| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2254846
![]()
METHOD OF REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
The name of the inventor: Prokofiev A.B. (RU); Mironchev O.V. (RU); Tinkov A.N. (RU); Makshantsev SS (RU); Durmanov I.P. (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Limited Liability Company "Volga-Ural Research and Design Institute of Oil and Gas"
Address for correspondence: 460000, Orenburg, ul. Pushkinskaya, 20, LLC "VolgoUralNIPIgaz", head of the patent department of Pat. BA Dronov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.07.22
The invention relates to medicine, namely cardiology. Simultaneously with therapeutic exercise, a course of adaptation to periodic barocameral hypoxia from 22 three-hour sessions in a low-pressure pressure chamber is used. The first sessions are carried out with a gradual increase in altitude, starting from 1000 m, adding 500 m daily to reach a maximum "altitude" of 3,500 m (460 mm Hg) at a speed of "ascent" and "descent" of 2-3 m / s. The method allows to increase the capacity of the coronary bed, to increase coronary blood flow, to increase efficiency, to reduce the number of heart rhythm disturbances.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely cardiology, and can be used for the rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction during scarring.
It is known that myocardial infarction (MI) is one of the main causes of death, disability and temporary disability of the population of Russia. Given the effective implementation of rehabilitation measures, these indicators are significantly reduced. In connection with this, improving the quality of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction is one of the main problems of modern cardiology.
It is also known that the treatment of patients with myocardial infarction includes a traditional complex of pharmacotherapy, physical and psychological rehabilitation (see, for example, RF patent No. 2198674, IPC 7A 61 K 35/78, 33/00, A 61 P 9/10, 2003).
At present, rehabilitation programs for patients with myocardial infarction have been formed (see Zakharov VN et al. Recommendations for physical rehabilitation of patients who underwent myocardial infarction (inpatient-sanatorium-polyclinic): Methodological recommendations / MH RSFSR, 4th Main Directorate for MH - M., 1986, - 47. Nikolaeva LF, Aronov DM Rehabilitation of patients with ischemic heart disease (Moscow: Meditsina, 1988, 287 pp.) Gorbachenkov AA, Pozdnyakov Yu.M. Physical training in cardiological practice (Moscow: Meditsina, 1996, 16 pp.).
The basis of these and all existing rehabilitation programs for today are long physical training in the form of curative gymnastics according to the generally accepted physical activity regimes. This method is the closest to the claimed method for its intended use and adopted as a prototype.
The disadvantage of the known method of treatment is that a number of patients can not achieve the desired effect, using only physical training, and even with a good effect, the intake of medications is necessary in full.
The claimed method solves the problem of increasing the effectiveness of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction.
To solve this problem, the course of adaptation to periodic hyperbaric hypoxia (APPG) is applied in the claimed method for the rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction during the period of cicatrization simultaneously with therapeutic physical training.
Adaptation to periodic hyperbaric hypoxia (APPG) is used to treat a number of diseases, such as bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis (Brimkulov NN and Mirrahimov MM High-altitude climatotherapy as a non-drug treatment for patients with bronchial asthma / Vysokogornaya Climatotherapy of internal diseases: Materials of the All-Union Seminar, Bishkek, 1991, p.18-21), blood diseases (Mirrahimov MM Treatment of Internal Diseases in the Mountain Climate, Leningrad, 1977; 207 pp.), Obstetrician-gynecological patients With skin diseases and other pathological conditions (Strelkov RB Normobaric hypoxia / Methodological recommendations, Ministry of Health of Russia, 1994, 14s, Meerzon FZ, etc. Method of adaptation to periodic hypobaric hypoxia in therapy and prevention: Methodological recommendations, MZ RSFSR, Moscow, 1989, 14 pp.).
However, no attempts have yet been made to evaluate the possibility of using APPG in a complex of rehabilitation measures in patients with myocardial infarction.
The novelty of the claimed method is that for the first time it is proposed to apply for the rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction during the period of scarring the course of adaptation to periodic barocameral hypoxia in combination with physiotherapy exercises.
The course of adaptation to periodic barocameral hypoxia consists of 22 three-hour sessions at a "height" of 3,500 m (460 mm Hg), conducted daily in a pressure chamber of reduced pressure, for example, of the Ural-1 type. The first sessions are conducted with a gradual increase in height from 1000 m and further, adding 500 m daily, until reaching the maximum "height" (3,500 m). The speed of "lifting" and "descent" was 2-3 m / s.
The beginning of adaptation from a height of 1000 m is due to the fact that this level of ascent is a threshold for untrained patients, the initial elimination of which at their final height is associated with the development of negative reactions. At the beginning of the rise within the given height, no adverse reactions were observed. The choice of a final height of 3,500 m is due to the fact that it achieves a clinical effect, in addition, its excess can cause a number of adverse reactions in the form of fatigue, increased drowsiness, a sense of discomfort. The time of finding a patient at a maximum "height" of 2 hours is optimal for a given nosology.
