does not exceed 64%.
2. The method does not allow to conduct research in dynamics.
3. Endometrial biopsy is traumatic, it can be accompanied by complications that are dangerous not only for health, but also for a woman's life:
- Perforation of the uterus,
- Bleeding,
- Damage to the intestines, bladder,
- The formation of synechia in the uterine cavity,
- Formation of isthmico-cervical insufficiency,
- Infectious complications,
- Complications during anesthesia, etc.
4. The risk of infection with hepatitis, AIDS is not ruled out.
5. Endometrial biopsy is performed in a specially equipped room for small gynecological operations. The woman is released from work, which is connected with economic damage.
6. Specialized methods and equipment are required for pathomorphological units.
7. This method continues over time (histological examination is carried out for 5 to 7 days), which leads to untimely treatment.
These disadvantages can be eliminated in the proposed method.
The aim of the invention is to increase the accuracy and simplify the diagnosis of chronic endometritis in women in terms of soluble antigen content of leukocytes-2 (PAL-2) in menstrual blood.
The goal is achieved by the fact that the content of RAL-2 is determined in a woman's menstrual blood and at a level of 640 mcg / ml and above, the presence of chronic endometritis is diagnosed in 76.9% of cases.
The novelty of the invention lies in the fact that for the first time the diagnosis of chronic endometritis in women according to the definition of RAL-2 in menstrual blood is proposed. Earlier studies of menstrual blood of women on RAL-2 for the diagnosis of inflammatory processes of the uterus were not carried out.
Soluble antigen of leukocytes-2 (PAL-2) was first described in 1982. Petrunin et al. [7]. This glycoprotein with a molecular mass of 90000 ± 7000 D and electrophoretic mobility of alpha-2 globulins can withstand heating to 100 ° C for 1 hour. A large amount of PAL-2 is contained in extracts of organs rich in lymphoid tissue, as well as in sperm. In endometrium, in menstrual blood and mucus of the cervical canal, RAL-2 is found in small amounts, and its indices are independent of the phase of the menstrual cycle and the function of the ovaries [8].
An important property of RAL-2, like most other antigens of the RAL system, is its high resistance to enzymatic actions. Having high resistance to the action of proteolytic enzymes, RAL-2 can fulfill its biological function in the foci of destruction and inflammation, where lysosomal proteolytic enzymes from leukocytes are concentrated [9]. With chronic salpingo-oophoritis, the content of PAL-2 in the serum of women increases [10 and 11].
The method is carried out as follows. In women on the 1-2 day of menstruation, up to 15 drops of menstrual blood are collected by inserting a spoonful or bivalve mirror into the vagina, on which blood is stored in the vagina and draining from the outer throat of the cervix. Mirror is extracted, menstrual blood from it merges into a test tube. A woman can collect her menstrual blood in a clean bottle herself at home and store it in a normal freezer at a temperature below 0 ° C before the study. When the test is done, the menstrual blood is thawed at room temperature. The investigation of PAL-2 is carried out by the method of double immunodiffusion in agar with a standard test system against RAL-2. Semiquantitative method. Before the analysis, a number of dilutions of the menstrual blood in the distilled water in the wells of the polyethylene matrix are prepared, respectively, 1: 1, 1: 2, 1: 4, 1: 8, 1:16, 1:32, 1:64, 1: 128, 1 : 256. The reaction is carried out on degreased slides filled with a melted 1% Difco-type agar solution with 2.5% sodium chloride solution at a rate of 5 ml gel per analysis. When the agar is frozen, holes are pierced with a special standard "seven" stamp. On one glass make two "sevens". Agar from the wells is removed with a thin needle. An antiserum against PAL-2 is poured into the central well of each of the "sevens" using a Pasteur pipette, two opposing solutions of the standard antigen, and the remaining four - the test menstrual blood in different dilutions. The glasses are placed in a Petri dish with a moist medium. Immunogenesis lasts 18-24 hours. The results are read the next day in transmitted light. It takes into account the last bend of the line of targeting near the hole with the corresponding dilution of the blood being examined. This dilution is multiplied by the sensitivity of the method - 5 μg / ml. Thus, a semiquantitative estimate of the result is obtained. The result is compared with the normative parameters of female-menstrual blood RAL-2. When a reaction to RAL-2 is performed, one slide with agar is used for one analysis.
Essential differences of the prototype method from the claimed method are:
Firstly, a diagnostic parameter in the form of PAL-2 menstrual blood is suggested, corresponding to a chronic endometrium of 640 μg / ml and above.
Secondly, another biological medium is used - menstrual blood (in the prototype method a scraping of the mucous membrane of the uterus is used).
The essence of the method is explained by the following examples:
Example 1 . Patient A, 25 years old, turned to a doctor obstetrician-gynecologist about the issue of contraception. Based on clinical and laboratory data, obstetric-gynecological history was diagnosed: practically healthy. The ultrasound examination was carried out - the pathology of the pelvic organs was not revealed. Histological examination of the endometrial scraping revealed a secretory-menstrual endometrium. According to the claimed method, the content of PAL-2 was measured in menstrual blood, the value of this indicator was 10 μg / ml. The conclusion is given: contraindications for intrauterine contraception have not been revealed. The patient's patient was diagnosed, there were no pathological changes.
