| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2260453
![]()
METHOD OF TREATMENT acute cholecystitis
Name of the inventor: Malkov IS (RU); Alukaev MI (RU); Chagaev ZI (RU); Chernov SA (RU); Kirshin AP (RU); Kozlov RK
The name of the patentee: Kazan State Technical University. AN Tupolev (RU); Malkov Igor (RU); Alukaev Marat Ildarovich (RU); Chagaev Zezag Imranovna (RU); Sergey Chernov (RU
Address for correspondence: 420111, Kazan, st. Karl Marx, 10, Kazan State Technical univesritet them. AN Tupolev, the patent department
Starting date of the patent: 2003.11.27
The invention relates to medicine, surgery, physiotherapy. In the gallbladder cholecystitis impose decompression. Through her conduct lavage gallbladder. Then fill the cavity of the gallbladder antibacterial drug. Through electrodes set according to the polarity of the drug in the cavity, and gall bladder externally on the patient's skin in the projection area of hepatobiliary organs, electrophoresed directly in the inflammatory changes. The method shortens treatment time.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, particularly to minimally invasive methods for the treatment of acute cholecystitis, and can be used for the treatment of acute cholecystitis complicated perivesical infiltrative processes in space during decompression after application cholecystostomy as preoperative preparation.
The problem of acute cholecystitis medical outgrown the scope and acquired social significance. The main reason for this evolution was the high incidence of gallstone disease with a trend towards a permanent increase (Vafin AZ, ID Naumov et al // Diagnostics and treatment of diseases of the bile ducts: Conference Proceedings - Tula, 1991. - p.. 27-28.) - [1].
If patients young and middle age with acute cholecystitis main task surgeons - is to improve the long-term results of operations for the older age groups, it is to reduce postoperative complications and mortality (Yefimkin AS, SY Nikulenko rehabilitation and Endoscopic obliteration gallbladder - an alternative to cholecystectomy in acute cholecystitis in patients with senile and elderly // Proceedings 22 conference - 20-21 May 1994 Smolensk -.. Moscow edited by Prof. Zaitseva EI, str.392) - [2].
In the numerous publications of the last decade did not cease lively discussions on acute cholecystitis and its complications. Almost not found papers on perivesical infiltrate arising in 24-37% in acute cholecystitis (Beburishvili AG, Golbrayh VA, Belov VP and other co-authors // Diagnostics and treatment of benign bile duct diseases: Proceedings conference - Tula, 1991. - p.132) - [3].
Massive inflammatory infiltrates in the field of obstructive considered a major factor (56%), predisposing damage to the bile ducts and blood vessels hepatoduodenal zone during cholecystectomy (Nechay AI, Novikov KV // Journal of Surgery - 1991, №1, - p.15) - [4].
The key to successful treatment of these patients has become a two-stage surgical approach - decompression of the gallbladder and delayed surgery (Ignatiev SV, SY et al Nikulenko // paravesical infiltration in emergency surgery of acute cholecystitis: 22 Proceedings of the conference on 20-21 May 1994 Smolensk -.. Moscow, under the editorship of Professor Zaitseva EI str.-397) - [5].
Are well-known conservative (starvation diet, different types of novocaine blockades, infusion, antibacterial, antispasmodic therapy) and surgery (cholecystectomy) methods for the treatment of acute cholecystitis. With the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment in cases where the severity of the patient's condition is caused by underlying medical conditions, considered optimal minimal intervention (decompression cholecystostomy under ultrasound or laparoscopy), followed by open or laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Under the control of ultrasound or laparoscopy punctured the gallbladder and evacuate its contents (bile, pus), and then in the lumen of the bladder set flexible catheter to aspirate the contents and topical antibiotics. This allows you to stop the progression of the inflammatory process, including the development of destructive changes in the gallbladder wall, quickly achieve a positive effect, to avoid the forced, high-risk patient for surgical intervention at an altitude of acute cholecystitis without adequate preoperative preparation. Treatment produced against a background of antibiotic therapy. However, intramuscular or intravenous antibiotics is ineffective, since the necessary zone creates insufficient drug concentration.
Electrophoresis has considerable advantages over other methods of drug administration:
- A higher therapeutic efficacy of the latter; introduction into the body tissue without disturbing its integrity;
- The possibility of simultaneous administration of several drugs in any size and location area;
- Creation of tissue "depot" of drug ions and particles that enter the lymph and blood flow, providing uniform and prolonged (keeping the pharmacological activity of up to 3 weeks) exposure;
- Concentrated impact at the desired location;
- Minimal side effects.
Very active famakologicheskoe effect of small doses of drugs - is 8-10 times less than the usual method of administration, due to increased sensitivity to them under the influence of specific factors - DC, creating an opening for Replicate (Sosin IN, Kariev MH Physiotherapy in surgery, traumatology and neurosurgery -. Tashkent, 1994 - page 7) - [6].
Electrophoresis can have very different effects on the orientation: symptomatic, anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, trophic, resorption, detoxification, anti-bacterial, etc. [6] - page 8..
