|
Начало раздела Производственные, любительские Радиолюбительские Авиамодельные, ракетомодельные Полезные, занимательные |
Хитрости мастеру Электроника Физика Технологии Изобретения |
Тайны космоса Тайны Земли Тайны Океана Хитрости Карта раздела |
|
| Использование материалов сайта разрешается при условии ссылки (для сайтов - гиперссылки) | |||
Навигация: => |
На главную/ Каталог патентов/ В раздел каталога/ Назад / |
|
ИЗОБРЕТЕНИЕ
Патент Российской Федерации RU2051707
![]()
СПОСОБ ПРЕРЫВАНИЯ БЕРЕМЕННОСТИ РАННИХ СРОКОВ
И УСТРОЙСТВО ДЛЯ ЕГО ОСУЩЕСТВЛЕНИЯ
Имя изобретателя: Грицюк Вадим Иванович; Шеин Владимир Петрович; Редискин Александр Иванович
Имя патентообладателя: Грицюк Вадим Иванович; Шеин Владимир Петрович; Редискин Александр Иванович
Адрес для переписки:
Дата начала действия патента: 1992.03.06
Изобретение относится к магнитотерапевтическим аппаратам с использованием магнитных полей. Использование: в гинекологии, для прерывания беременности ранних сроков. Сущность изобретения: способ включает создание направленного концентрированного воздействия знакопеременного магнитного поля напряженностью 150-200 Э на тело матки и плодное яйцо и дополнительное воздействие знакопеременного магнитного поля на рецептурную зону наружного зева шейки матки. Заданное индуктором в виде меандра чередование макрополюсов N и S на внутренней поверхности магнитофорного колпачка обеспечивает перемещение силовых магнитных линий при ходьбе пациентки относительно шейки матки и воздействие знакопеременного магнитного поля на чувствительные нервные окончания рецепторов, окружающих цервикальный канал, которые, возбуждаясь под действием этого поля, вызывают шеечно-гипофизарный рефлекс матки. Магнитофорный колпачок содержит усеченный конус с одним дном. Стенка конуса выполнена с одинаковой толщиной по всей ее высоте, а внутренний диаметр основания конуса определен больше наружного диаметра шейки матки на 1,5 - 2 мм. При этом дно конуса колпачка может быть снабжено дренажными отверстиями.
ОПИСАНИЕ ИЗОБРЕТЕНИЯ
Изобретение относится к магнитотерапевтическим аппаратам с использованием магнитных полей, а именно к способам и устройствам для прерывания беременности ранних сроков, и может быть использовано в амбулаторной гинекологической практике.
Известен способ прерывания беременности ранних сроков, включающий создание направленного концентрированного воздействия знакопеременного магнитного поля напряженностью 150-200 Э на область тела матки и плодное яйцо с помощью намагниченного магнитофорного колпачка, расположенного на шейке матки [1]
Известен и, выбранный в качестве прототипа, способ прерывания беременности ранних сроков, включающий воздействие на плодное яйцо неоднородным постоянным магнитным полем напряженностью 150-200 Э с помощью источника постоянного магнитного поля, закрепленного на шейке матки [2]
Недостатком способа-прототипа является невозможность обеспечения воздействия магнитного поля на часть шейки матки, наиболее снабженную рецепторами и расположенную в непосредственной близкости дна и боковой поверхности магнитофорного колпачка, что снижает эффективность прерывания беременности.
Кроме того, предлагаемый способ не предусматривает оттока отторгаемых тканей содержимого матки без снятия магнитофорного колпачка, что усложняет проведение манипуляции прерывания беременности и создает угрозу возникновения гнойно-септических заболеваний.
Известно и устройство для прерывания беременности ранних сроков, содержащее источник постоянного магнитного поля в виде магнитофорного шеечного колпачка [1]
Однако, эффективность такого колпачка составляет 50%
В качестве прототипа выбрано устройство для прерывания беременности, содержащее колпачок "Кафка" источник постоянного магнитного поля, расположенный во влагалище, на шейке матки, у которого дно выполнено из магнитотвердого материала (магнитофора) [2]
Недостатком такого устройства является наличие отбортовки у колпачка, магнитное поле которой воздействует на окружающие матку ткани, что приводит к ослаблению его воздействия на шейку матки и, следовательно, снижает эффективность прерывания беременности ранних сроков.
