| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2142828
![]()
THE LASER METHOD OF TREATMENT OF AIDS
The name of the inventor: Ovsyannikov Victor Andreevich; Sizova Natalia Vladimirovna
The name of the patent holder: Ovsyannikov Viktor Andreevich; Sizova Natalia Vladimirovna
Address for correspondence: 194021, St. Petersburg ul.Shatelena 2, building 2, ap. 36, Ovsyannikovu A.А.
Date of commencement of the patent: 1996.03.15
The invention relates to laser medicine and is intended for the treatment of HIV-infected patients in the stage of the AIDS-associated complex and in the stage of AIDS. A complex percutaneous exposure is made to the radiation of an infrared blood laser in the ulnar veins and to the following areas of the body: the sternum region, the projection of the liver and spleen from the front, the region of the iliac wings, and the region of the paravertebral zones. The wavelength is 700-1000 nm. The method allows to achieve normalization of blood composition, improvement of the general condition of patients.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to methods of treating HIV-infected patients in the stage of the AIDS-associated complex and in the stage of AIDS (HIV-virus of human immunodeficiency, AIDS-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
Currently, there are a very limited number of ways to treat AIDS patients and, unfortunately, these methods do not lead to recovery of patients. The main direction of treatment of HIV-infected patients is antiviral therapy.
A medicamentous way of treating AIDS with the help of an antiviral drug azidothymidine (AZT, zidovudine, retrovir) is known [1]. However, it turned out that antiretroviral therapy only AZT is ineffective. In addition, the use of AZT has a number of side effects, such as dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite), allergic reactions and oppression of hematopoiesis.
The method of extracorporeal photophoresis closest to the claimed one can be considered [2]. The essence of this method is that patients are selected a small amount of blood, this blood is divided into fractions, and blood leukocytes are extracorporeally irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. In this case, before taking blood, patients are given 8-meta-oxapsporalene as a photosensitizer. After irradiation, the lymphocytes are returned to the blood of the same patients.
Disadvantages of this method are obvious: selection of blood from patients, separation of blood into components, use of a chemopreparation - photosensitizer, return of irradiated lymphocytes to the body, while traumatizing the body, and the possibility of introducing additional infections into the body during these manipulations, but also using a rather complex and expensive Equipment and the need for long-term treatment.
Laser methods of treating AIDS, which could be considered a prototype of the claimed invention, are not known to the authors. Laser methods for treating other diseases can not be mechanically transferred to AIDS treatment in connection with the specificity of this disease.
In the proposed method, laser radiation is used for percutaneous exposure not only to blood, but also to areas of the bone marrow in which new blood cells are created (the areas of the sternum and iliac wings), the parts of the nervous system (paravertebral zones), and the zones Location of the liver and spleen. In this case, there is no violation of the skin, and completely excludes injury to the body and the possibility of introducing additional infections into the body.
Clinical studies have shown that such a complex laser treatment is effective and effective. It leads to effective normalization (modulation) of the blood composition, improvement of the general condition of patients, preservation of their life and improvement of their quality of life by eliminating some of the AIDS-associated diseases. Researches have shown, that positive results of treatment remain at patients after its termination long enough time - from 6 till 12 months.
The essence of the proposed method is that the treatment of patients is carried out by complex transdermal exposure to laser radiation on the patient's blood and certain areas of his body, namely:
A) for blood in large ulnar veins - with radiation with an average power of 5-10 mW for 1-3 min on each arm,
B) on the sternum in the projection of the thymus - radiation with an average power of 10-20 mW for 3-5 minutes,
C) on the area of the projection of the liver from the front - radiation with an average power of 10-20 mW for 3-5 minutes,
D) on the area of the projection of the spleen from the front - radiation with an average power of 10-20 mW for 3-5 minutes,
E) on the region of the "iliac wings" - radiation with an average power of 15-25 mW for 5-8 min,
E) on the area of the paravertebral zones from the back, along the spine - radiation with an average power of 10-20 mW for 5-10 minutes.
The laser action is carried out sequentially on the indicated areas of the patient's body in one session, and the sequence of irradiation of the sections during the session does not matter.
Infrared laser radiation with a wavelength in the range 700-1000 nm is used for irradiation.
Before the beginning of the course of this laser therapy, 1 to 2 test sessions of laser therapy are performed to determine the nature of the patient's response to laser exposures with exposure time 2 to 3 times lower than indicated above.
