| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2115357
![]()
METHOD OF TREATMENT acute cholecystitis
Name of the inventor: Kulikov Leonid K.; Wieszczycki Vladimir Petrovich
The name of the patentee: Kulikov Leonid K.; Wieszczycki Vladimir Petrovich
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1994.07.19
The invention relates to medicine, namely to surgery, and can be used in the treatment of acute cholecystitis. Perform laparoscopy, drain the gallbladder. Sanitize the gallbladder antiseptic solutions, further comprising the immobilized enzyme immoizim. Activity immozima 150-250 PE, the exposure time in the gallbladder is I, 5-2ch. This reorganization is performed 1 time per day for 5-10 days. The method allows to reduce the terms of relief of acute inflammatory process in the gall bladder.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely to surgery, and can be used in the treatment of acute cholecystitis, including in elderly persons. A method of treating acute cholecystitis by laparoscopy, including a blockade of the round ligament of the liver and gallbladder drainage and sanitation of its solutions of antibiotics. The catheter is removed from the gallbladder after decrease in acute phenomena for 12 -14 hours [1]. However, this method has the following disadvantage: not always possible to stop the acute inflammation of the gall bladder.
The closest to the proposed method is the treatment of acute cholecystitis, including laparoscopy, drainage of the gallbladder, reorganize its antiseptic solutions and the removal of drainage. However, this method does not allow to quickly arrest the acute inflammation of the gall bladder (to the relief of up to 2.5 - 3 weeks). [2]
The main task to be solved by the invention as claimed, is more rapid relief of acute inflammation in the gallbladder, using a combined treatment of drugs immobilized proteolytic enzymes and objective methods of diagnosis of inflammation in the gallbladder, but also to improve the results of treatment of patients with acute cholecystitis, especially with a high degree of operational risk individuals.
The aim of the method is to reduce the timing of the relief of acute inflammatory process in the gall bladder. The essence of the method is as follows: perform a laparoscopy, drainage of the gallbladder, reorganize its antiseptic solution, additionally containing an immobilized proteolytic enzyme activity immozim 150 - 250 PE. Readjustment is carried out once a day for 5 - 10 days. Then drain removed.
Comparative analysis with the prototype showed that the proposed method differs from the known fact that the reorganization is carried out with an antiseptic solution, additionally containing an immobilized proteolytic enzyme activity immozim 150 - 250 PE, exposure time 1.5 - 2 hours, while the reorganization is carried out once a day for 5 - 10 days. Thus the proposed technical solution meets the criterion of invention "novelty."
From the analysis of the patent and technical literature the authors found that the proposed method has the features distinguishing it not only from the prototype, but also other technical solutions in this and related fields. The available literature has not found a method for treating acute cholecystitis, gallbladder including sanitation solutions containing immobilized proteolytic enzymes. Using these solutions allows for readjustment shorten the relief of acute gallbladder inflammation (up to 5 - 10 days) by reducing the microbial step and traumatic inflammation contributes to the early development stage of an inflammatory proliferative. This solution can be used in all methods of drainage and sanitation of the gallbladder (controlled ehosonografii, CT).
This method is simple, accessible and does not require expensive equipment and drugs and can be used in all departments of surgery, both specialist and generalist. In addition, when using this enzyme there is no specific complication of medicines. Thus, the proposed technical solution meets the criteria of the invention "industrial applicability" and "inventive step".
The process is as follows: produce a puncture of the anterior abdominal wall and using laparoscopy establish the degree of inflammatory changes in the gallbladder, and when indicated produce percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage flexible radiopaque drainage diameter of 1.8 - 2.0 mm. The resulting bile examined by native microscopy. Samples of bile 5 ml immediately after preparation was centrifuged for 10 min at 1500 rev / min. Thereafter, a precipitate drop placed on a slide and examined under an optical microscope at a magnification of 40 x 7. The study was conducted at room temperature immediately after preparation of the drug. In the register of the presence of formed elements, the number (white blood cells, red blood cells). The large number of white blood cells (20 - 30 in the field of view) speaks during the acute inflammatory process in the gall bladder and bile ducts. Then washed with gall bladder antiseptic solutions. Then spend sanitation gallbladder immobilized proteolytic enzymes. In the gallbladder through laparoscopic mikroholetsistostomu administered drug immozim activity 150 - 250 proteolytic units (PU) in antiseptic solution (20 - 30 ml). Exposure immozima gallbladder 1.5 - 2 h. Remediation of the gall bladder is carried out once a day for 5 - 10 days (to the relief of acute inflammation). After removal of acute inflammation of the gall bladder drainage is removed. In addition, patients underwent conservative therapy including antibiotics, antispasmodics and analgesics.
In order to control the flow of the inflammatory process in the gallbladder bile studies conducted as described above in the first day and in the following third, fifth and seventh days of starting treatment. On 4 - 5 hours cholecystocholangiography conducted to clarify the diagnosis and detection of impaired patency of the biliary tract.
Monitoring the effectiveness of the treatment is carried out clinically, blood laboratory data, but also microbiological, cytological and biochemical studies of bile and ehosonografiey.
If you have complications of acute cholecystitis (cholangitis, jaundice, choledocholithiasis, disabled gall bladder) drainage is continued until the elimination of these complications or surgical treatment.
