| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2205658
![]()
METHOD OF CORRECTION OF BIOCHEMICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL VIOLATIONS IN THE CONDITIONS OF EXPERIMENTAL ACUTE TOXIC HEPATOPATHY SUPPOSED BY IMMUNOLOGICAL REACTIVITY IMPROVEMENT
The name of the inventor: Smakhtin M.Yu . ; Konoplya AI; Severyanova LA; Bobyntsev II
The name of the patent holder: Smachtin Mikhail Yurievich ; Konoplya Alexander Ivanovich
Address for correspondence: 305041, Kursk, ul. K. Marx, 3, KSMU, Patent Department, Z.N. Kupriyanovoy
The effective date of the patent: 2002.02.11
The invention relates to medicine, namely to hepatology and immunology, and concerns the development of a method for correcting biochemical and immunological shifts in experimental acute toxic hepatopathy, accompanied by an increase in immunological reactivity. To this end, a tripeptide of H 2 N-Gly-L-His-L-Lys-COOH dissolved in physiological sodium chloride solution in a dose of 1.5 μg / kg of body weight parenterally (intraperitoneally) is injected intravenously at an interval of 24 hours between injections. The method ensures the coping of the hyperactivation of the immune system, which prevents the development of an autoimmune process.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The proposed method refers to medicine, namely to hepatology and immunology, and can be used to correct and prevent biochemical and immunological shifts in toxic hepatopathies.
Reactivity of the immune system in various forms of liver pathology plays an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease, which is caused by the direct influence of the body's immune system on the development of autoimmune complications of toxic and infectious liver damage, on the transition of the acute form of liver disease to chronic and cirrhosis of the liver. Immunological aspects of chronic liver diseases // Wiss. Beitr. M.- Luther-Univ. Halle-Wittenberg R.-1987.- 99.-R.192-198.), But also in maintaining the chronic course of the pathological process (Yakhontova O .I., Karashurova LL, Starkova SA Some immunological changes and their diagnostic significance in chronic liver diseases. // Vocabulary. -1988.- 4.- С. 39-42.) Many issues of connections Liver and immune system are solved in the experiment when modeling the pathological process in the liver with the help of various hepatotropic substances (Alekseyeva IN, Bryzgina TM, Pavlovich SI, Ilchevich NV Liver and immunological reactivity. -Kyiv: Science. Dumka, 1991.-C.5). The reaction of the immune system depends not only on the damaging agent, but also on its dose, multiplicity and mode of administration. In conditions of toxic hepatopathies, one can expect a decrease in immunological reactivity (Molotkov AO Violations of the physiological mechanisms of regulation of the immunity system in acute poisoning with organophosphorus compounds of carbophos: Author's abstract for the degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences - Saratov, 2002.- С. 20 ), And its increase (Konoplya AI Endogenous immunomodulators as a factor of preservation of homeostasis in the pathology of the liver: Author's abstract for the academic degree of the doctor of medical sciences - Kiev, 1989.-P.39). Such dysfunction in the immune system requires appropriate immunocorrective therapy (Alekseyeva IN, Bryzgina TM, Pavlovich SI, Ilchevich NV Liver and immunological reactivity.-Kiev: Science of the Doom, 1991. - C.43-45). It can be effective only if the stage of the disease, the nature and degree of immune disorders are strictly taken into account. Since in the conditions of toxic hepatopathies, a different reaction of the immune system can be observed, the effectiveness of treatment in some cases with immunostimulants, and in others with immunosuppressants is shown. Immunostimulants are effective in fighting immunodeficiencies, observed in some forms of liver pathology, and for activating regenerative processes in the organ. But the use of immunostimulants (thymogen) in conditions of liver pathology with increased reactivity of the immune system and a high level of immunoglobulins in the blood often leads to an exacerbation of the pathological process (BI Kuznik, VG Morozov, VH Khavinson, Year experience of experimental and clinical research., St. Petersburg .- "Science" .- 1998.-P.197-198.). Immunosuppressors are indicated in order to avoid damaging effects of immune mechanisms on the liver (Alekseeva IN, Bryzgina TM, Pavlovich SI, Ilchevich NV Liver and immunological reactivity .- Kiev: Science Duma , 1991.-P.43), since the activation of the immune response may indicate the onset of autoimmune mechanisms of liver damage (Ibid., P. 77).
The closest method of correction in the conditions of acute toxic damage of the liver CCL 4 (carbon tetrachloride (CTC)), another name for carbon tetrachloride (CHCU), is the use of a polysaccharide complex extracted from the roots and rhizomes of the six-petalled falciparum (PSK LS), which has immunosuppressive activity (Mansimova O. In the polysaccharide complex of the rhizomes and roots of the six-lobe nursery, glucose is contained - 13.6%, arabinose - 8.5%, xylose -%, galactose -%, mannose - 3.5%, rhamnose - 7.1% .In conditions of increased immunological reactivity caused by the introduction of CCL 4 , PSK LS shows a significant immunocorrecting effect, that is, reduces the increased immunological reactivity to the level of healthy animals. Such normalization of immunological reactivity is accompanied by a decrease in the severity of biochemical symptoms of liver damage: cytolysis syndromes (activity of alanine and aspartate aminotransferases), cholestasis (bilirubin concentration, cholesterol concentration) and hepatodepressive syndrome (fibrinogen concentration), which indicates improvement in liver status. Thus, this method of correction limits the hyperactivation of the immune system, which can lead to the development of autoimmune complications, the chronization of the process and the deterioration of the liver, but immunodeficiency does not occur, since the reactivity of the immune system decreases to the level of healthy animals, but not below it.