Кроме того, "глухая" конструкция указанных колпачков способствует активному, за счет присасывающего эффекта, и пассивному забросу распадающихся тканей плодного яйца и микробной флоры цервикального канала в стерильную полость матки. Такой эффект "термостата" способствует бурному росту микробной флоры и способствует развитию септических состояний.
Техническим результатом предлагаемого изобретения является повышение эффективности прерывания беременности ранних сроков и снижение вероятности возникновения осложнений при проведении процедуры за счет увеличения зоны воздействия магнитного поля на снабженную рецепторами область шейки матки, расположенную в непосредственной близости дна и боковой поверхности магнитофорного колпачка, вызываемого при этом шеечно-гипофизарного эффекта, а и за счет обеспечения оттока из матки отторгающихся тканей плодного яйца во время проведения процедуры.
Поставленный технический результат достигается тем, что в способе прерывания беременности ранних сроков, включающем воздействие неоднородным магнитным полем напряженностью 11,9-15,9 кА/м на плодное яйцо, согласно изобретению, дополнительно воздействуют на шейку матки знакопеременным магнитным полем, неоднородность которого создают чередующимся расположением макрополюсов.
При этом величина магнитной индукции каждого макрополюса, составляет 20 млТл.
Поставленный технический результат достигается и тем, что в устройстве для прерывания беременности ранних сроков, выполненном в виде колпачка, часть которого выполнена из магнитофора, согласно изобретению, колпачок полностью выполнен из магнитофора на основе синтетического каучука, имеет форму усеченного конуса с одинаковой толщиной стенки и дна, при этом на внутренней поверхности колпачка сформированы области намагниченности в виде чередующихся макрополюсов. Кроме того, дно колпачка выполнено с дренажными отверстиями, макрополюса расположены с шагом, равным 2 мм. Магнитофор выполнен в виде однородной композиции синтетического каучука и феррита бария.
Дополнительное воздействие знакопеременного магнитного поля с заданной величиной магнитной индукции 20 млТл на наиболее снабженную рецепторами часть шейки матки область наружного зева позволяет охватить всю рецепторную зону шейки матки и вызвать значительный шеечно-гипофизарный рефлекс, изменяющий уровень гормональной регуляции, что обеспечивает повышение эффективности прерывания беременности.
Выполнение колпачка из магнитофора в виде усеченного конуса с одинаковой толщиной по всей его высоте позволяет исключить воздействие магнитного поля со стороны колпачка на окружающие матку ткани и, тем самым, усилить его воздействие на рецепторы шейки матки.
Наличие на внутренней поверхности колпачка областей намагниченности в виде чередующихся макрополюсов с шагом, равным 2 мм, обеспечивает чередование требуемого количества знакопеременных макрополюсов (N, S) в нем, воздействующих на рецепторы шейки матки, что увеличивает эффективность прерывания беременности.
Выполнение дренажных отверстий в дне колпачка дополнительно увеличивает отток распадающихся тканей из полости матки при обеспечении требуемой прочности дна колпачка за счет выполнения его из однородной композиции синтетического каучука и феррита бария.
Именно дополнительное воздействие знакопеременного магнитного поля на наиболее снабженную рецепторами часть шейки матки при указанном выполнении источника магнитного поля магнитофорного колпачка, обеспечивает усиление шеечно-гипофизарного рефлекса рецепторов шейки матки, приводящее к прерыванию беременности, и, следовательно, к достижению цели изобретения.
Это позволяет сделать вывод о том, что предложенные изобретения связаны между собой единым изобретательским замыслом.
Сравнение предложенных технических решений с прототипом позволило установить соответствие критерию "новизна". Изучение других известных технических решений в данной области техники показало, что предлагаемые изобретения вытекают из них неочевидным образом и, следовательно, соответствуют критерию "изобретательский уровень".
 |
 |
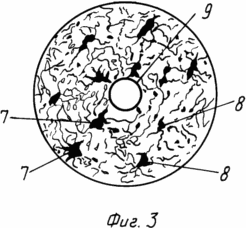 |
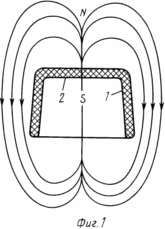
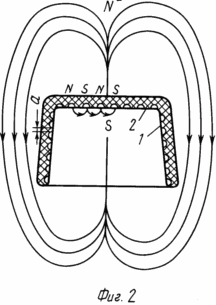
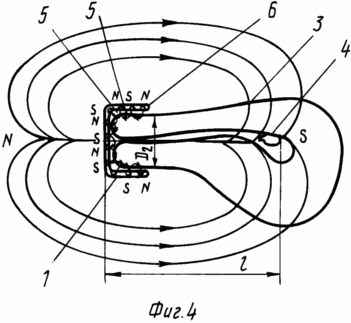
На фиг. 1 изображено распределение магнитных силовых линий (N, S) в зоне воздействия магнитофорного колпачка на тело матки с радиусом 5-7 см (зона плодного яйца); на фиг. 2 то же, и распределение магнитных силовых линий на внутренней поверхности магнитофорного колпачка, воздействующих на рецептурную область шейки матки; на фиг. 3 рецепторная область торца шейки матки, охватываемая воздействием магнитного поля внутренней поверхности дна колпачка.
