| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2080598
![]()
METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF ACTIVATED T-LYMPHOCYTES IN THE HUMAN ORGANISM
The name of the inventor: Frolov Alexander Kirillovich [UA]; Shipichyak Evstakhiy Grigorievich [UA]; Negustorova Alla Fedorovna [UA]; Lupinos Oksana Vitalevna [UA]; Piskun Marina Nikolaevna [UA]
The name of the patent holder: Zaporozhye State University (UA)
Address for correspondence:
The effective date of the patent: 1992.09.03
Use: in the field of medicine and concerns the detection in the human body of activated T-lymphocytes. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION: Blood is collected from a finger or vein into tubes with an anticoagulant, lymphocytes are isolated, lymphocytes obtained are used for spontaneous rosette formation with erythrocytes of a ram without cold incubation ("immediate rosettes") and the number of lymphocytes that attach more than 10 erythrocytes of a ram, . The method allows to increase the objectivity of the evaluation, simplify the definition and shorten the analysis of the functional activity of lymphocytes directly in the human body.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely to immunological methods of investigation, and concerns the detection of activated T-lymphocytes in the human body.
A method for determining T-lymphocytes in the blood is known, which includes the isolation of lymphocytes, the addition of erythrocytes to the ram, incubation for at least one hour at 4 ° C, the preparation of preparations and their analysis by the number of attached red blood cells [1] T cells receive cells , Attached at least three erythrocytes ram. However, this method can only determine the number of T-lymphocytes, without determining their activity in the body.
A method for the detection of activated T-lymphocytes in human blood is known, including culturing lymphocytes 48 54 hours in a nutrient medium with mitogen phytohemagglutinin (PHA), stimulating T-lymphocytes to proliferate under culture conditions, administering colchicine stopping lymphocyte division in the metaphase phase, Chromosome preparations and their cytogenetic analysis [2] This method is based on the analysis in the lymphocytes passing the first mitotic division of the associations of acrocentric chromosomes, which are a cytogenetic trace of their previous proliferation and migration from the peripheral lymphoid organs in the human body. For activated, lymphocytes without associations and with two associating acrocentrics formed as a result of a series of mitotic divisions in which associations are destroyed are taken. This method is rather complicated (it is necessary to cultivate lymphocytes under sterile conditions, stop cell division by colchicine, since chromosomes can be studied only at the stage of metaphase of mitosis), which is inaccessible for mass implantation (necessary reagents, expensive equipment), and certain qualifications of the performer Value of cell culture, possession of the cytogenetic method). This method is not objective enough, as in the culture part of the lymphocytes die and not all of the living lymphocytes enter the mitotic cycle for the period of cell fixation.
The aim of the proposed method is to increase the objectivity of the evaluation, simplify the determination and shorten the analysis time of the functional activity of lymphocytes directly in the human body.
The goal is achieved by the fact that in a known method, including the determination of lymphocyte activity according to the remaining signs of their antigen-dependent activation and proliferation in the peripheral lymphoid organs, spontaneous rosetting with erythrocytes of ram is carried out without cold incubation ("immediate rosettes"), the amount of attached erythrocytes of ram To T-lymphocytes (avidity), and the number of T-lymphocytes that attach more than 10 erythrocytes of the ram is determined to be activated.
A comparative analysis of the proposed solution with a prototype shows that the claimed method differs from the known one in that the number of activated T lymphocytes is determined by analyzing the avidity of T lymphocytes to erythrocytes of a ram in a smear prepared by spontaneous rosette formation with erythrocyte ram without incubation (" "). For activated T-lymphocytes are adhered, attaching more than 10 erythrocytes of a ram. Therefore, the sample of lymphocytes obtained should not be cultured, in addition, its volume may be minimal (0.5 0.6 ml) and allows objectively to isolate lymphocytes from whole blood for rosette tests, which greatly simplifies the method and makes it available for scratched studies. Thus, the claimed solution meets the criterion of "novelty".
Technical solutions for setting up the method of spontaneous rosette formation with erythrocytes of a ram without cold incubation ("immediate rosettes") are known (2, 4, 5). However, in these technical solutions (3, 4, 5), the avid class of T-lymphocytes was not isolated and functionally substantiated, attaching more than 10 erythrocytes of the ram, which did not allow achieving the goal, namely, to isolate the activated T-lymphocytes in the body. Therefore, the methods (3, 4, 5) of setting and analyzing "immediate outlets" are quantitative, not qualitative.
There are no known technical solutions in which the activity of lymphocytes in the blood is determined by the number of erythrocytes attached to them with the immediate method of setting the outlets. Determination of activated T-lymphocytes by a rosette test without their cold incubation according to the proportion of lymphocytes highly-erythrocyte to erythrocytes (attached more than 10 erythrocytes of a ram) in the preparation should not be explicitly known from the prior art. Proceeding from this, the claimed solution corresponds to the requirement of "inventive level".