The disadvantage of this method of correction is the laboriousness of obtaining the CPM LS, the difficulty in its standardization, since the percentage of active substances in the PUK LS can depend on the quality of the initial raw materials and the conditions of separation, in addition, it is not clear what is the main active substance in this complex, from which Its effects depend on the exact percentage of monosaccharides or their sequence in polysaccharides.
The object of the invention is to develop a method for correcting biochemical and immunological shifts in experimental acute toxic hepatopathies accompanied by an increase in immunological reactivity.
The object of the invention is achieved by administering to the experimental animal (rat) with toxic hepatopathy accompanied by increased immunological reactivity parenterally (intraperitoneally) dissolved in physiological saline solution of sodium chloride, the suppressive immune response of the tripeptide H 2 N-Gly-L-His-L- Lys-COOH (the chemical name is glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) (hereinafter referred to as Gly-His-Lys) at a dose of 1.5 μg / kg body weight tenfold, with an interval of 24 hours between injections.
In the correction method developed by us, a tripeptide with a weak immunosuppressive effect is used, and a dose and a multiplicity of its administration are selected, which, without causing immunodeficiency, limits the hyperactivation of the immune system. It can be argued that such immunocorrection positively affects the liver, as the severity of biochemical symptoms of its defeat (inflammation syndrome and partly cholestasis) decreases.
This peptide is isolated from the blood plasma and its stimulating effect on hair growth, collagen synthesis by fibroblasts, accumulation of intercellular substance of connective tissue is known, which explains in many respects the accelerated healing of wounds and ulcers under its influence and on the basis of which the hypotheses about the physiological role of this peptide are suggested On the wound healing stimulant (Maquart FX, Pickart L., Laurent M., Gillery P., Monboisse JC, Borel JP. Stimulation of collagen synthesis in glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine-Cu 2 + // FEBS Lett, 1988. Vol 238. N2 P.343-346; Trachy RE, Fors TD, Pickart L., Uno H. The hair follicle-stimulating properties of the peptide copper complexes. // Ann. NY Acad.Sci 1991. Vol. 642. P.468-469.) Gly-His-Lys binds bivalent copper and thus can participate in the activation of copper-containing enzymes, thereby providing antioxidant processes, cell bioenergetics, synthesis Elastin, collagen, catecholamines (Maquart FX, Bellon G., Chaqour B., Wegrowski J, Patt LM, Trachy RE, Monboisse JC, Chastang F, Birembaut P, Gillery P. In vivo stimulation of connective tissue accumulation by the tripeptide-copper Complex glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine-Cu 2+ . // J. Clin. Invest. 1993 Vol. 92. N5. P. 2368-2376; Linder MC Biochemistry of Copper. E. Freiden, Ed. Plenum Press. 1991).
At the moment, since the chemical formula of this peptide is known precisely, it can be synthesized in any peptide synthesis laboratory or purchased from companies supplying biologically active compounds (Sigma, ICN, Merk, Bachim, etc.). We used a preparation synthesized in the Research Institute of Chemistry of St. Petersburg State University.
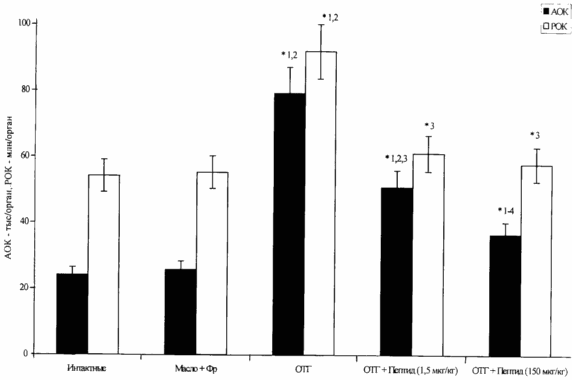
The figure shows a histogram showing the immunocorrecting effect of the Gly-His-Lys peptide under conditions of toxic damage of the liver with carbon tetrachloride.