Sessions of laser therapy during the 1-st week are conducted daily, one session per day. Then break 1 week and cycle of 6 sessions for one session in two days. Then repeat these cycles with breaks of 5-7 days for 2-4 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient. During the laser therapy course, the patient's immune status is monitored.
Examples of treatment of AIDS patients with a laser method.
1. Patient Irina M., born in 1956, istb.ball. N 1868 (here and in other examples - the city AIDS center, St. Petersburg).
Diagnosis: HIV infection in stage 3B (according to the Pokrovsky classifier), HIV-encephalopathy, candidiasis of the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus, persistent generalized lymphadenopathy, recurrent chronic bronchitis, chronic recurrent herpetic infection, mycosis and onychomycosis of the feet, asthenoneurotic syndrome.
How HIV-infected was detected in 1988, the estimated date of infection in 1987
Until 1992 I felt good. In 1992 and 1993, Has transferred or carried herpes Zoster. Since 1993, increased fatigue, night sweats, dizziness, frequent headaches, fainting, tremor of hands, unsteadiness of gait, lability of mood, sleep disturbance. The so-called chronic fatigue syndrome developed. On a computer tomography in January 1995, signs of HIV-encephalopathy were revealed, and in this connection she was diagnosed with AIDS. The patient was appointed azidothymidine, but after 5 days she stopped taking him because of severe side effects (nausea, loss of appetite).
Since 1993, the patient is an invalid of the III group, and since March 1995 - the II group.
Since October 1995, the course of laser therapy has been started. Improvement of well-being (cessation of dizziness, reduction of weakness, normalization of sleep) was noted after 5 sessions. After the first course of 12 sessions, the immunological status improved almost twice (see table). Simultaneously, the general condition of the patient was continuously improved, and after 2 months she began to ask to be allowed to work.
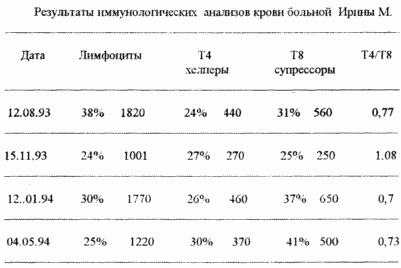 |
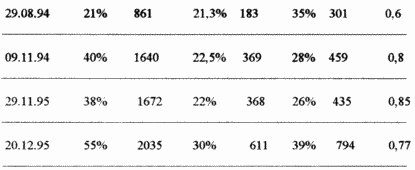 |
2. Patient Olga Ya., 1955, rozhd., The history of the disease N 3997.
Diagnosis: HIV infection in stage 3 AB (according to Pokrovsky's classifier), 10% body weight deficit, persistent generalized lymphadenopathy, chronic recurring herpetic infection, cytomegalovirus infection outside exacerbation.
Concomitant infections: chronic persistent hepatitis B, chronic bronchitis with frequent exacerbations.
HIV infection was detected in 1993, the estimated duration of infection was 1992.
Until November 1995, the patient's condition was stable. During the year she suffered 3-4 times ORZI with subsequent exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Immunological indicators were without deterioration.
Since November 1995, the patient's condition worsened: there was a sharp weakness, sweating at night, fatigue, constantly recurring herpes (Herpes labialis), the immune status indicators dropped sharply (see table).
Since 03.01.96 the course of laser therapy has been started.
After the course of laser therapy, the patient's well-being improved: weakness decreased, sweating disappeared, sleep normalized, immune status indicators improved (see table), the catarrhal phenomena disappeared and the patient returned to an active lifestyle.
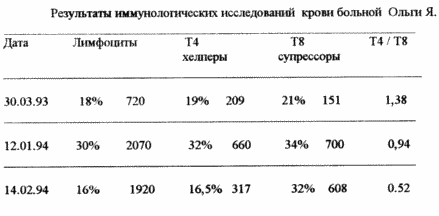 |
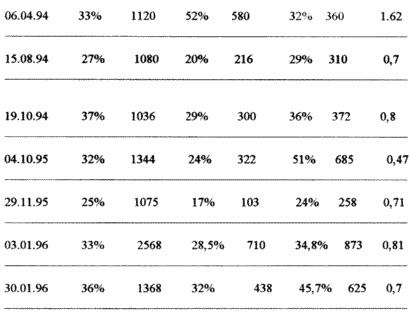 |
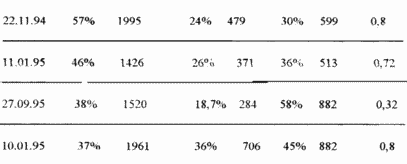
3. Patient Alexander M., 1945. rozhd. East. Disease N 5900.
Diagnosis of HIV infection in stage 3B (Pokrovsky classifier), persistent generalized lymphadenopathy, candidiasis of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal mucosa, catarrhal esophagitis, mycosis of the feet, chronic toxoplasmosis in the latent phase, chronic herpetic infection in the latent phase.
