| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2193865
![]()
METHOD OF REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS AFTER ISOLATED RADICAL DUODENOPLASTICS
The name of the inventor: Onopriyev VI; Korochanskaya NV; Klimenko LI
The name of the patent holder: Russian Center for Functional Surgical Gastroenterology; Vladimir Onopriyev; Korochanskaya Natalya Vsevolodovna; Klimenko Larisa Ivanovna
Address for correspondence: 350063, Krasnodar, ul. Gray, 4, KGMA, head. Patent Department TA Doronina
Date of commencement of the patent: 2000.10.31
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to gastroenterology, can be used in the postoperative period after radical duodenoplasty. Determine the predictors of the likelihood of recurrence of duodenal ulcers. Determine the predictors of the probability of patients' compliance with medical recommendations. Depending on the total value of the calculated coefficients on the basis of the values of the indices, the indications are determined either for conservative treatment or for performing selective proximal vagotomy. The method allows to increase the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures taking into account clinical, social and psychological factors.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to medicine, namely gastroenterology, and can be used in surgery in the postoperative period after isolated radical duodenoplasty (RDP).
One of the main tasks of clinical medicine is the timely diagnosis of recurrence of the disease, the forecasting of possible clinical course options and the selection of adequate treatment tactics. The wide introduction of mathematical methods for solving prediction problems (EV Gubler, 1978, A. Afifi, S. Eisen, 1982) proved its worth for more than two decades. School of Professor VI. Onopriieva has been developed and since 1977 it has been applied RDP, which allows eliminating complicated ulcers and cicatrical and ulcerative deformations, and decreasing the lethality in such complications of peptic ulcer of duodenum (STD) as stenosis, perforation, bleeding and penetration. After an isolated RDP in the postoperative period, a complex of rehabilitation measures is required to prevent recurrence of AJ.
In the work of A.Yu. Baranovsky, TL. Tsvetkova "Choice of tactics for treatment of gastroduodenal ulcers on the basis of predicting the variants of the clinical course" // Proceedings of the conference "The fate of patients after hospital treatment and surgical interventions." - Smolensk - Moscow, 1996. - p.8-14:
1) the presence of clinical prognostic factors was determined in non-operated patients with PKD;
2) clinical signs were ranked according to their differential informativity, calculated according to S. Kulbak's formula;
3) set thresholds for decision making;
4) the forecast was established after reaching the threshold value.
The disadvantage of this method is that it was used only in therapeutic gastroenterological patients (not undergoing surgical treatment), included complex quantitative methods that require special computer programs, which limits its use in the clinic.
In the method of V.G. Pleshkova, N.V. Zaprudinoy "Prediction of late complications of stitched perforated gastroduodenal ulcers and indications for their surgical treatment" // Proceedings of the conference "The fate of patients after hospital treatment and surgical interventions". - Smolensk - Moscow, 1996. - p.172-176:
1) in patients with YaD PDC after suturing perforated ulcers, the presence of clinical prognostic factors was determined;
2) for each patient, the coefficient K was calculated for each characteristic;
3) the total selection factor for postoperative (n / o) rehabilitation R was determined as the sum of the prognostic coefficients of K;
4) if the coefficient of choice for postoperative rehabilitation R ranged from 1.2 to 3.7, the patients needed a re-operative intervention.
The disadvantage of this method of choosing the tactics of n / o rehabilitation is the lack of consideration of social factors and quality of life parameters (QoL) of patients, which reduces the accuracy of the forecast.
Prototype. In the invention of VI. Onopriyeva, O.V. Kokuyeva, N.V. Korochanskaya "The method of prediction of recurrence of duodenal ulcer (AJ) in patients who underwent isolated radical duodenoplasty" (patent 2143221 from 27.12.99):
1) a comparative analysis of the clinical and social characteristics of patients with early relapses of AE after and without RDP;
2) comprehensive psychometric testing of patients with early relapses of AE after and without RDP;
3) the risk factors for early relapses for a number of clinical, social and psychological parameters were calculated;
4) threshold values of the average choice of tactics for rehabilitation have been established, on the basis of which three groups of risk have been identified. Subject to an average coefficient of more than 2.1, a high risk of developing early relapses was determined-a surgical method of rehabilitation (SLE) was recommended for this group of patients, a small and average probability of relapse of duodenal ulcer was observed from 0 to 2-these groups of patients underwent conservative postoperative rehabilitation.
The disadvantage of this study is that the tactics of rehabilitation were built on the basis of objective criteria for the postoperative course of the disease and did not take into account the clinical, social and psychological predictors of active participation of patients after RDP in rehabilitation activities.