The speed of "lifting" and "descent" of 2-3 m / s allows to prevent undesirable phenomena in patients with myocardial infarction during the period of entering the therapeutic "height". The duration of the course is 22 sessions, tk. From the data obtained, the shorter course duration does not give the maximum effect, and the larger one does not increase the effect.
The technical result achieved in the implementation of the invention is that a new method for the rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction allows, by increasing the capacity of the coronary bed, increasing the coronary blood flow, increasing the power of the antioxidant systems of the body, increasing the density of M-cholinergic receptors in the heart, and economizing the use of oxygen by tissues to improve Clinical results of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction, namely, to increase efficiency, reduce the number of cardiac arrhythmias, pain and painless episodes of myocardial ischemia, and increase myocardial contractility of the left ventricle.
We examined 56 men with myocardial infarction who were divided into 2 equal groups. The first group was a control group, the average age of patients was 46.8 + 1.24 years. Patients of this group underwent a course of physical rehabilitation according to the prototype method (Methodological recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the RSFSR for the physical rehabilitation of patients who underwent myocardial infarction, 1986). The second group - experienced patients included, whose average age was 48.1 + 0.76 years. Patients of this group used a combination of curative physical education with a course of adaptation to periodic barocamera hypoxia according to the claimed method.
All patients received nitrates, beta-blockers, calcium antagonists, ACE inhibitors and antiaggregants in individually selected doses, taking into account contraindications.
Rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction using the claimed method was carried out on the basis of a written permission of the Republican Problem Commission "Circulatory failure and heart rhythm failure" about the advisability of using hypoxic therapy in patients with myocardial infarction N 23-3 / 61 from 03.04.01.
The monitoring of the patients' condition was carried out during the entire rehabilitation period. Prior to the start of the rehabilitation course and, accordingly, after its completion, an in-depth medical examination including a veloergometric test (VEMP), ECG monitoring by the Holter method, echocardiography (ECHO) was carried out.
During the course of adaptation to periodic hyperbaric chamber hypoxia, the onset of positive changes in the state of health of patients with myocardial infarction was manifested no earlier than 7 sessions ("height" of 3,500 meters), which became more pronounced as the timing of adaptation increased. At the same time, a number of patients had a later clinical effect - from the 16-18th session, and in a part of the patients (11%) it was fixed only after the end of the course. Thus, after completion of the 22nd session, the clinical effect of the treatment was observed in 89% of the patients.
The clinical efficacy of the claimed method of rehabilitation was determined by the reduction or disappearance of certain complaints due to coronary heart disease in the examinees, and by the reduction of symptoms that were nonspecific.
These effects have reduced the number of antianginal drugs used by patients as maintenance therapy (long-acting nitrates, beta-blockers, calcium antagonists). Almost all patients recorded a faster onset of analgesic effect with nitroglycerin, and 84% of patients clearly noted a decrease in the intensity of the pain syndrome. In connection with the foregoing, almost all patients began to perform a greater amount of physical exertion without the retrosternal pains and other equivalents of angina pectoris.
The established reduction in the number of cardiac disruptions in most patients was confirmed by electrocardiography, but in a number of cases (14%) the subjective perception of the extrasystoles became less significant for the examined patients or, if they were present, was not felt by the patients.
In patients with myocardial infarction under the influence of APPG, an increase in exercise tolerance occurs, expressed as a reliable increase in maximum power at a load height of 46% and an increase of 37% from the initial values of the bicycle ergometric test time, accompanied by an increase in the double product 44%. It is noteworthy that with the increase in the amount of work performed, the recovery time after the cessation of pedaling was not significantly different from the initial one. These indicators in the control group were 27%, 26% and 24%, respectively, which is significantly lower than the increase in physical performance in persons of the experimental group who did not undergo hypoxic training.
When carrying out a pair correlation analysis between the dependent indicators according to the bicycle ergometric test, some regularities were revealed. It was found that the lower the initial tolerance to physical activity in the patients studied, the higher the increase in indicators characterizing the level of physical working capacity.
As a result, the data obtained make it possible to conclude that APBG allows to increase tolerance to physical activity to a greater extent and, thus, to increase the effectiveness of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction.
