| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2202964
![]()
METHOD FOR TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS, COMPLICATED WITH THE HOLANGITOM, IN THE POST-OPERATING PERIOD
The name of the inventor: Veksler N.Yu . ; Mukhin AS; Boyarinov GA; Sazonova LF
The name of the patent holder: Military Medical Institute of the Federal Border Service of the Russian Federation at the Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy
Address for correspondence: 603001, Nizhny Novgorod, Nizhne-Volzhskaya nab., 1/1, VMI FPS of the Russian Federation at the National Medical Academy, NIRIO
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.06.15
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to surgery, and can be used to treat patients with acute cholecystitis complicated by cholangitis. Conduct cholecystectomy, intraoperative cholangiography. Drains the holedoch through the stump of the bladder duct with a rolled catheter according to the Halstead-Pikovsky technique. In the postoperative period, the bile duct is sanitized. A pre-prepared 0.06% sodium hypochlorite solution of 40 ml volume is injected through the catheter at a rate of 50 drops per minute. Daily for 5 days before regression of bacteriological parameters of bile. The method makes it possible to lower the microbial titer in the bile culture. This increases the effectiveness of treatment.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to practical public health and can be used in surgery for postoperative treatment of patients with acute cholecystitis complicated by cholangitis.
The problem of treating patients with acute cholecystitis complicated by cholangitis is still very relevant today because of the lethality, which is more complicated with this complication than with uncomplicated cholecystitis. So, according to BA Korolyov and DL Pikovskiy [5], the lethality with complicated cholecystitis is 5-15%, while in uncomplicated cholecystitis, 1-2%. According to V. Ya. Vasyutkov, GG Gviniashvili and SE Kozlova / 1 /, the total postoperative mortality in patients with choledocholithiasis complicated by purulent cholangitis is 11.5%, whereas in uncomplicated forms of cholelithiasis - 0.8-2.4%. The frequency of purulent cholangitis in the last 15 years, according to G.I. Veronsky and SG Shtofina / 3 / is 10.4 - 10.5%. As can be seen from the sources of information, the lethality remains quite high. The main role in the development of cholangitis is caused by infection. In the monograph by BA Korolyov and DL Pikovsky (5) it is noted that the issues of combating bacterial infection in patients with acute cholecystitis, especially complicated forms, remain relevant. It is emphasized that even the absence of growth of microbes on ordinary media does not mean sterility of the material. According to MI Kuzin et al. (1986), the so-called sterile contents of the gallbladder with gangrenous cholecystitis can mean the presence of anaerobic neklostridialnoy infection. The data of V. A. Golbraich (1986) that in the first 72 hours after the first attack of cholecystitis are not uninteresting, the seeding of bacteria increases to 92%. Thus, the problem of fighting infection in patients with complicated cholecystitis is topical.
IL Menshikov, AI Korabelnikov and co-authors. (6) describes the method of ozonotherapy with purulent cholangitis. It consists in introducing into the bile ducts an ozone-oxygen mixture with an ozone concentration of 5 mg / l in a volume of 30-40 ml. At the same time, the authors state that the concentration of ozone in the bile was 2,5 mg / l when using this method. This method seems irrational for the following reasons. First, the introduction of gaseous ozone into the bile duct (in this case an ozone-oxygen mixture) can lead to hypertension to the biliary tract and cause complications of the disease. By the way, the authors themselves observed and described complications in the application of their method in the form of pain, a feeling of raspiraniya, which was regarded by them as a manifestation of intraprostatic hypertension. Secondly, when using an ozone-oxygen mixture with an ozone concentration of 5 mg / l, it is unclear how the concentration in the bile is 2 mg / l. In our opinion, it may be even less, given the solubility of ozone in biological media. To achieve ozone concentration in an isotonic solution of sodium chloride, for example, the ozone concentration at the outlet should be set at 10 mg / l, and in bidistilled water - 20 mg / l. Studies on the solubility of ozone in bile have not been carried out to date and have not been described in the literature. Therefore, we are not sure how accurately it is possible to control the concentration of ozone when ozone-oxygen mixture is introduced into the biliary tract.
N. E. Chernehovskoy, R. B. Mulladze, A. P. Steltsovsky, and co-authors. (9) a method for the treatment of cholangitis including cholecystectomy, choledochhotomy, drainage of the common bile duct, administration of the drug to the inflammation zone, characterized in that the preparation is ozonized isotonic sodium chloride solution, which is introduced into the common bile duct during choledochoscopy in The operation time and additionally the same solution is injected into the lumen of the common bile duct along the T-shaped drainage tube after the operation until the color and transparency of the bile are normalized. Use a solution with an ozone concentration of 5 mg / l in an amount of 40 ml.