The development of the Complaince strategy, the strategy of cooperation between the doctor and the patient, provides for the selection of optimal rehabilitation measures, taking into account both objective (presence or absence of relapse of duodenal ulcer in patients who underwent RDP) and subjective (degree of participation of patients in rehabilitation activities) criteria for postoperative course of the disease. Until recently, when choosing the tactics of postoperative rehabilitation, the level of compliance between the doctor and the patient was not taken into account, which worsened the postoperative course of the disease.
The goal is to improve the efficiency of postoperative rehabilitation on the basis of clinical, social and psychological predictors of patients' participation in rehabilitation activities after organ-saving operations and on their basis to determine the way of rehabilitation of patients in the postoperative period.
OBJECTIVES OF THE INVENTION
1. Conduct a comparative analysis of clinical, social factors and parameters of QOL patients participating in drug rehabilitation and not taking medications (hence, subject to surgical treatment), and based on the analysis, calculate the probability of the patient's compliance with medical recommendations.
2. Calculate the total selection factors for the tactics of rehabilitation after taking into account the risk factors for relapse AJ and the probability of the patient's compliance with medical recommendations.
3. Establish threshold values for the average selection factor for tactics of rehabilitation and on their basis individualize rehabilitation schemes after the RDP.
4. To distinguish 3 groups of dispensary observation of patients with different tactics of rehabilitation measures: conservative treatment with the frequency of medical monitoring of the patient's condition once a quarter and once a month, a surgical method of rehabilitation and on their basis to reduce the frequency of AE relapses, reduce the costs of medical therapy , Reduce the frequency of implementation of SPS, reduce the time of temporary incapacity for work and ensure a higher quality of life for the patient.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In addition to the objective criteria for the postoperative course of the disease (the method for predicting AE relapses in patients who underwent isolated radical duodenoplasty, Patent 2143221 of 27.12.99), a comprehensive assessment of the clinical, social and psychological predictors of patients 'participation in rehabilitation activities is conducted, the coefficients of probability of patients' On the basis of summation, the coefficients for choosing tactics for rehabilitation are calculated and under the condition of a total coefficient of less than 20.7 - rehabilitation measures are carried out within the framework of conservative treatment with periodicity of medical monitoring of the patient's condition once a quarter, from 20.8 to 41.4 - conservative Treatment with monthly medical control, and with a total score of more than 41.5 - patients are shown a surgical way of rehabilitation - performing an antacid operation - selective proximal vagotomy.
The method is carried out in the following way: fill in the standard map of clinical and social indicators in patients with YaD PDK. They conduct complex psychometric testing, presenting patients with standard forms of psychometric testing developed by L.N. Sobchik (1990), including modified tests of Lusher's color choice, Leary's interpersonal relations and the standard multifactorial method of personality research (SMIL) and on their basis evaluate the individual-personal type and type of attitude to the disease. To select the tactics of postoperative rehabilitation, Wald's sequential analysis is used, based on probabilistic methods of comparing the frequency of each of the analyzed indicators (symptoms) in the compared states-participation in drug rehabilitation or refusal to take medications.
The vast majority of patients who have undergone an isolated RDP need long-term maintenance antisecretory therapy. However, not all patients strictly comply with medical recommendations, which significantly reduces the effectiveness of surgical intervention and increases the likelihood of an early postoperative relapse of duodenal ulcers. This justifies the importance of studying the factors that affect the participation of patients in rehabilitation activities, their readiness to perform medical recommendations. However, the reasons for refusing patients from antisecretory anti-relapse therapy under conditions of a surgical clinic have not yet been studied.
