| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2150880
![]()
METHOD OF DIAGNOSTICS OF ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE
The name of the inventor: Sumin A.N . ; Galimzyanov DM; Kiniv DN; Gaifulin R.A.
Name of patent holder: State Scientific and Clinical Center for Miners' Health Protection
Address for correspondence: 654080, Kemerovo Region, Novokuznetsk, Stroiteley 5 Avenue, GIDUV, Patent Department
Date of commencement of the patent: 1997.09.02
The invention relates to medicine, namely cardiology. The velocities of the drain diastolic flow (G) during the load at the closure point of the mitral valve flaps and at a distance of 3 cm towards the top of the left ventricle (G1) are measured. Calculate the relations G1 / G. With the obtained values of this ratio less than 0.8, ischemic heart disease is diagnosed. The method allows for more accurate diagnosis of early stages of ischemic disease, accompanied by predominant violations of the diastolic function of the heart, without changes in regional violations of contractility and electrocardiographic signs of ischemia.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely cardiology.
Early diagnosis of coronary heart disease is important in preventing the development of heart failure and invalidization of cardiac patients. In this regard, it remains urgent to develop and implement in a wide clinical practice new highly informative, but at the same time relatively affordable and inexpensive non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease, in the early stages of its development. The use of already available diagnostic equipment for these purposes allows conducting diagnostics even in outpatient settings.
There is a known method for diagnosing coronary heart disease by evaluating ECG changes in the course of accelerated transesophageal electrical stimulation of the atria (Kozlov SG, Mironova I.Yu., Lyakishev AA // Ter.arch.- 1991.- N1 .- S. 108-111).
The disadvantage of the method is the impossibility of using ECG at initial changes and the relatively low frequency of ischemic ECG changes in comparison with echocardiographic methods.
A method for diagnosing coronary heart disease is known by echocardiographic evaluation of the regional systolic function of the left ventricular myocardium in stress tests (Chapman PO, Doule, TR, Troup PJ et al., Circulation.-1984.- Vol. 70.- P. 445- 450).
The disadvantage of the method is the subjective nature of the evaluation of violations of myocardial contractility of the left ventricle, the dependence on the qualification of the researcher and the inability to identify early stages of ischemia, characterized by violations of active myocardial relaxation.
A Doppler method for estimating the diastolic function of the left ventricle is known from the ratio of the rates of early and late transmittal fluxes (Iliceto S., Amico A., Marangelli V., D'Ambrosio G., Rizzon P. Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of the effector of atrial pacing-incluced Ischemia on left ventricular filling in patients with coronary disease (J Am Coil Cardiol 1988; 11: 953-61).
The disadvantage is the impossibility of assessing diastolic function directly during the test due to the fusion of Doppler spectra of early diastolic filling and atrial systole as a result of tachycardia (at a heart rate of over 90 beats per minute). Therefore, the evaluation of the parameters of the diastolic function is performed in the early post-stimulation period, which causes certain difficulties in the registration of parameters, requires mandatory termination of the study and affects the informative nature of the sample. Evaluation of the parameters of the diastolic function directly with the load in this case makes it possible to increase the sensitivity of the method.
The closest to the claimed method is the method for evaluating the diastolic function using a new marker of diastolic function - the velocity of the early diastolic filling wave in the left ventricular cavity at rest, since it is known that in patients with diastolic dysfunction of the myocardium the progressive spread of the early diastolic filling wave (Yamamoto K., Masuyama T., Tanouchi J., et al., Intraventricular dispersion of early diastolic filling: A new marker of left ventricular disfunction, Am Heart J 1995; 129: 291-9) . However, the use of this method with a loading sample is not possible due to the fusion of Doppler spectra of early and late diastolic filling under load.
It is an object of the present invention to conduct a more accurate diagnosis of early stages of ischemic disease accompanied by predominant disturbances in the diastolic function of the heart without altering regional contractility disorders and electrocardiographic features of ischemia. The task is accomplished by measuring the velocity of the discharge diastolic flow during the load at the point of closure of the mitral valve flaps and at a distance of 3 cm towards the top of the left ventricle, calculating the Gl / G ratio, where Gl is the drain flow rate measured at a distance of 3 cm from the point Closing of the valves of the mitral valve, towards the top of the left ventricle; G - drainage flow rate measured at the closure point of the mitral valve flaps, and with the values <0.8, ischemic heart disease is diagnosed.
