| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2237251
![]()
FORECASTING METHOD OF suppurative complications
The surgical treatment of duodenal ulcer, STENOSIS COMPLICATED
Name of the inventor: Nesterova IV (RU); Fomichev EV
The name of the patentee: Russian Center of Functional Surgical Gastroenterology (RU); Nesterova Irina Vadimovna (RU); Eugene V. Fomichev
Address for correspondence: 350063, Krasnodar, ul. Sedin, 4, Kyrgyz State Medical Academy, Patent Department, TA Doroninoj
Starting date of the patent: 2002.11.14
This invention relates to immunology and surgical gastroenterology and may be used in the clinic for predicting postoperative complications. To do this, determine the ratio of spending myeloperoxidase in neutrophil granulocytes as the ratio of the level of its activity in the stimulated and spontaneous test version. Provided the value of spending ratio 0.32-0.38 define low risk of complications, but when you reject the coefficient of expenditure myeloperoxidase in neutrophil granulocytes from these values determine the risk of postoperative surgical complications. The method allows to reveal the risk of septic complications in the postoperative period, thus it is necessary to spend for these patients immunotherapy, with the result that the risk of repeat operations will be optimized to be excluded treatment and rehabilitation of patients, reduced length of stay of patients in hospital.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to immunology and surgical gastroenterology and may be used in the clinic for predicting postoperative complications.
At the present time it is not in doubt that the disturbances in the immune system not only accompany many diseases, but often cause significant contribution to the mechanisms of development of pathological processes, and contribute to their weights. In recent years, we obtained objective evidence. that the pathology of the immune system plays an important role in the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In the pathogenesis of common diseases such as duodenal ulcer, fully manifested dysfunction of the immune system (Aruin LI 1983; Malov Yu, 1984; Zimmerman YA.S, 1998).
Neutrophil granulocytes as the category Highly reactive cells are a sensitive indicator of various disorders of homeostasis, which is used as a diagnostic and prognostic test in clinical practice. In connection with this great interest is the cytochemical labeling of neutrophils, which is associated with the accessibility and sensitivity of such reactions. To study neutrophil bactericidal systems determine myeloperoxidase activity by cytochemical analysis. Myeloperoxidase is an enzyme that, along with oxygen radicals, hydrogen peroxide, halogens is oxygen-dependent effector unit Devices bactericidal of neutrophils. The activity of myeloperoxidase is determined by the method of Sato and Sekija (1928). The principle of the method is based on the oxidation of benzidine peroxides-peroxidase system to benzidine blue. The results are taken into account by using an immersion microscopy and then calculating the mean in units cytochemical index. The clinic used to determine the activity of myeloperoxidase in the differential diagnostic purposes (eg, myocardial infarction and angina, stroke and transient cerebral circulatory disorders, bacterial or viral infections, etc.) and to control the dynamics of the pathological process.
However, according to many researchers, myeloperoxidase activity in patients with ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum varies widely and does not always correspond to the severity of chronic process (Ashkenazi VI, Mayanskaya IV et al, 2000;. Diaghilev OA, Bykov IA et al., 2001). Such studies do not reflect the full potential of neutrophilic granulocytes and this disease do not have enough predictive information content.
For a prototype accepted method for determining the functional capacity of neutrophils to implement the non-enzymatic cationic protein (Nesterova IV, Svetlichnaya MA, 1987). The essence of this method in determining the content of cationic proteins in intact neutrophils and neytrofidah undergoing activation complex multivalent antigen. When comparing the level of consumption of activated cationic protein, and intact cells determine the coefficient of implementation of cationic proteins, and then to change the rules concerning the implementation rate is judged on the presence or absence of a pathological condition (Pediatrics -. 1984. - №9). We have used this method for the evaluation of patients with duodenal ulcer complicated by stenosis prior to surgery, but the ratio of the cationic protein is within the values of healthy controls did not reflect the severity of the disease process and could not be used to determine the reserve capacity of neutrophils in this pathology. We have been tasked to develop a new test for cytochemical an adequate solution to this diagnostic problem.
The applicants propose to determine the level of consumption of the myeloperoxidase in the cytoplasm of neutrophils using a load test in artificial activation of neutrophilic granulocytes bacterial antigen under conditions in vitro, which is an adequate model of the pathological process of manifestation and allows better estimate mobilization potential granular unit neutrophils, and to determine the reserve capacity of these cells . When uncomplicated course of the disease potential of neutrophils is not fully realized, but subsequently may have a significant impact on the course of the disease in the event of aggravation, which is extremely important for clinical and laboratory practice.
The invention consists in the fact that determine the rate of spending of myeloperoxidase in neutrophil granulocytes as the ratio of the level of its activity in the stimulated and spontaneous test version. Provided the value of spending ratio 0.32-0.38 define low risk of complications, but when you reject the coefficient of expenditure myeloperoxidase in neutrophil granulocytes from these values determine the risk of postoperative surgical complications.