Example 2 . Patient S., 25, who has a history of a spontaneous miscarriage, turned to a doctor obstetrician-gynecologist with complaints of periodic pain in the lower abdomen, mucus-yellowish leucorrhoea from the genital tract. On examination: the cervix is clean, without defects; The outer yawn will close. Uterus not enlarged, dense, slightly painful on palpation. Attachments are not increased. Allocations are mucous. In clinical and biological analyzes of blood and urine, pathology was not detected, in smears - III degree of purity of the vagina, gonococcus and Trichomonas were not detected. At carrying out of ultrasonic research of a pathology from bodies of a small basin it is not revealed. The histological examination of endometrium of the middle phase of secretion, chronic endometritis, performed on day 22 of the cycle. The menstrual blood is taken and according to the proposed method, the content of RAL-2 is studied. The concentration of protein in menstrual blood is 640 μg / ml. The conclusion: in patient S. - chronic endometritis.
Example 3 . Patient A., 30 years old, with primary infertility for 5 years. Has addressed on reception to the doctor to the obstetrician-gynecologist with complaints on absence of pregnancy, periodic pains in the bottom of a stomach and in the field of a sacrum, intermenstrual bloody allocation from sexual ways. On examination: cervix without defects, clean; The outer yawn will close. The uterus is not enlarged, mobile, dense, with palpation a little painful. Attachments are not enlarged, mucus discharge. In clinical and biochemical analyzes of blood and urine, pathology was not detected, in smears - grade II purity of the vagina, gonococcus and Trichomonas were not detected. At ultrasound examination of a pathology from bodies of a small basin it is not revealed. Examination by the prototype method: in the histological examination of scrapes of the endometrium, an early phase of secretion, chronic endometritis, was detected. When examined by the declared method: RAL-2 in menstrual blood was found at a concentration of 1: 256, which is 1280 μg / ml. Conclusion: chronic endometritis.
Advantages of the claimed method.
1. High accuracy of the forecast - 76.9%.
2. Absolute safety and availability of the method is associated with the study of menstrual blood on RAL-2, which allows to evaluate the results of treatment in dynamics.
3. The simplicity and accessibility of the use of test systems on RAL-2 allow it to be widely used in practical health care.
As can be seen from the table, the accuracy of the claimed method is 76.9%, the prototype is 66.7%. The use of this method allows to achieve the set goal - to perform the diagnosis of CHE with an accuracy of 76.9% and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
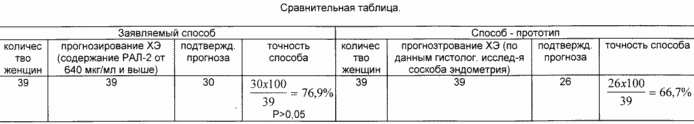
Thus, the claimed method of diagnosing chronic endometritis in women provides, along with high accuracy and ease of implementation, complete safety for the woman and availability of use compared to the prototype method.
The use of the proposed method will allow timely start a full-fledged treatment, which will help reduce the incidence of inflammatory diseases of the genitals and violations of the reproductive function of women.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Bodyazhina V.I. Chronic nonspecific inflammatory diseases of female genital organs. -M .: Medicine, 1978, p. 319.
2. Kate L and Berger G. Causes of infectious diseases of the pelvis. // Reproductive health. Ed. Keita L. and others. With the English. - M .: Medicine, 1988. vol.1, - Ch. 1, p. 123 - 231.
3. Savelyeva GM and Antonova L.V. Acute inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs of women. - Moscow: Medicine 1987, p.158.
4. Bodyazhina VI, Smetnik VP, Tumilovich LG Non-operative gynecology. - M .: Medicine, 1990 p.316-319.
5. Volkova O.V. And Yeletsky Yu.I. Basics of histology with histological technical. - Moscow: Medicine, 1992, 202 p.
6. Petrova E. N. Histological diagnosis of uterine diseases. - Moscow: Medicine, 1959, p. 93-94.
7. Petrunin D.D. Lopukhin Yu.M., Molodenkov MN And Olefirenko G.A. Immunochemical identification of thermostable alpha-glycoprotein in blood serum for some diseases with pathology of the immune system. - Byull. Expert. Biol, 1982, N 4 s. 66-68.
8. Shevchenko OP, Pshenichnikov T.Ya., Volkov N.I. And Petrunin D.D. Immunological studies of antigens of indometry. - Immunology, 1985. N 3, c. 73 - 74.
9. Petrunin D.D. And Lopukhin Yu.M. Comparative immunochemical and physico-chemical radiation of a system of soluble antigens of human leukocytes. - Hematology and Transfusiology, 1985, T 11, p. 3 - 7.
10. Strizhova N.V. Gasparyan NN, Petrunina Yu.A. And Tumenova SK Comparative immunochemical radiation of a system of soluble leukocyte antigens in women with chronic salpingophoritis in remission. - Obstetrics and Gynecology, 1987, N 3, p. 44-46.
11. Strizhova N.V. Petrunina Yu.A. And Gasparyan N.N. Immunochemical radiation of a system of soluble antigens of leukocytes in patients with exacerbation of chronic salpingo-oophoritis. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 1984, N 2, p. 58 - 59.
CLAIM
Method for the diagnosis of chronic endometritis by definition of the immunochemical parameter, characterized in that in the menstrual blood as the immunochemical parameter the level of soluble antigen of leukocytes-2 (PAL-2) is determined and at a level of PAL-2 equal to or above 640 μg / ml, chronic endometritis is diagnosed .
print version
Date of publication 27.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.