The essence of the proposed method is to measure the spread velocity of the discharge diastolic flow in the left ventricular cavity with accelerated transesophageal atrial stimulation to assess the diastolic function in patients with coronary heart disease and use this parameter as an early marker of myocardial ischemia. With an increase in the heart rate, the need for cardiac muscle in oxygen increases, which, under conditions of existing coronary insufficiency, leads to its ischemia. Myocardial ischemia leads to a disruption in the energy supply of intracellular calcium ion exchange mechanisms, manifested by delayed relaxation and increased diastolic stiffness of the left ventricular wall. Under these conditions, the end-diastolic pressure in the left ventricle increases and the pressure gradient decreases, which leads to a drop in the flow rate of the diastolic filling.
The method is carried out as follows. Transesophageal electrical stimulation of the atria (CPPS) is performed in combination with Doppler echocardiography on the ACUSON 128XP / 10s ultrasound system (USA) according to a standard procedure. The CPPP is carried out with the help of the probe-electrode PEDSP-2 and the pacemaker ECSC-02. The initial stimulation rate is 100 cpm for 2 min and every 2 min is increased by 20 beats / min. Criteria for discontinuation of the sample are: achievement of a heart rate of 160 per min, an attack of angina pectoris, the presence of an obvious ischemic reaction according to ECG data. Evaluation of the diastolic function of the left ventricle is performed in the pulsed Doppler echocardiography with a frequency of 2.5 MHz from the apical access. The control volume is located in the cavity of the left ventricle at the level of the tips of the mitral valve flaps so that the amplitude of the diastolic flow is maximal, then moves deeper into the left ventricle toward its apex by 3 cm. The exact orientation of the ultrasound beam is maximally parallel to the direction of the transmittal blood flow, Color Doppler mapping. The study is conducted first at rest and at the 2nd minute of each stage of stimulation. An ECG in 12 leads is recorded during the whole sample on the CARDIOVIT AT-6 electrocardiograph (Schiller, Sweden). Common electrocardiographic criteria for myocardial ischemia are used. The following Doppler parameters G, Gl are the maximum velocities of the drain diastolic flow at the tips of the mitral valve flaps, and at a distance of 3 cm towards the top of the left ventricle, respectively; Their ratio Gl / G is calculated. This ratio judges the presence of ischemic disease in the absence of such data from the results of standard stress tests: the ratio <0.8 indicates the presence of ischemic disease, the ratio> 0.8 - the absence of ischemic disease.
We analyzed the results of tests in 20 patients. 13 patients had atypical pain syndrome in the chest and negative stress tests according to veloergometry and stress ECHO. In 7 patients there was a typical clinic of ischemic heart disease, positive results of VEM and stress ECHO. Three patients from this group later underwent coronary angiography, all of them showed a narrowing of the coronary arteries more than 75% of at least one coronary artery. The results of the comparison of the Doppler parameters of the intraventricular flow proposed by us are presented in the table.
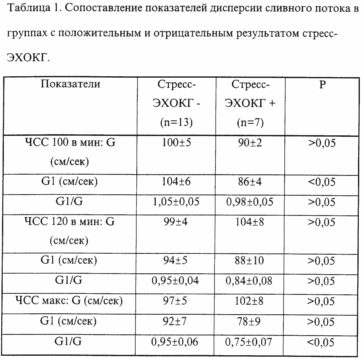 |
As can be seen from the data presented, in patients without ischemic reactions during atrial stimulation, the ratio of the discharge flow rate at the depth of the left ventricle to the draining flow rate of the mitral flow moderately decreases with an increase in the rate of stimulation, without decreasing below 0.95 at the maximum stimulation frequency. Patients with coronary heart disease with a positive echocardiographic test had lower rates of this ratio at all stages, with a maximum load during the onset of myocardial ischemia, this ratio became below 0.8 and became statistically significant compared to the control group. Thus, a decrease in the ratio below 0.8 during the atrial stimulation test indicates the occurrence of myocardial ischemia, accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the active relaxation of the ischemic myocardium and a corresponding decrease in the pressure gradient in the early diastole phase, which was manifested by a decrease in the flow rate in the left ventricular cavity. The method we proposed for assessing diastolic function directly during the test helps to better diagnose early manifestations of myocardial ischemia in patients with coronary heart disease during a noninvasive stress test with atrial stimulation. |