 |
|
|
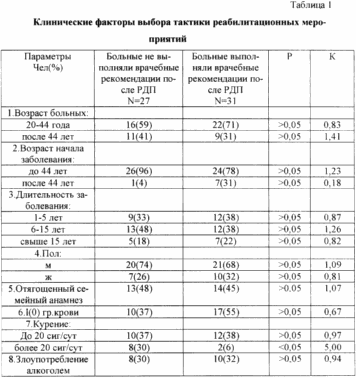
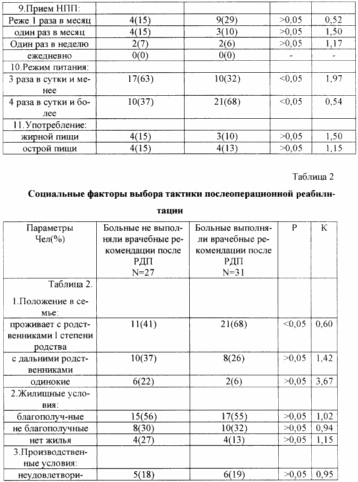
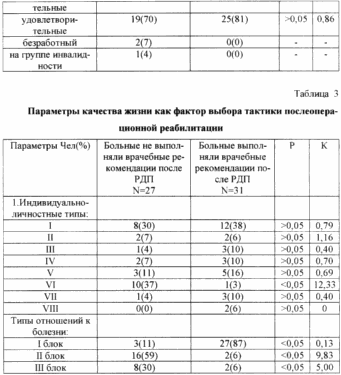
The prognostic model included 11 clinical indicators (Table 1), 3 social (Table 2), 8 individual-personality types and 3 blocks of types of attitude towards the disease (Table 3). For each indicator, the risk factor (K), sensitivity, specificity and effectiveness of prognostically significant parameters were calculated. As was to be expected, those who did not follow the medical recommendations were, as a rule, "malicious" smokers and did not eat regularly. For them, VI was an individual-personal type (sensitively-pessimistic). The main features of the personality were pessimism, introvertedness, anxiety, obediently dependent style of interpersonal behavior. In this group, the II and III blocks of the relationship type to the disease were more common. The second unit combines anxious, hypochondriacal, neurasthenic, melancholic and apathetic types of attitude towards the disease, characterized by the presence of disadaptation with intrapsychic orientation. The third block includes sensitive, egocentric, paranoid and dysphoric types of attitude towards the disease, reflecting a sensitized attitude toward the disease, which has an extrapsychic orientation of maladaptation due to the disease. When studying the prognostic value of the indicators, it was revealed that the residence with relatives of 1 degree of kinship and 1 block of types of attitude to the disease (without disrupting social adaptation due to the disease) are favorable for the implementation of medical recommendations. |
It is generally accepted that the tactics of postoperative rehabilitation determines the variant of the clinical course of the disease in the postoperative period, on the one hand, and the patient's readiness to perform medical recommendations, on the other. Previously, we proposed a method for predicting recurrences of duodenal ulcers in patients who underwent duodenoplasty (patent 2143221). The total coefficient of tactics choice for postoperative rehabilitation is calculated by summing the risk factors for AE relapse and the probability of the patient's compliance with medical recommendations (Table 6).

The formalization of the prognostic procedure undertaken by us can find application in the use of machine methods of diagnosis and prognosis, which becomes especially relevant in connection with the task of dispensary observation of all patients who underwent radical duodenoplasty at the Republican Center for Functional Surgical Gastroenterology.
The developed mathematical total selection factors of tactics of post-natal rehabilitation allow individualizing ways of managing patients who underwent radical duodenoplasty: conservative medical treatment (eradication therapy, supporting antisecretory therapy, antisecretory therapy on demand); Surgical method - addition of duodenoplasty with an antacid operation - selective proximal vagotomy.
We give examples of calculating the average choice of tactics for the rehabilitation of patients after isolated radical duodenoplasty.
Example 1
Patient S.V., 46 years old. On 20.10.98 the operation of the RDP for decompensated duodenal stenosis was performed in a planned manner. He was discharged from the hospital on the 9th day of the uncomplicated postoperative course, a dispensary observation card was entered into the patient on the patient's discharge, a standard map of clinical and social indicators was filled, on the basis of which the risk factor for AJ relapse was calculated, which was 1.41. Consulted by a clinical psychologist, conducted a comprehensive psychometric testing with an assessment of the individual-personal type and type of attitude towards the disease, based on which the prognosis of the probability of participation of the patient in rehabilitation activities K = 1,2 was estimated. The total choice factor for tactics of postoperative rehabilitation was 2.6. He was on dispensary observation for two years with a frequency of observation 1 time per quarter. In the postoperative period, I received supportive antisecretory therapy with H-2 blockers (famotidine 1 tonne per night). With dynamic dispensary observation: there are no complaints, with FGDS control - the condition after RDP. Catarrhal antrum-gastritis. In view of clinical and endoscopic remission, it is recommended to continue antisecretory therapy with H-2 blockers "on demand". Two-year follow-up of the patient with a multiplicity of 1 time per quarter, subject to compliance with the patient's medical recommendations, determined a high rehabilitation prognosis - no relapse of AD for the period of observation.
Example 2
Patient KO, 31 years old. 17.10.99. Was performed urgently by the RDP for bleeding duodenal ulcers. He was discharged from the hospital on the 10th day, the p / o period was without any peculiarities. It is taken to dispensary records. Based on the completed standard charts of clinical and social indicators, a high risk of recurrence AJ-K = 18.63 was determined. Based on standard psychometric testing, including modified tests of Lusher's color choice, Leary's interpersonal relations and standard multifactorial method of personality research, the coefficient of probability of patient participation in rehabilitation activities was determined, which was 14.8. The total coefficient of choice of postoperative rehabilitation tactics was 33.43. In the postoperative period the patient was on sanatorium-resort rehabilitation with recommendations for antisecretory therapy and subsequent dispensary control after 1 month. Re-examined on 18.11.99. Clinically, complaints of episodic heartburn. With FGDS-control - the state after RDP. Lack of cardia. Erosive duodenitis. Hp (+++). The patient is recommended to conduct a course of eradication therapy according to the scheme (omeprazole 20 mg h 2p + amoxicillin 0.25 mg h 4p + trichopolum 0.25 mg h 3p, then omeprazole 1 ton n / night 3 weeks) followed by a sign for eradication control after 4 Weeks after the end of the course of treatment. 28.12.99 is called for dispensary control actively. The eradication course was conducted in full. Clinically, episodic heartburn persists. With FGDS-control - the state after RDP, cardiac insufficiency. Catarrhal antrum-gastritis. Duodenitis. Hp (0). Supportive antisecretory therapy is recommended. Active participation of the patient in rehabilitation activities with a high risk of recurrence allows postoperative rehabilitation within the framework of conservative treatment with the frequency of medical supervision once a month.