The proposed method is carried out as follows. Blood is drawn from a finger or vein into tubes with anticoagulants, lymphocytes are isolated, their concentration is adjusted to 2.0 × 10 6 cells per 1 ml of a nutrient mixture consisting of 199 and 10% fetal bovine serum adsorbed against erythrocytes of ram and human, Inactivated at 56 ° C for 30 minutes. Then 0.1 ml of the resulting lymphocyte suspension is mixed with 0.1 ml of a 0.5% slurry of washed erythrocyte ram, diluted in the same nutrient medium as the lymphocytes. The cells are incubated in a thermostat for 10 minutes at 37 ° C., centrifuged at 200 5 minutes, the rosettes fixed with 0.05 ml of 3% glutaraldehyde solution (pH 7.2 7.4) for 20 minutes at room temperature, washed off with excess Distilled water and centrifugation at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes. The supernatant is removed, leaving a volume of 0.1 to 0.2 ml, in which the cells are thoroughly resuspended and smears are prepared on the defatted slides. The smears are fixed for 5 minutes in methanol, stained and microscopic. In the preparation, up to 400 lymphocytes are studied in four different parts of the drug. The rosette-forming lymphocytes are grouped into three avid classes: 1st class 3 6 attached erythrocytes of ram, 2nd class 6 10 and 3rd class more than 10 erythrocytes of ram. According to the fraction of the last class, activated T-lymphocytes are determined at the time of taking a blood sample for analysis.
The basis for the assertion that a subpopulation of circulating lymphocytes that attach more than 10 erythrocytes of a ram is a subpopulation of activated lymphocytes is data on their specific dynamics in healthy and sick persons (see table), and the detected high (r 0.8-0.9 ) A positive correlation of this lymphocyte count with the frequency of lymphocyte classes without association and with two associating acrocentrics. According to the prototype, these cytogenetic classes of lymphocytes are activated antigens formed in the peripheral lymphoid organs after a series of mitotic divisions in the immunogen. A high positive correlation of the compared indicators obtained by different methods, indicates the homogeneity of the analyzed subpopulations among circulating lymphocytes. These subpopulations are part of the post-proliferative pool of lymphocytes newly formed in the peripheral lymphoid organs during immunogenesis in response to numerous antigens and autoantigens present in the body. Consequently, these lymphocytes are activated. After a series of mitotic divisions (6-10 times), activated subpopulations of lymphocytes migrate from the peripheral lymphoid organs to the general circulation and become available for analysis when taking blood. When the chromosomes move, chromosome associations are destroyed or they remain minimal, that is, they constitute a class of lymphocytes without associations and with two associating acrocentrics. In addition, in the newly formed T-lymphocytes, a high density of membrane SD 2 antigens is preserved. Therefore, they are highly-viscous to erythrocytes of the ram and, upon contact with them, attach more than 10 erythrocytes of the ram. In long-circulating (days, weeks, months) intact lymphocytes, the density of SD 2 antigens decreases, because This stage-specific antigen takes part mainly in the processes of antigen-independent activation of lymphocytes. Therefore, non-activated (temporarily intact) T-lymphocytes attach a smaller number (<10) of erythrocytes of the ram.
The frequency of activated lymphocytes among the circulating pool of lymphocytes depends on the intensity of their formation in the peripheral lymphoid organs, and on the activity and direction of their migration to the antigenic pathological foci, which is reflected in the table.
The frequency of activated lymphocytes was studied using the claimed method and prototype from the following contingents:
- Healthy donors 10 people;
- Oncogenic patients with exudative pleurisy of carcinogenic etiology of 9 persons.
The table shows the results of the frequency of rosette-forming T-lymphocytes obtained by the cold incubation method, characterizing the total number of T-lymphocytes, and without cold incubation, "immediate rosettes" characterizing the subpopulations of T-lymphocytes with an increased density of receptors for erythrocyte ram (DM 2 antigen) .
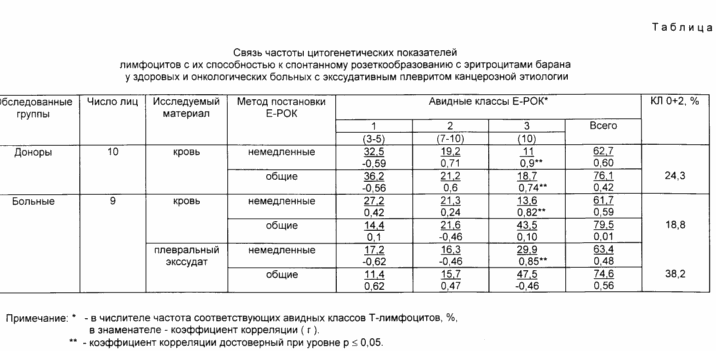
It can be seen from the table that the total frequency of "immediate outlets" in all samples of lymphocytes is significantly less than the frequency of common sockets and corresponds to the literature [3]. Without the cold incubation, only lymphocytes with an increased density of SD-2 receptors manage to form receptacles. Analysis of the frequency of avid classes in the blood And pleural exudate shows that only highly araised T-lymphocytes belonging to the third class, with an immediate method of setting up the outlets, exhibit dynamics characteristic of the given immunological situation. Thus, the frequency of lymphocytes that attached more than 10 erythrocytes of a ram in pleural exudate was 1.5 2 or more times higher than the frequency of such lymphocytes in the blood. Similar dynamics in blood and plasma was detected for a class of lymphocytes without associations and with two associating acrocentrics (CL 0 + 2).