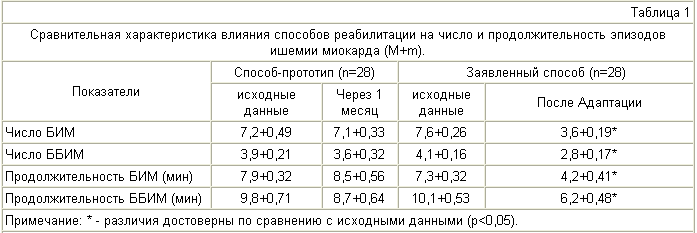
When conducting daily ECG monitoring, it was found that under the influence of APPG in MI patients, the number of pain (BIM) and by 32% the number of painless episodes of ischemia (BBM) was more than halved. It is important to emphasize that the number of ischemic episodes in the night and early morning hours has been particularly reduced. It was found that hypoxic training contributed not only to a reduction in the number, but also to a decrease in the duration of both BIM and BIMM (by 42% and 47%, respectively). At the same time, there was no statistically significant dynamics of the studied parameters during the daily ECG monitoring in the control group.
Table 1 gives data on the effect of APPG on the number and duration of BIM and BWM.
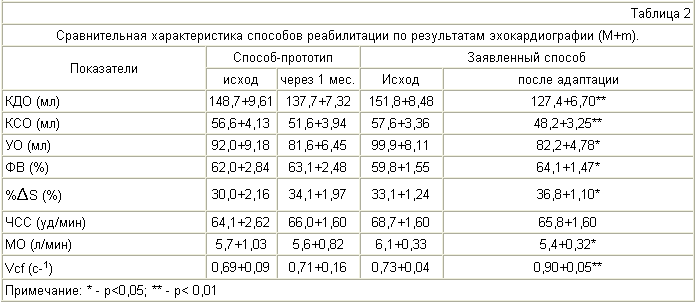
Table 2 shows that immediately after the impact of the course of hypobaric hypoxia in patients with MI, the end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes of the left ventricle significantly decreased by 8% and 11%, respectively. This largely determined the statistically significant increase in the ejection fraction and the percentage of shortening of the anterior-posterior size of the left ventricular myocardium to the systole, indicating an increase in the contractile function of the left ventricular myocardium. Despite an increase in the striking volume of the left ventricle by 18%, the minute volume of blood, on the contrary, significantly decreased from 6.1 to 5.4 l / min, which indirectly indicates a decrease in the oxygen and metabolic demands of peripheral tissues.
From the same table it can be seen that in the control group for the same period of time there were no statistically significant changes in the studied indicators.
Thus, the authors found that the use of therapeutic physical training in combination with adaptation to periodic barocamera hypoxia significantly improves the effectiveness of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction during scarring.
The method is carried out as follows
For the rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction in the period of scarring, they are prescribed a course of adaptation to periodic barocameral hypoxia in combination with physiotherapy exercises.
The amount of physical activity during physical training of patients with myocardial infarction is determined depending on the functional class of patients (I-IV functional class).
APBG is conducted with the help of the first domestic medical vacuum unit - the Ural-1 pressure chamber, installed on the basis of the Orenburg Regional Clinical Hospital No. 2, built on the basis of a medical and technical assignment jointly developed by the Institute of General Pathology and Pathological Physiology of the USSR Academy of Medical Sciences and the Orenburg Medical Institute in NGO Cryogenmash (Meerson FZ, Tverdokhlib VP, Rybnikov VV et al. Vacuum medical installation Ural-1 / Proceedings of VNIIIMT, 1987, issue 3, p.26-28).
The pressure chamber consists of a housing, vacuum and air conditioning systems, located in a separate room and providing a metered dilution of air in the pressure chamber, and control systems. The technical parameters of the pressure chamber are as follows: the volume of 134 cubic meters. M, hull diameter 3200 mm, number of seats 30, working pressure when conducting a session in a pressure chamber up to 6.1 × 104 Pa (460 mm Hg), ventilation air flow per person 15 m3 / h, installed capacity 70 KW, power consumption 45 kW, water consumption 4.2 m3 / h. The mass of the pressure chamber is 25 000 kg, the length of the case is 17 000 mm, the material is stainless steel 12x18NIOТ.
To provide comfortable conditions for the patients in the pressure chamber, 27 aircraft seats with adjustable backrest inclination and 5 medical couches are installed.
The case of the treatment compartment is equipped on both sides with illuminators 500 mm in diameter. At the ends of the altitude chamber, and between the treatment compartment and the lock, vacuum doors are installed that open outward. The pressure chamber is equipped with a gateway, which allows, if necessary, to enter the pressure chamber during the session or to leave it without disturbing the patients. In the airlock there are two toilet rooms equipped with running water and sewerage.
The body of the pressure chamber is equipped with two safety valves, which prevent a decrease in pressure below 400 mm Hg. Vacuuming and air conditioning systems are provided by BBN-12 pumps and UKV-2 air conditioners, a stainless steel piping system, shut-off and control valves and instrumentation.