 |
 |
 |
 |
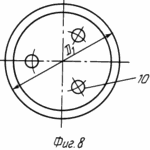 |
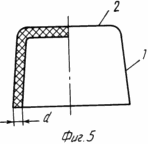
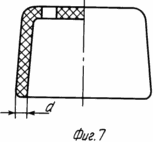
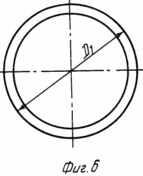
на фиг. 4 распределение магнитных силовых линий в зоне плодного яйца и рецепторной зоне щей ки матки при расположении магнитофорного колпачка на шейке матки; на фиг. 5 общий вид магнитофорного шеечного колпачка (в разрезе); на фиг. 6 то же, вид сверху; на фиг. 7 то же, с дренажными отверстиями, выполненными в его дне (в разрезе); на фиг. 8 то же, вид сверху.
СПОСОБ ОСУЩЕСТВЛЯЕТСЯ СЛЕДУЮЩИМ ОБРАЗОМ
После осмотра пациентки определяют срок беременности, и, если он не превышает 2-3 недель, определяемых уровнем хронического гонадотрапина, на шейку матки одевают шеечный магнитофорный колпачок 1.
На фиг. 1, 2, 4 показано расположение макрополюсов N, S магнитного поля магнитофорного колпачка, охватывающих тело матки 3 и плодное яйцо 4 в зоне на расстоянии L, равном 5-7 см от дна 2 колпачка (см. фиг. 1, 4), и расположение макрополюсов N, S на внутренней поверхности колпачка, охватывающих прилегающую к ней рецепторную зону 5 наружного зева (фиг. 2, 4) шейки матки. Магнитное поле, распространяемое от дна колпачка с напряженностью 11,9-15,9 кA/м охватывает область тела матки 3 и плодное яйцо 4 и составляет 0,3-0,7 кА/м на расстоянии L 7 см. Магнитное поле распространяется от внутренней боковой поверхности 1 и дна 2 магнитофорного колпачка, охватывает рецепторную зону 5 матки. Конфигурация этого магнитного поля, т.е. распределение макрополюсов N, S, на внутренней поверхности магнитофорного колпачка и в зазоре 6 между стенкой шейки матки 3 и колпачком сформирована магнитным полем индуктора, выполненного в виде миандра, а величина его магнитной индукции составляет 20 млТл через каждые 2 мм поверхности колпачка, соответствующие шагу "а" (см. фиг. 2).
Такое чередование макрополюсов N, S на внутренней поверхности магнитофорного колпачка вызывает перемещение полюсов относительно шейки матки при ходьбе и воздействие знакопеременного магнитного поля на чувствительные нервные окончания 8 рецепторов 7, окружающих цервикальный канал 9, которые возбуждаются под действием этого поля и вызывают шеечно-гипофизарный рефлекс матки.
Магнитофорный колпачок снимают, когда возникает менструальноподобное кровотечение. Отделяемое от колпачка подвергают интологическому контролю для диагноза беременности.
Предлагаемое устройство для осуществления данного способа изображено на фиг. 5-8.
Устройство выполнено в виде колпачка, содержащего стенку 1 и дно 2, образующие усеченный конус. Стенка усеченного конуса выполнена с одинаковой толщиной d по всей ее высоте, а основание выполнено открытым, и его внутренний диаметр D1 подбирается больше наружного диаметра D2 шейки матки на 1,5-2 мм.
Дно 2 усеченного конуса колпачка может быть снабжено дренажными отверстиями 10 (диаметром 3 мм), например тремя, расположенными на равных расстояниях по окружности (см. фиг. 7, 8) или одним отверстием, в центре (не обозначено). Выполнение большего числа отверстий, чем три, нецелесообразно, так как приводит к снижению прочности дна колпачка. Колпачок выполнен из композиционного материала, содержащего синтетический каучук и порошок феррита бария, образующих однородную композицию, обеспечивающую требуемую прочность колпачка.