Example 3
Ill PO, 52 years old. 06.08.99 in a planned manner performed the RDP for subcompensated duodenal stenosis. It is taken to dispensary records. The total selection factor for tactics of postoperative rehabilitation was K = 43.61 (high risk of early recurrence - K = 21.41, high probability of failure to perform medical activities with K = 24.2). In view of the pronounced Hp contamination, the patient was recommended to perform an outpatient course in the postoperative period according to the following scheme: (omeprazole 20 mg H 2p + Flemoxin solutab 0.5 g 2p + clacid 0.25 g 2p, then omeprazole 20 ing n / night in For 3 weeks) with the subsequent appearance on the control of eradication 4 weeks after the end of the course of treatment. 10.09.99 on "D" - the control did not appear. Active call 12.09.99, 14.10.99. 27.12.99 appearance on dispensary control with complaints of heartburn, pain in the epigastric region, nausea. The prescribed treatment was not carried out because of the economic inaccessibility of drugs. With FGDS-control - the state after RDP, cardiac insufficiency. Erosive antrum-gastritis. Relapse of duodenal ulcer. The patient was hospitalized in the hospital, where the course of antiulcer therapy was conducted, after which the patient was treated with an antacid operation - SPV. The high risk of recurrence of AE when a patient refuses to follow a doctor's recommendation makes it possible to recommend a surgical method of rehabilitation for this group of patients without the cost of conservative treatment.
Medico-social effectiveness
The method will allow individualizing the tactics of postoperative management of patients. A differentiated approach will increase the effectiveness of rehabilitation, reduce the frequency of duodenal ulcer relapse, reduce the cost of medical therapy, reduce the frequency of implementation of SLE as the second stage of surgical treatment, prevent disability of patients and reduce the periods of temporary disability, will contribute to achieving a higher quality of life of the patient.
CLAIM
The method of rehabilitation of patients after isolated radical duodenoplasty, including the determination of the indices of the prognosis of the probability of recurrence of duodenal ulcers after radical duodenoplasty: 1 - the intensity of acid formation is decreased, 2 - I block of types of attitude towards the disease, 3 - bridged radical duodenoplasty is executed, 4 - lives with relatives of 1 degree of kinship , 5 - the operation is performed in the phase of remission of duodenal ulcer, 6 - does not receive anti-relapse treatment, 7 - radical duodenoplasty is performed, 8 - the operation is performed in the relapse phase of duodenal ulcer, 9 - maximum contamination with pyloric Helicobacter, 10 - II block of types Attitude to the disease, 11 - the patient smokes more than 20 cigarettes a day, 12 - the patient is lonely; Which have the corresponding values of the coefficients: 1 - 0.25; 2 - 0.30; 3 - 0.44; 5 - 0.47; 6 - 1.83; 7 - 2.15; 8 - 2.78; 9-3.24; 10-3.48; 11 to 4.09; 12 - 7.50, determination of the prognosis of the probability of the patients' compliance with medical recommendations: 1 - I block of types of attitude towards the disease; 2 - the patient eats 4 times a day, 3 - the patient lives with relatives of 1 degree of relationship, 4 - eats 3 times a day or less; 5 - the patient smokes more than 20 cigarettes a day, 6 - III block of types of attitude to the disease, 7 - II block of types of attitude to the disease, 8 - VI individually personal type, which have the corresponding values of the coefficients: 1 - 0.1; 2 - 0.5; 3 - 0.6; 4 - 1.9; 5 - 5.0; 6 - 5.0; 7 - 9.8; 8 - 12.3, summarize the values of all coefficients and, provided that the total value of these coefficients is less than 20.7, the rehabilitation of the patient is carried out by conservative treatment with periodicity of medical monitoring of the patient's condition 1 time per quarter, provided the sum of these coefficients is 20.8-41, 4 prescribe conservative treatment with monthly medical control of the results of treatment, and with a value of the sum of coefficients more than 41.5 perform selective proximal vagotomy.
print version
Date of publication 29.03.2007гг




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.