This method, in our opinion, has serious shortcomings.
We believe that, instead of traumatic choledochotomy, drainage of choledoch through the stump of the vesicular duct by a 2 mm catheter is preferred, which has a folded distal end and 4 scalloped orifices around the periphery that increase the resorption capacity of atraumatic drainage and the possibility of microlith migration. Our opinion is in complete agreement with the literature data / 5 /. In addition, with the use of choledochotomous drainage of the bile ducts, it is possible to leak bile around the drainage and prematurely drop it, which leads to the formation of bile deposits and abscesses of the abdominal cavity, diffuse peritonitis, suppuration of the operating wound, and other complications causing recourse.
Normalization of color and transparency of bile is not an objective criterion of the result of treatment. Our research shows that even with the normalization of color and transparency of bile, it can retain sufficiently high titers of microbial bodies. That is why bacteriological control is more objective in our opinion.
The ozone concentration of 5 mg / l is by no means safe. So, back in 1997, Yu.P. Potekhina / 7 / showed that ozone in concentration above 4 mg / l causes significant activation of lipid peroxidation (LPO) processes without compensation from the antioxidant defense system and significant changes in peroxide membrane resistance Erythrocytes according to blood biohemiluminescence data. In addition, high doses of ozone (more than 3 mg / l), activating LPO processes with the accumulation of LPO products, promote hyperproteolysis with the release of tissue enzymes into the blood and hypercoagulation (4). This action of ozone in conditions of cholangitis can be regarded as undesirable. Thus, the ozone concentration of 5 mg / l is not safe.
Introduction to holedoch (even very slowly, for 5 min) using a syringe 40 ml of liquid can cause bile hypertension, which leads to an exacerbation of pancreatitis, which manifests itself in the relevant clinical and laboratory syndrome that we had the opportunity to observe in our clinic.
The aim of the proposed invention is to increase the effectiveness of treatment of patients with acute cholecystitis complicated by acute cholangitis in the postoperative period.
The goal is achieved by the fact that after the operation of cholecystectomy (by open method or from mini-access), intraoperative cholangiography, drainage of choledoch through the stump of the bladder duct, using the Holsted-Pikovsky method, with the purpose of sanitizing the bile ducts, a drip of 0.06 % Solution of sodium hypochlorite in a volume of 40 ml until regress of bacteriological parameters of bile.The rate of sodium hypochlorite injection is 50 drops per minute, the course of treatment is 5 days daily.
This method is more reliable for the following reasons. Investigations by N. Yu. Veksler showed that the 0,06-th solution of sodium hypochlorite is superior in its detoxifying effect to the ozonized isotonic sodium chloride solution (2). This solution is stable, whereas the half-life of ozone is 30 minutes. Thus, even with slow jet administration of the ozonized solution, on the one hand, the risk of developing bile hypertension is maintained, and on the other, a decrease in the ozone concentration in the solution is possible. Stability of solutions of sodium hypochlorite allows for their drip introduction, which excludes the possibility of developing bile hypertension.
The method is carried out as follows. Sodium hypochlorite is prepared on the EDO-4 apparatus. 40 ml of a 0.06% solution of sodium hypochlorite are introduced into the holedoch through the Holsted-Pikovskiy drainage at a rate of 50 drops per minute. We determined the sowing of bile before and after the injection, and the next day; The course of treatment was 5 days daily.
In total, this technique was used in 15 patients.
Also, as a comparison group, 15 patients were injected with a conventional isotonic solution of sodium chloride with heparin. As before and after the introduction, bile was determined for sowing. There were no significant differences in the crops before and after the introduction in this group.
As shown by our studies, the introduction of 40 ml of a 0.06% solution of sodium hypochlorite reduces the microbial titer in the bile culture, and it remains lowered the day after the administration. The data are presented in the table.