In a correlative analysis of the CL 0 + 2 frequency in blood and plasma, it was found that this cytogenetic indicator of T-lymphocyte activity was significantly high (r 0.82 and 0.85, respectively), correlated only with the frequency of T-lymphocytes that attached more than 10 erythrocytes in the formulation Method of rosetting without cold incubation.
Such differences in activated T-lymphocytes in cytonetic and rosette tests in blood and pleural exudate arose due to their redistribution, that is, migration from the blood and deposition in the lungs, where a powerful antigenic focus (tumor metastasis) is localized.
In the blood of healthy donors, the average frequency of "immediate outlets" and below the total outlets and this decrease was due to the proportion of high-grade T-lymphocytes of the third class. In addition, there was a closer positive correlation between them and the CL 0 + 2 frequency.
The obtained frequency dynamics of high-ity to erythrocytes ram of T-lymphocytes and their close correlation with the frequency of CL 0 + 2 confirm their immunological activity. Therefore, the frequency of T-lymphocytes that have attached more than 10 erythrocytes of the sheep in the test of "immediate outlets" is a functional test of the activity of circulating T-lymphocytes. The summary indices of the frequency of rosette-forming lymphocytes from cold and without cold incubation remain quantitative tests and do not reliably correlate with functional parameters of T-lymphocytes.
T-lymphocytes circulating in the body, which have attached more than 10 erythrocytes of the ram, have a high density of the corresponding receptors (CD 2 antigens), as a residual sign of their previous activation in the peripheral lymphoid organs. DM 2-antigen participates in intercellular contacts, causing antigen-dependent (nonspecific) proliferation and differentiation of comitized lymphocytes [6] Its complementarity to erythrocytes of the sheep, and consequently, the connection with them, is random. This is evidenced by data on the increase in avidity of lymphocytes (the number of attached erythrocytes of the ram) during their nonspecific mitogenic stimulation with lectins under cultivation conditions in a test tube, already an hour after the addition of the mitogen (phytohemagglutinin, concavanavalin A, mitogen of the lakonos) even in the absence of DNA synthesis [7, 8]
Therefore, an increase in the density of the DM 2 antigen is an early sign of activation of T lymphocytes. In peripheral lymphoid organs, lymphocytes after antigen-specific and antigen-specific activation are transformed into blast cells with high density of CD2 antigen, and consequently, with high avidity to erythrocytes of the ram. Then such lymphocytes are mitotically divided 6 10 times and differentiate into a clone of antigen-reactive T-lymphocytes that leave the lymphoid organ, including a pool of circulating T-lymphocytes. The newly formed T-lymphocytes retain a high density of the SD 2 receptors and become available for analysis when taking a blood sample. In the course of further ontogeny of T-lymphocytes, the density of membrane SD2 antigen decreases.
Thus, according to the dynamics of highly-araised T-lymphocytes, which attach more than 10 erythrocytes of the ram, are determined by the method of "immediate outlets" and operatively control the intensity of proliferation and migration of activated T-lymphocytes; Their redistribution in the body to the locations of antigen deposition; Study the intensity of immunity and its correction with the help of immunotropic therapy.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. E.F. Chernushenko, L.S. Kogosova, S.I. Goncharova et al. Unified immunological methods for examining patients at inpatient and outpatient stages of treatment. Guidelines. Kiev, 1988, 18 p.
2. А.К. Frolov, V.K. Frolov. Method for the determination of activated T-lymphocytes in the blood. A.S. N 1024839 C 01 33/50, 1986, prototype.
3. G. Frimel. Immunological methods / Transl. With him. M. Medicine, 1987, 472 p.
4. A. N. Cheredeev, D.V. Plaedra, K.K. Stolongo. Study of spontaneous rosette-forming cells of human peripheral blood. Lab. Case, 1976, No. 6, 350-354 p.
5. J. I. Karpova, E.N. Mokhova, N.I. Volkov. The reaction of spontaneous rosette formation of lymphocytes isolated from capillary blood. Lab. Case, 1984, No. 7, 427-429 p.
6. Clinical immunology and allergology. In 3 volumes. T. 1. Per. With him. Ed. Yeager. 2 nd ed. Processed and supplemented. M. Medicine, 1990, 528 p.
7. Ju David, Tar Jan. Heman lymphosyte subpomilation: gigant human red Blood cell rosetfes J. Jmmand. Meth. 1977. v.15 N1. P. 67 76.
8. Richie E. Patchen M. Correlation and lymphocyte commitment achivation. Ceen. Jmnuind. N, 73). 1978 v 11. N 1, p. 88 97.
CLAIM
A method for the detection of activated T-lymphocytes in the human body, comprising collecting blood and isolating lymphocytes from it, characterized in that the spontaneous rosette formation with erythrocytes of a ram without cold incubation is performed with the obtained lymphocytes and the number of lymphocytes that attach more than 10 erythrocytes of the ram is determined by activated T- Lymphocytes in the body.
print version
Date of publication 02.04.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.