In order to increase tissue permeability to drugs ion electrophoresis is often carried out after the heat treatments (high-frequency therapy). In recent years, along with electrophoresis combine inductothermy, magneto because the total effect thus higher than when separate use of physical methods. [6] - p.10.
In addition, electrophoresis antibacterial drugs can be effective in the field of impaired microcirculation (due to capillary stasis, thrombosis, necrosis or infiltration), which is observed in acute obstructive cholecystitis.
However, due to cutaneous electrode arrangement does not create an optimal electric field. This is due to high resistance arising in the way of its passage through the skin, which prevents the penetration and accumulation of drugs in the tissues and prolongs treatment and reduces its effectiveness.
The introduction of drugs into the cavity, followed by electrophoresis, it enables you to create the optimal concentrations and prolonged action in the body wall, increasing the efficiency of therapeutic action.
According to the known method for the treatment of suppurative cholangitis (patent №2098146, method of treatment of suppurative cholangitis and device for its implementation, A 61 M 31/00, A 61 N 2/06, published on 10.12.1997, at Bull №34..) - [ 7], when after laparotomy performed choledochotomy eliminated the causes suppurative cholangitis and obstructive jaundice in choledoch set endobiliary drainage with a magnetic device, which is output to the outside. Under the control of X-ray settings via the drainage introduced a mixture of magnetic fluid with an antibiotic to completely fill the space between the drain and the common bile duct. Magnetic screen allows you to absorb the magnetic field within the device, thereby to ensure the free flow of magnetic fluid and an antimicrobial drug in the bile ducts and maximize their focus outside of the drainage along the common bile duct, and a maximum concentration vozdeystvat to suppurative inflammation in the wall of the common bile duct.
The disadvantages of this method are:
- Use it only after laparotomy;
- The use of X-ray installation considerably complicates the methodology and, in addition, has a radiation dose to the patient;
- A constant magnetic field does not create conditions for optimal concentration and a long-acting drug of the drug in the patient's body wall.
A method of treating cholangitis (copyright certificate №1537277, cholangitis method of treatment for patients in the postoperative period, A 61 N 2/00, published on 23.01.1990, at Bull №3..) - [8], which can be used in the period after operations on the biliary tract and pancreas. After cholecystectomy through stump of the cystic duct into the lumen of the common bile duct is administered a combined PVC probe comprising at the distal part of the AC magnetic field. The proximal part of the probe output to the outside through counteropening in the left upper quadrant. The source of the alternating magnetic field can influence the microflora of the biliary tract, improves microcirculation and acceleration of regenerative processes in tissues.
The disadvantages of this method are:
- Use it after laparotomy;
- A constant magnetic field does not allow to create optimal concentrations of antibacterial drugs in the pathological focus area that extends treatment and reduces its effectiveness.
A method of treating suppurative cholangitis (copyright certificate №1319862, method of treatment of suppurative cholangitis, A 61 N 1/20, published on 30.06.1987, at Bull №24..) - [9], in which, after surgery on organs of hepatobiliary zone and external drainage of the bile duct retrograde through the drain tube into the segmental ducts of the right and left lobes of the liver two catheter is introduced through which postoperative lavage spend dialysate (solution with antibacterial properties). The next day on the liver affected by the electric field. Thus, cholestasis eliminated, which leads to normalization of liver secretory pressure passage and normalization for intrahepatic biliary bile paths contributes to the elimination of infection in the biliary system.
The disadvantages of this method are:
- Use it only after laparotomy;
- Removal of the outside dialysate;
- The impact of the electric field long after the introduction of the dialysate;
- Cutaneous electrode placement does not create an optimal electric field that extends the course of treatment and reduces its effectiveness.
The closest way, taken as a prototype, is a method for treating inflammatory diseases hepatopancreatoduodenal zone (copyright certificate №2089234 method for treating inflammatory diseases hepatopancreatoduodenal zone, A 61 N 1/30, published on 10/09/97, at Bull №25...) - [ 10]. The essence of the invention is that at the end of the operation on the top floor of the abdomen (usually in the biliary tract) obstructive in space pose a drainage tube. After 2-3 days to carry out additional regional obstructive lavage solutions of antibiotics or dioksidina. Then, through a drain wire electrode is introduced into a sterile somewhat greater length than the drainage nazagastralno second electrode to the duodenum papilla of Vater. The drainage tube is introduced drug mixture immediately before the procedure. Taking into account the polarity of the electrodes is connected to the drug unit "Feed-1". Creates an electric field of direct current strength 0.3-0.8 mA, duration of a session of 10-15 minutes. A session is carried out once a day for 5-8 days.
The disadvantages of this method the prototype are:
- The possibility of using it only after laparotomy;
- Not create optimal concentrations and prolonged effects of drugs in the body wall of the inflammatory changes as medications drugs are not introduced into the cavity of a diseased organ (hepaticocholedochus, gall bladder, pancreas);
- The electrodes are not installed under the supervision of, and therefore the passage of the electric field lines directly through the difficult area of inflammatory changes;
- Use of the process without decompression of the gallbladder may trigger the progression of inflammation in the gallbladder and hepatobiliary zone.