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
Example 1. Patient C-ing (N 956) in '63 he entered the surgical department of 09.25.93 on the basis of complaints, objective data and ultrasound data abscess diagnosed with acute cholecystitis. In view of the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment (preservation of pain, negative dynamics of the US) was held 05.10.93 therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy. Diagnosed Acute phlegmonous cholecystitis, pericholecystitis. Superimposed percutaneous transhepatic mikroholetsistostoma, drainage subhepatic space. Reorganization carried gallbladder cavity with antiseptic solutions and introducing the immobilized proteolytic enzyme immozima at 200 - 250 PE 20 ml of the antiseptic solution with an exposure of 1.5 - 2 hours for 7 days once a day. Against the background of positive dynamics of complex treatment of relief of acute inflammatory process in the gall bladder. On the sixth day made cholecystocholangiography through laparoscopic mikroholetsistostomu (LMHS) - gall bladder with clear contours contrast to the common bile duct, which is not expanded, stones are not defined. The contrast in the duodenum. The dynamics of the main indicators are presented in Table. 1.
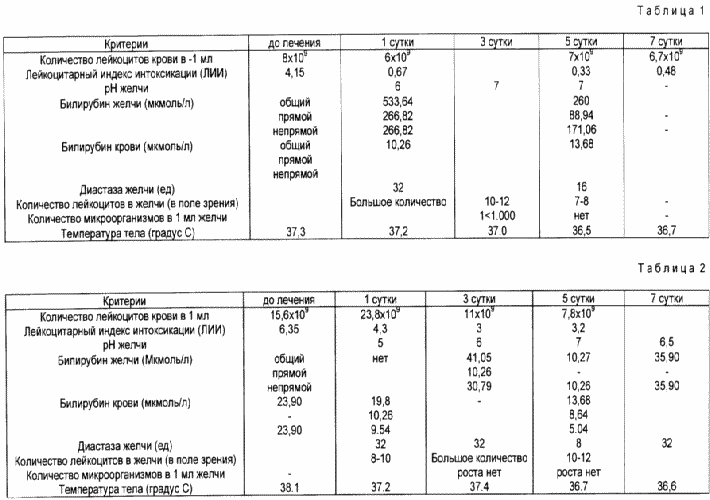
Mikroholetsistostoma removed on day 7, the control ehosonografii data for chronic cholecystitis, pericholecystitis. The patient was discharged from the department for 9 hours after application of laparoscopic mikroholetsistostomy. The total number of hospital days 19. Surgical treatment is recommended in a month due to the presence of chronic bronchitis in the stage of incomplete remission in a planned manner.
it can be concluded treatment of an acute inflammatory process in the gall bladder for 6 days of treatment immobilized proteolytic enzymes Based on objective data.
Example 2. The patient Mr (N 736) 69 l. He admitted to the surgical department of 11.22.93 on the basis of complaints, objective data and ehosonografii diagnosed with acute calculous cholecystitis. Due to the negative dynamics on the background of conservative therapy of 11.24.93 held medical diagnostic laparoscopy, during which found acute calculous cholecystitis and abscess imposed transhepatic mikroholetsistostoma, drained obstructive space. Reorganization carried gallbladder cavity with antiseptic solutions and introducing the immobilized proteolytic enzyme immozima at 150 - 200 PE 20 mL antiseptic solution with an exposure of 1.5 - 2 hours for 9 days, once a day. On day 4 cholecystocholangiography conducted through laparoscopic mikroholetsistostomu - gall bladder with clear contours, extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts do not contrast. In contrast no duodenum. On day 9 of intravesical proteolysis immozimom patients were operated routinely for chronic calculous cholecystitis. Operation "cholecystectomy" was held 03/12/93 The postoperative course was satisfactory, discharged from offices on the 10 th day after the operation. The histological conclusion - 3217 / (11414-418) chronic calculous cholecystitis. The total number of hospital days 21. Drainage of the gallbladder using immobilized proteolytic enzymes was carried out for 9 days.
On the basis of objective data, clinical data acute inflammatory process in the gall bladder failed to stop for 7 days using intravesical prolonged proteolysis immozimom.
The dynamics of the main indicators are presented in Table. 2.
The proposed method of treatment used in 22 patients. In all patients, an acute inflammation of the gall bladder was docked for 5 - 10 hours. All patients returned to normal blood count indices, liver function indicators, a strong trend towards normalization of leukocyte index of intoxication (LII) for 5 - 6 days. On 5 - 7 hours in most patients disappeared pathogenic flora during bile crops, the number of white blood cells in the bile is significantly reduced by 5 - 8 days. Of the 22 patients with acute inflammation docked operated routinely 6 patients in a period of 7 to 14 days. In all cases, histological studies have found chronic inflammation. Rehospitalization for recurrent acute cholecystitis was not.
Thus, this method allows a relatively short time (5 - 10 days) to arrest the acute inflammatory process in the gall bladder, thus reducing mortality and the number of intra- and postoperative complications of acute cholecystitis, especially in patients with middle and old age. The method is effective, simple, accessible and does not require expensive equipment and medications, and can be widely used in medical practice.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. V.M.Buyanov, G.I.Perminova, N.Yu.Shestakov. // Treatment of acute cholecystitis in patients with middle and old age. // Surgery. 1986. N 2. p. 23 - 32.
2. P.M.Postolov, G.I.Zhidovinov, A.V.Bykov, A.N.Ovcharov, S.S.Nesterov. // Medical tactic after laparoscopic cholecystostomy in patients with acute cholecystitis. // Surgery. 1991. N 1. c. 76 - 79.
CLAIM
A method of treating acute cholecystitis, including laparoscopy, gallbladder drainage, its sanitation antiseptic solutions, and then removing the drainage, characterized in that the sanitation is carried antiseptic solutions additionally containing immobilized enzyme immozim activity 150 - 250 PU, the exposure time in the gallbladder 1.5 - 2 hours at this reorganization is performed 1 time per day for 5 - 10 days.
print version
Publication date 28.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.