Example 1 . The patient Korotkov AG, 56 years old, was on examination and treatment in the cardiology department from 26.05.97 to 09.06.97 with the diagnosis: IHD. Stenocardia of tension 3 FC. Hypertensive disease of the 2nd stage, compensation of NK-1. At admission the patient complained of burning pains behind the breastbone with a duration of 3-4 minutes, without irradiation, arising during fast walking, stopping themselves. He was hospitalized in accordance with the planned procedure for examination and treatment in the cardiac department of the SSCC OZSH. Upon admission, treatment is prescribed: enap, aspirin, atenolol, tiklid. The electrocardiogram of rest of ischemic changes was not recorded. At an echocardiographic research in rest of disturbances of contractile function of a myocardium of a left ventricle it is not revealed. According to veloergometry: tolerance to physical activity is 75 W (average). The criterion for discontinuation of the test is painless depression of the ST segment in the apex-lateral region. The sample is positive. On coronaventricularography, the patient was diagnosed with a three-vessel lesion of the coronary arteries. On 10.06.97 the patient underwent Doppler echocardiography study in combination with CHPP. At the first stage of stimulation (100 cpm) the following values were obtained: G = 87 cm / s, Gl = 73 cm / s, Gl / G = 0.84. At the second stage of stimulation (120 imp / min.) - G - 91 cm / s, Gl - 59 cm / s, Gl / G - 0.65. At the third stage of stimulation (140 imp / min), the indices were G = 92 cm / s, Gl = 63 cm / s, Gl / G - 0.68. In the post-stimulation period after the 2nd stage, ST depression in V3-V6 leads> 2 mm was recorded on the ECG. Decrease in the ratio Gl / G <0,8 at the 2- and 3-rd stages of the load indicates the presence of a patient with ischemic heart disease.
Example 2 . Patient Putintsev Yu.B. 46 years old, was on an examination in the cardiac department of the SSCC OLSh from 05.01.97 to 16.01.97 with the aim of excluding coronary heart disease. Upon admission, the patient complained of pains in the chest compressive nature, arising out of connection with physical exertion, stopping alone or after taking vali, nitroglycerin, after 10-20 minutes. Duration of the disease is about 1 month. According to the survey: on the electrocardiogram of rest - diffuse changes of a metabolic nature. In echocardiography, no disturbance of systolic and diastolic functions was detected in rest. According to the veloergometric test, latent coronary insufficiency was not revealed (TFN -125 W. CAT - muscle fatigue). On January 15, 1997, the patient underwent Doppler echocardiography study in conjunction with the CHPP. At the first stage of stimulation (100 imp / min) the following parameters were recorded: G - 82 cm / s, Gl - 90 cm / s, Gl / G - 1,1. At the second stage of stimulation (120 imp / min) the indices were: G -92 cm / s, Gl - 97 cm / s, Gl / G - 1.05. At the third stage of stimulation (140 imp / min) the following indices were noted: G - 95 cm / s, Gl - 95 cm / s, Gl / G - 1.0. The electrocardiogram was not recorded at all stages of ischemic reactions. The presence of the ratio Gl / G> 0.8 at all stages of the load indicates that there is no coronary heart disease in this patient. The patient was discharged with a diagnosis: neurocirculatory dystonia of moderate severity according to the normotensive type with cardialgic syndrome, in the phase of exacerbation.
Thus, the proposed method of carrying out stress-Doppler echocardiography with an estimate of the rate of intraventricular spreading of the discharge diastolic flow makes it possible to assess the diastolic function directly at the peak of the load, which increases the sensitivity of the method and facilitates the detection of earlier stages of myocardial ischemia.
CLAIM
A method for diagnosing coronary heart disease based on measuring the velocity of diastolic flow in the left ventricular cavity, characterized in that the velocity of the discharge diastolic flow is measured during the load at the point of closure of the mitral valve flaps and at a distance of 3 cm towards the apex of the left ventricle, Ratio G1 / G, where: G1 - drainage flow rate, measured at a distance of 3 cm from the valves of the mitral valve towards the top of the left ventricle; G - the drainage flow rate measured at the closure point of the mitral valve flaps, and at a value of <0.8, the presence of coronary heart disease is diagnosed.
print version
Date of publication 05.04.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.