The invention solves the problem of increasing the effectiveness of minimally invasive treatments for acute cholecystitis complicated infiltrative processes perivesical space and reduce the time of treatment of patients by speeding up the relief of the inflammatory process in the gall bladder and resorption perivesical infiltrate through the creation of optimal concentrations and prolonged exposure to the antibacterial drug (antibiotic or antiseptic) on the wall of the gall bladder and the creation of optimal conditions for surgery, reducing the risk of intra- and postoperative complications.
This object is achieved in that the method for the treatment of acute cholecystitis, comprising drainage, lavage, administration of antibacterial agents and the impact of a constant electric field, on the gallbladder impose decompression cholecystitis, through which carried lavage gallbladder, then the cavity of the gall bladder filled with antibacterial drug, and influence of a constant electric field lead through electrodes set according to the polarity of the drug in the cavity of the gallbladder and externally on the patient's skin in the projection bodies hepatobiliary zone electrophoresis was carried out directly in the inflammatory changes, thereby creating optimum concentrations and prolonged exposure to antibiotic on gall bladder wall and perivesical space.
Before filling the cavity of the gallbladder antibacterial drug and the effects of constant electric field is carried out for 10-15 minutes PMP or UHF-therapy at doses of nonthermal hepatobiliary zone.
Filling of the gallbladder antibacterial drug is carried out within 30 minutes after the PMP or UHF-therapy, prior to exposure to static electric field in the gall bladder and perivesical space amperage 0.5-0.8 mA lasting 10-15 minutes, exercising session 1 times daily for 5-6 days.
The extent of regression of the inflammatory process in the gall bladder and perivesical space controlled ultrasonic methods of research in the process of treatment.
Brief Description of the drawing.
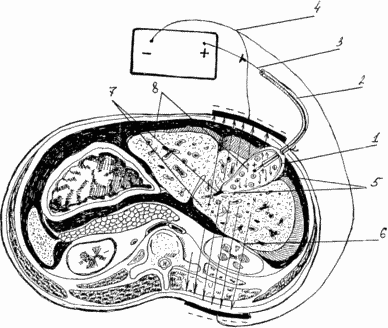 |
Here: 1 - the gall bladder; 2 - decompression cholecystostomy; 3 - intracavitary electrode; 4 - cutaneous electrodes; 5 - perivesical space; 6 - the force lines of the electric field; 7 - hepatobiliary zone; 8 - directed action antibiotic. |
Method is as follows
After 24 hours, after the imposition of decompression cholecystostomy 2 lavage and gallbladder 1 solution of antiseptics on hepatobiliary zone 7 act for 10-15 minutes, alternating magnetic field (PMP) or nonthermal doses of the electric field of ultrahigh frequency (UHF), which improves the microcirculation in the wall of the gall bladder 1 and perivesical space 5. after 30 minutes, the gall bladder cavity 1 through decompression cholecystitis 2 fill antibacterial drug (antibiotic or antiseptic, having a positive or negative charge). Formation of the electric field carried different polarities electrodes 3 and 4 immediately after filling antibacterial drug gall bladder, the first three of which positive (or negative - depending on the polarity of the antibacterial drug) is set in the cavity of the gall bladder 1 through the decompression cholecystitis 2, and the other 4 with opposite charge - in the right upper quadrant and right lumbar region so that the electric field lines 6 pass through the gallbladder and 1 perivesical space 5. in the light of preparations polarity electrodes 3 and 4 are connected to the unit "Feed-1". Create a constant electric field strength of 0.5-0.8 mA current with a duration of 10-15 minutes a session. By directional 8 antibiotic in a constant electric field 6, generated by the potential difference between the electrodes 3 and 4, create optimal concentration and prolonged its effect on the gallbladder wall 1 and 5 perivesical space, accelerating the processes of resorption perivesical infiltrate. This exercise prevention of intra- and postoperative complications. The course of treatment is 5-6 sessions. The extent of regression of the inflammatory process in the gall bladder, perivesical space controlled ultrasonic methods of research (US) during the treatment.
Thus, the proposed method for the treatment of acute cholecystitis complicated infiltrative processes perivesical space does not require sophisticated technical and medical support, easily performed in the surgical hospitals, has a significant economic impact.
CLAIM
A method of treating acute cholecystitis, including drainage, lavage, administration of antibacterial agents and the effect of a constant electric field, characterized in that the gallbladder is applied decompression cholecystitis, through which is carried lavage gallbladder, after which the hole gallbladder filled antibacterial drug, and the impact direct electric field through electrodes are set according to the polarity of the drug in the cavity, and gall bladder externally on the patient's skin in the projection area of hepatobiliary organs, electrophoresed directly in the inflammatory changes.
print version
Publication date 28.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.