Устройство применяют следующим образом:
Колпачок устанавливают пациентке на шейку матки 3. Благодаря зазору 6 между стенками 1 колпачка и шейки матки 3 знакопеременное магнитное поле на внутренней поверхности колпачка с величиной напряженности 20 млТл через каждые 2 мм поверхности создает переменное воздействие этого поля на нервные окончания 8 рецепторов 7 рецепторной зоны 5 шейки матки 3. Перемещение силовых магнитных линий вызывает в указанном зазоре 6 при ходьбе пациентки дополнительное раздражение нервных волокон и чувствительных окончаний 8 рецепторов 7. При этом за счет выполнения стенки 1 усеченного конуса 1 колпачка с одинаковой толщиной d по всей ее высоте исключает воздействие магнитного поля со стороны колпачка на окружающие матку 3 ткани, что и усиливает воздействие на рецепторную зону 5 шейки матки 3.
Отток распадающихся тканей плодного яйца 4 из матки 3 обеспечивается и зазором 6 между стенкой 1 колпачка и охватываемой им стенкой матки 3. Дополнительно отток из матки можно увеличить с помощью дренажных отверстий 10 дна 2 колпачка.
Пример 1. Пациентке установлен на шейку матки магнитофорный колпачок на пятнадцатый день беременности, определенный в результате ультразвукового исследования установкой японской фирмы "Алок". Магнитофорный колпачок создает знакопеременное поле с напряженностью 12,7 кА/м. Прерывание беременности произошло на пятые сутки, что определяется наличием плодного яйца и менструальноподобных выделений в колпачке. Колпачок изготовлен из материала, содержащего полидиметилсилоксановый каучук с винильными группами 10 мас. феррит бария 90 мас.
Пример 2. Пациентке установлен на шейку матки на двадцатый день беременности магнитофорный колпачок, который создает знакопеременное магнитное поле со следующими параметрами: напряженность 14,3 кА/м. Прерывание беременности наступило на третьи сутки. Колпачок изготовлен из композиционного материала, содержащего полидиметилсилоксановый каучук с гидроксильными группами 10 мас. феррита бария 90 мас.
Таким образом, предлагаемое изобретение позволяет за счет дополнительного переменного воздействия знакопеременного магнитного поля на рецепторную зону шейки матки при указанном выполнении магнитофорного колпачка, с одной стороны, обеспечить воздействие на рецепторную зону шейки матки и, следовательно, увеличить эффективность прерывания беременности ранних сроков до 70% и более и регуляции менструального цикла по сравнению с прототипом (данные клинических испытаний Института Акушерства и Гинекологии АМН СССР им. Д.О. Отта от 17.06.91 N 550, 1-ой кафедры акушерства и гинекологии ГИДУВа г. Санкт-Петербурга от 06.10.91), а, с другой стороны, увеличить отток разлагающихся тканей плодного яйца и матки, что снижает вероятность инфекционных заболеваний по сравнению с прототипом.
ФОРМУЛА ИЗОБРЕТЕНИЯ
1. Способ прерывания беременности ранних сроков, включающий воздействие неоднородным магнитным полем напряженностью 11,9 - 15,9 кА/м на плодное яйцо, отличающееся тем, что дополнительно воздействуют на шейку матки знакопеременным магнитным полем, неоднродность которого создают чередующимся расположением макрополюсов.
2. Способ по п.1, отличающийся тем, что напряженность макрополюсов составляет 20 млТл.
3. Устройство для прерывания беременности ранних сроков, выполненное в виде колпачка, часть которого выполнена из магнитофора, отличающееся тем, что колпачок полностью выполнен из магнитофора на основе синтетического каучука, имеет форму усеченного конуса с одинаковой толщиной стенки и дна, при этом на внутренней поверхности колпачка сформированы области намагниченности в виде чередующихся макрополюсов.
4. Устройство по п. 3, отличающееся тем, что дно колпачка выполнено с дренажными отверстиями.
5. Устройство по пп.3 и 4, отличающееся тем, что макрополюса расположены с шагом, равным 2 мм.
6. Устройство по пп.3 и 5, отличающееся тем, что магнитофор выполнен в виде однородной композиции синтетического каучука и порошка феррита бария.
Версия для печати
Дата публикации 27.03.2007гг
Created/Updated: 25.05.2018