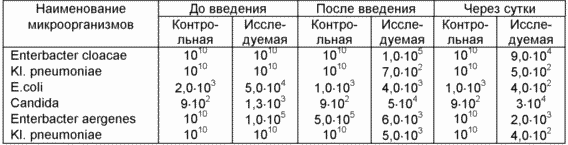
We present clinical observations
Example 1
Patient Chumakova IF, 52 years old, a medical history of 2846, was operated on for gangrenous cholecystitis, complicated by purulent cholangitis. Analysis of 594 bile for sowing from April 4, 2001: before the introduction of sodium hypochlorite was determined by Enterobacter aerogenes 1,0 · 10 5 . Analysis of 595 bile for sowing on April 4, 2001: 1 hour after the administration of sodium hypochlorite was determined by Enterobacter aerogenes 9.0 · 10 3 . The titer of microorganisms on the day after the procedure (analysis 597) decreased to 2.0 × 10 3 . After 5 days, only Enterobacter aerogenes 2.0 · 10 4 were detected. The patient is discharged in a satisfactory condition 10 days after the operation.
Example 2
Patient Voloshina NP, 75 years old, a case history of 4050, was operated for gangrenous cholecystitis complicated by cholangitis. Analysis 734 of April 17, 2001: before the introduction of sodium hypochlorite, E. coli 5.0 · 10 4 were determined. Analysis 735 of April 17, 2001: after the administration of sodium hypochlorite, E. coli 4.0 · 10 3 was determined. The next day - 4,0 · 10 2 and after 5 days - the same title. The patient is discharged in a satisfactory condition 8 days after the operation.
Example 3
Patient Poleshchuk SI, 59 years old, a case history of 3896, was operated for gangrenous cholecystitis complicated by cholangitis. Analysis 750 from April 24, 2001: before the introduction of sodium hypochlorite was determined by Enterobacter cloacae 10 10 . Analysis 751 of April 24, 2001: after the administration of sodium hypochlorite, Enterobacter cloacae was determined 1,0 · 10 5 . Analysis 755 of April 25, 2001. - 9.0 · 10 4 . 5 days after the administration of sodium hypochlorite - 2 · 10 1 . The patient is discharged in a satisfactory condition 10 days after the operation.
All patients who were treated with the proposed method did not experience any complications. The procedure was well tolerated. All patients are discharged in satisfactory condition.
Thus, the proposed method allows us to stop the infectious process, is reliable, does not entail any complications.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. Vasyutkov V.Ya., Gviniashvili G.G., Kozlov S.E. Treatment of purulent cholangitis in patients with choledocholithiasis // Annals of surgical hepatology. - T.4. - 2. - 1999. - P.88.
2. Veksler, N. Yu. Application of sodium hypochlorite and ozonized physiological solution in a complex of intensive therapy in patients with infective endocarditis. - Author's abstract. Diss. Candidate honey. Sciences. - Moscow, 1998. - 26 p.
3. Veronsky GI, Shtofin SG Acute purulent cholangitis as a complication of calculous cholecystitis // Annals of surgical hepatology. - T.4. - 2. - 1999. - P.89.
4. Kontorschikova K. N., Efremenko Yu.R., Okrut I.E. Dose-dependent effect of ozone on proteolytic systems of the organism // News of science and technology. - Information book "Reanimatology and Intensive Therapy. Anesthesiology". - 4. 2000. - Appendix. - Ozone and methods of efferent therapy in medicine. -Matt.4 All-Russian scientific-practical conference. -C.24-25.
5. Korolyov BA, Pikovsky DL Emergency surgery of the biliary tract. - Moscow, Medicine, 1990.- 239 p.
6. Menshikov IL, Korabelnikov AI, Andreev GN The technique of ozonotherapy with purulent cholangitis // Annals of surgical hepatology. - T.4. - 2. - 1999. - P.117.
7. Potekhina Yu.P. Clinical and experimental substantiation of ozonotherapy in patients with compression-ischemic neuropathies. -Diss. Candidate honey. Sciences. - Nizhny Novgorod, 1997. - 176 p.
8. Rodionov VV, Filimonov MI, Moguchev V.М. Calculous cholecystitis. - Moscow, Medicine, 1991. - 319 p.
9. Chernehovskaya N. Ye., Mumladze R.V., Seltsovsky A.P. Et al. A method of treating cholangitis. - Patent 2157660 dated October 20, 2000
CLAIM
The method of treatment of patients with acute cholecystitis complicated by cholangitis in the postoperative period, including cholecystectomy, intraoperative cholangiography, drainage of choledochus through the stump of the bladder duct by a rolled catheter according to the Holsted-Pikovsky method, characterized in that the patient is administered, through the indicated catheter, for the sanation of the bile ducts through said catheter Drip pre-prepared 0.06% solution of sodium hypochlorite in a volume of 40 ml at a rate of 50 drops per minute, daily for 5 days before regress of bacteriological parameters of bile.
print version
Date of publication 28.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.