The method is carried out as follows. As a model of acute toxic hepatopathy (OTS) accompanied by stimulation of immunological reactivity, we selected a model of hepatopathy caused by the poisoning of carbon tetrachloride (CTC), since this model has a great similarity in the mechanisms of development of liver damage with clinical forms of acute, chronic hepatopathy and cirrhosis of various Etiology in humans (Bluger AF, Maiore A.Ya., Gorshtein ES, etc. Characteristics of integrity disorders of liver cell membranes for some types of organ damage. // Uspekhi hepatologii. / Under the editorship of AF Bluger .-Riga.-1981.-Iss. 9.-P.5-24.). Experimental animals (rats) were injected intramuscularly with a 50% solution of CTC in vegetable oil at a dose of 3 ml / kg body weight for 5 consecutive days. Simultaneously with the receipt of hepatotropic venom, before and after it, ten times (once a day), 0.1 ml of a solution containing Gly-His-Lys peptide at a dose of 1.5 μg / kg of mass dissolved in a sterile isotonic chloride solution is injected intraperitoneally Sodium. At such a multiplicity of administration, the peptide has a corrective effect on a number of biochemical parameters, such as the level of beta-lipoproteins and the severity of the thymol sample, and a weak immunosuppressive effect that, without significantly weakening the immune system, prevents further immunological reactivity, which can lead to Hyperactivation and possible development of autoimmune complications. When the peptide is administered in the same dose, but the fivefold normalizing biochemical shifts, the effect is less pronounced, and the immunological reactivity, which is elevated under the conditions of CTC poisoning, practically does not decrease. Exceeding the recommended dosage more than 10 times (doses of 50 and 150 μg / kg) is accompanied by a more pronounced suppressive effect of the peptide and a simultaneous increase in biochemical disorders, such as the activity of alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, bilirubin concentrations, and beta-lipoproteins in the blood, and the severity Thymol test, indicating a deterioration in the functional activity of hepatocytes.
Example of specific implementation
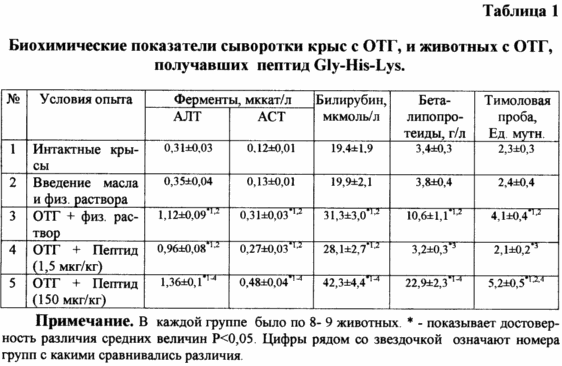
Wistar rats were divided into groups of 8-10 rats each. Groups of animals are presented in Table 1. The Gly-His-Lys peptide was administered to the animals tenfold (once a day) intraperitoneally at a dose of 1.5 μg / kg and 100 μg at a dose of 150 μg / kg. OTG was caused by a five-fold (once a day) intramuscular injection of a 50% solution of CTC in vegetable oil in a dose of 3 ml / kg of mass, alternating the paws. The peptide was administered before and simultaneously with the administration of CXM. The day after the last injection of CTC, rats were sacrificed by bleeding under ether anesthesia, and blood serum was obtained, which was used for biochemical studies. Under OTS conditions, an increase in activity of alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, a level of bilirubin, beta-lipoproteins and thymol test is observed, which indicates liver damage and the development of cytolysis, cholestasis and inflammation syndromes. Under these conditions, the corrective action of the peptide at a dose of 1.5 μg / kg of mass was observed on the concentration of beta-lipoproteins and the level of thymol sample, and a tendency towards normalization with respect to other biochemical parameters was observed, while the use of the peptide at a dose of 150 μg / kg Mass led to an increase in biochemical disorders (Table 1).
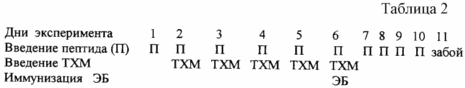
The same groups of animals were taken to study the state of immunological reactivity. The intensity of the humoral immune response (GMO) was judged by the number of antibody-forming (AOK) and rosette-forming (ROC) cells in the spleen on the 5th day after the immunization of experimental animals (rat) (Malberg, K., Zigl E. Immunological Methods. G. Frimel, Translator from the German AP Tarasova, M., 1987-p. 273-282.). The erythrocytes of the ram (EB) were used as an antigen. The peptide was administered both before and after immunization according to the scheme in Table 2
The results of the experiment are shown in the drawing. The introduction of CXM is accompanied by the development of OTG and stimulation of GMOs by T-dependent antigen-EB. The introduction of the peptide under these conditions reduces immunological reactivity, which can be used for the purposes of immunological correction.
Thus, the use of the proposed tripeptide at a dose of 1.5 μg / kg tenfold, intraperitoneally to experimental animals (rats, mice) significantly reduces the increased immunological reactivity, thereby preventing its hyperactivation and development of autoimmune complications, and normalizes a number of biochemical parameters of serum that Indicates a corrective effect of the peptide on the functional activity of hepatocytes. Thus, the Gly-His-Lys tripeptide in this mode of administration has a simultaneous corrective effect both with regard to the functional activity of hepatocytes and with respect to immunological reactivity.
CLAIM
A method for correcting biochemical and immunological disorders under conditions of experimental acute toxic hepatopathy accompanied by an increase in immunological reactivity, characterized in that parenterally once a day for ten consecutive days, the suppressive immune response of the H 2 N-Gly-L-His-L-Lys tripeptide -COOH in a dose of 1.5 μg / kg of weight.
print version
Date of publication 02.04.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.