The systems provide a speed of "lifting" and "descent" from 2 to 10 m / s. Management of them is manual, carried out from the operator's panel. The control system consists of the operator's console, the doctor's console inside the pressure chamber, the control cabinets of the pumps, the power supply and the relay.
The oxygen system consists of cylinders with gaseous compressed oxygen, located outside the pressure chamber, stop valves, oxygen pressure gauges, reducers, pipelines and a complex oxygen device for collective use KP / 56 with oxygen masks inside the pressure chamber.
The APGE course consists of 22 three-hour sessions at a "height" of 3,500 m (460 mm Hg), conducted daily. The first sessions are carried out with a gradual increase in height from 1000 m and on, adding 500 m every day to reach the maximum "height" (3,500 m). The speed of "lifting" and "descent" was 2-3 m / s.
Examples of specific implementation of the claimed method
Example 1
Patient M., 36 years old, enrolled for the course of APHG with the diagnosis of IHD, Q-myocardial infarction of the anterolateral wall of the left ventricle, the period of scarring, stress angina, 3 FC, frequent ventricular extrasystole, CH 2 FC.
Prior to the rehabilitation, he noted chest pains, dyspnea when performing insignificant physical exertion (walking on level ground for 200 m), a feeling of irregular heart and heartbeats, amplifying and under load. The patient received nitrates, aspirin and beta-blockers in the medium-therapeutic doses.
During the adaptation course, the exit to the "plateau" was carried well, which was confirmed both subjectively and with the active monitoring monitoring data for the patient during the stay in the pressure chamber. Starting with the 10th session, I began to notice some improvement in the condition, expressed in a decrease in heart disruptions, shortness of breath, normalization of night sleep. After the completion of the adaptation course, exercise tolerance increased significantly from 50 to 125 W, based on the results of 24-hour ECG monitoring, ventricular extrasystoles became rare, and the total duration of episodes of myocardial ischemia decreased by half. These effects have reduced the number of antianginal drugs used by patients as maintenance therapy.
Example 2
Patient A., 45 years old, entered the course of APBG with diagnosis of ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction without Q posterior wall of the left ventricle, scarring period, stress angina, 2 FC, supraventricular extrasystole, sinus bradycardia, transient sinoatrial blockade of 2nd degree, CH 1 FC.
Prior to the course of adaptation, he noted pressing pains behind the breastbone with physical activity (rise to the 3rd floor), a feeling of sinking heart, weakness, malaise. I took nitrates, antiaggregants, calcium antagonists.
The course of adaptation has gone well. Starting with the 14th session, he noted a decrease in heart disruptions, a decrease in intensity and duration of pain.
In the examination after the completion of the rehabilitation course, exercise tolerance by the results of VEMP increased from 75 to 125 W, the number of extrasystoles decreased, and there were no episodes of both pain and painless ischemia, and periods of sinoatrial block 2 degree with ECG monitoring, which allowed to cancel Nitrates and reduce the dose of calcium antagonists by 1.5 times.
Example 3
Patient P., 52 years old, entered the course of APHG with diagnosis of ischemic heart disease, repeated myocardial infarction without Q anterolateral wall of the left ventricle with grip, scarring period, stress angina, 3 FC, paired ventricular extrasystoles, CH 2 FC.
Prior to the course, APBG noted typical angina pectoris when walking 150-200 meters along an even terrain, shortness of breath both during walking and at rest in the morning, which required the use of 2-3 tablets of nitroglycerin.
The yield to the medical "height" was satisfactory. Attacks of angina did not arise, the parameters of monitoring monitoring in the pressure chamber (BP, heart rate, ECG) were stable. Improvement in the state began to be noted from the 17th session, which was expressed in the reduction of pain and increase in the level of the transferred physical load.
After the completion of the rehabilitation course, there was an increase in exercise tolerance from 50 to 100 W, a decrease in the number of ventricular extrasystoles and disappearance of paired extrasystoles, a decrease in the number and duration of episodes of myocardial ischemia, and an increase in myocardial contractility according to the results of echocardiography.
Thus, the proposed method allows to improve the clinical results of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction, namely, to increase efficiency, to reduce the number of cardiac arrhythmias, pain and painless episodes of myocardial ischemia, and to increase myocardial contractility of the left ventricle. In this regard, the proposed method of treatment can be recommended for improving the effectiveness of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction.
CLAIM
The method of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction during scarring, including physical training, characterized by the fact that, simultaneously with therapeutic exercise, a course of adaptation to periodic barocameral hypoxia is used out of 22 three-hour sessions in a low-pressure pressure chamber, the first sessions being carried out with a gradual increase in altitude starting from 1000 m , Adding daily 500 m until a maximum "altitude" of 3,500 m (460 mm Hg) at a speed of "ascent" and "descent" of 2-3 m / s.
print version
Date of publication 06.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.