Method is as follows
For the study, blood is taken from a vein, stable antikoogulyantom. The 2 wells of the plate for immunological studies were placed 100 ml of blood. In one well add 100 ul of saline (spontaneous test), the other - 100 l of bacterial suspension St. aureus at a concentration of 1x10 6 microbial cells in 1 ml saline (stimulated test). The well contents mixed gently, then incubated in a thermostat at +37 ° C for 1 hour. After incubation, the wells is mixed and prepared drop-preparation on a clean, well-skim slide. Glass placed in a moist chamber for settling cells strictly horizontal. After 10 minutes, excess liquid was removed gently tilting the glass at an angle of 45 ° and dried smears in air for 6-12 hours. The dried smears were fixed in 40% formalin vapor for 3-4 minutes and washed in running water for 1-2 minutes and air-dried. Then swab dipped in a 0.5% solution of copper sulfate for 1 minute and then transferred to a freshly prepared solution of benzidine with two drops of hydrogen peroxide (benzidine solution was prepared by dissolving 100 mg of benzidine in 100 ml of distilled water by heating to 80 ° C, solution was stored in the refrigerator). Thereafter, smears were washed in running water for 1-2 minutes and dokrashivayut for 30-60 seconds in a 0.5% neutral red solution, again rinsed with tap water and air dried.
When the microscope stained smears browsing 100 neutrophils. Intracellular myeloperoxidase activity evaluated semiquantitatively in arbitrary units by calculating the average cytochemical index (cms) on the basis Kaplow (1955). By calculating the ratio of the myeloperoxidase activity in the stimulated embodiment to that in spontaneous form, determine the expenditure ratio (CR):
![]()
which demonstrates the functional activity of neutrophils and their back-up capabilities. Given its value 0,35 ± 0,03 establish low risk of complications, and rejecting the values of said level determining the risk of septic complications.
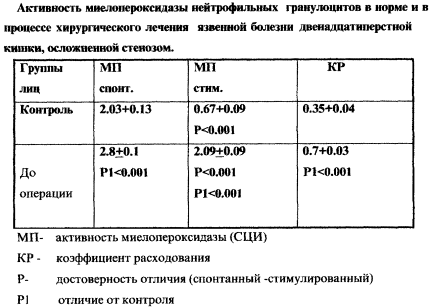
Using this test, it was investigated peripheral blood of 20 apparently healthy individuals and 60 patients with duodenal ulcer complicated by stenosis who underwent radical duodenoplasty V.I.Onoprievu at the Russian Center of Functional Surgical Gastroenterology (Table. 1).
The study confirmed that the expenditure ratio meloperoksidazy is a high indicator of standby capacities of neutrophilic granulocytes, which allows use of the test in clinical practice for predicting the risk of surgical complications of duodenal ulcer complicated by stenosis.
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
PO 1. Patient 50 years. 17/10/99 routinely performed radical duodenoplasty about decompensated stenosis. In determining the level of myeloperoxidase activity in spontaneous SDH test was equal to 2.3. When determining the same period in the stimulated version of the test was equal to 2.07 cms, thus spending myeloperoxidase coefficient calculated by privedenenoy above formula, was 0.90, indicating that the deep oxygen-defect mechanism of neutrophil microbicidal system. Based on clinical data and the results of immunological studies defined high risk of postoperative complications. The patient before surgery was prescribed a course of corrective immunotherapy. As a result of preoperative postoperative complications were absent. The patient was discharged on the 8th day from the hospital.
2. Patient S. 46 years. 20.10.01 has been implemented as planned radical duodenoplasty about subcompensated stenosis. consumption ratio determined by the algorithm above, is 0.38. The postoperative course was smooth and there are no complications, was discharged on day 9.
3. Patient K. 31 year. 17.10.99 has been implemented urgently radical duodenoplasty about decompensated duodenal stenosis. As a result of an immunological study detected serious irregularities in the functioning of neutrophil microbicidal system expenditure coefficient of myeloperoxidase, determined by algloitmu above, is 0.82. Appointed immunologist treatment is not carried out due to economic inaccessibility of drugs. The postoperative course was difficult, peritonitis, wound surgical wound by secondary intention. The patient was discharged on day 32.
At the risk of revealing the development of septic complications in the postoperative period should be carried out for these patients immunotherapy, which will result in no risk of re-operation, it will be optimized for the treatment and rehabilitation of patients, reduced length of stay of patients in hospital.
CLAIM
A method for predicting suppurative complications in the surgical treatment of duodenal ulcer complicated by stenosis, wherein the determining factor spending myeloperoxidase in neutrophil granulocytes as the ratio of the level of its activity in the stimulated and spontaneous version of the test and provided its value is set 0.32-0.38 a low risk of complications, and rejecting the values of the specified level of expenditure determine the risk of septic complications.
print version
Publication date 29.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.