Concomitant diseases: chronic sinusitis, chronic pneumonia, peptic ulcer of the duodenum without exacerbation.
How HIV-infected was detected in May 1994, the estimated duration of infection in 1990
Since 1995 he began to notice increased fatigue, malaise, frequent ARI, exacerbation of sinusitis and pneumonia: the immune status decreased.
Since December 1995, severe weakness, sweating at night, subfebrile temperature, constant dry cough, decreased immune status.
Since January 16, 1996, a course of laser therapy has been conducted.
After three sessions, signs of clinical improvement appeared: the temperature decreased, weakness and sweating decreased. After four sessions, coughing disappeared, nasal breathing improved. By the end of the first course of treatment, the temperature normalized, weakness and sweating disappeared, began to make long country walks, returned with enthusiasm to normal work, immunity parameters improved (see table).
 |
 |
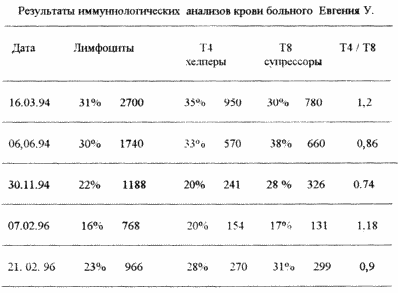
4. Patient Evgeny U., 1961, rozh., Ist. Disease # 4336.
Diagnosis: HIV infection in stage 3B (AIDS), weight loss of more than 10%, pneumocystis pneumonia in November 1995, chronic, frequently recurring herpetic infection, oral candidiasis, mycotic axillary skin lesions, cytomegovirus infection in the latent stage.
Concomitant diseases: syphilis early latent, toxic-allergic dermatitis.
As an HIV-infected person was identified in November 1993, the estimated duration of infection in 1989-1990 At detection the stage of the disease was regarded as 3A (according to Pokrovsky's classifier).
Since March 1994, the disease has rapidly progressed: there was a sharp weakness, sweating, developed a chronic fatigue syndrome, weight loss for 6 months 10 kg, was constantly fever with a swing of temperature 37.6-38.8 ° C, developed pancytopenia.
Since December 1994, he was diagnosed with AIDS. Traditional treatment was performed, but without significant results. In December 1994, developed toxic-allergic dermatitis, which was not amenable to treatment, since November 1995 - pneumocystis pneumonia.
Since April 1995 - disabled group I.
Since December 15, 1995, a course of laser therapy has been appointed. After the first sessions, the patient's itching of the skin decreased and the temperature decreased somewhat. Unfortunately, after four sessions in connection with the departure from Petersburg, the patient interrupted the treatment for 1.5 months. On the resumption of treatment from February 6, the patient's condition was regarded as severe: severe weakness, constant high temperature 38-39 o C, dyspnea at rest to 30 in 1 min, tachycardia up to 110 per 1 min, auscultatory in the lungs, weakened breathing site, extremely low rates Immune status. Categorically refused the proposed hospitalization. Since it was impossible to exclude the relapse of pneumocystis pneumonia, the patient was assigned biseptol in combination with laser therapy. After the first sessions of laser therapy, the patient's condition began to improve: it became easier to breathe, it was better to cough up phlegm, the temperature dropped to subfebrile values, weakness decreased, dry and itchy skin decreased, and felt more cheerful. Immunological indicators significantly improved (see table).
 |
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. LA Kozhemyakin, IG Bondarenko, AA Tyaptin "AIDS: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome". - L .: Knowledge, 1990. - 112 p.
2. E.Bisacca, C.Berger, ASKlainer "Extracorporeal Photopheresis in the Treatment of AIDS-Related Complex" - Annal of Internal Medicine. V. 111, N 4, p. 270-275 (1990).
CLAIM
Laser treatment of HIV-infected patients in the stage of the AIDS-associated complex and in the stage of AIDS, which consists in the fact that the treatment is performed by percutaneous exposure to radiation from an infrared laser with a wavelength of 700-1000 nm to the blood in the ulnar veins and to the following regions of the body: Sternum, area of projection of the liver and spleen from the front, area of the "iliac wings" and the area of the paravertebral zones.
print version
Date of publication 06.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.