| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2143930
![]()
METHOD OF EXPOSURE TO THE PSYCHOEMOTICAL STATE OF THE PERSON
AND DEVICE FOR ITS IMPLEMENTATION
The name of the inventor: Mikhail Y. Shmelev
The name of the patent holder: Mikhail Y. Shmelev
Address for correspondence: 197342, St. Petersburg, PO Box 168, Sandigursky O.L.
Date of commencement of the patent: 1998.09.01
The invention relates to medicine and can be used when the patient enters a trance state. The patient is presented with a visual dynamic image in the form of a collection of separate light sources. Change the brightness of the image by alternately turning on and off the light sources. The patient's attention is fixed on a stationary object between the patient and the set of light sources. A device is used to implement the method. The device is mounted from the light stimulus display unit in the form of a screen with the placement of separate light sources, a control unit and a power source. An element is attached to the screen to fix the person's attention. The method makes it possible to have an effective effect on the psychoemotional state of a person. The device is simple in design and does not require the constant presence of medical personnel.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of medicine and can be used to treat psychosomatic and somatic disorders of the body, in particular stress, depression, affective disorders, etc., but also to improve performance.
At present, non-pharmacological methods of treating various pathological processes are widely used.
There are known methods for regulating a person's psycho-physiological state, including presentation to the patient of visual images that vary with time, see, for example, the Russian Federation patent No. 2012364, cl. A 61 M 21/00 of 19.11.93. When this method is implemented, the patient is placed in the prone position. After its adaptation for 15-20 minutes, thermography is carried out, and the resulting thermogram is outputted to one part of the display screen; The reference thermogram of a healthy person is output to the second part of the screen. The screen is in the doctor's field of vision. Simultaneously with the recording of thermograms, the patient is videotaped. The image is displayed on the second screen, which is located above the patient at a clear vision distance. The video image is presented to the patient, after which the suggestive effect is performed.
The disadvantage of this method is the need for the availability of complex and expensive equipment, as well as the constant presence of a physician who has a suggestive effect. The effectiveness of this method is small, since for its implementation the patient must "get out of his body" and "unite with the visible image." This can not be done by every patient, especially since there are no criteria indicating that a "withdrawal from the body" has occurred.
A method of regulating a person's psychophysiological state is known, including presentation to the patient of a visual dynamic image, the brightness of which varies in proportion to loudness of sound, see, for example, the patent of the Russian Federation No. 2,033,818 on cells. A 61 M 21/00. This method, adopted as the prototype of the present invention, is implemented as follows.
They make a selection of musical compositions, each of which models a certain unchangeable emotional state with the help of means of artistic expressiveness. The classification of musical compositions is carried out by experts to assess the emotional states caused by each composition. The data submitted by the expert group is averaged and reduced to a user-friendly table containing the names of the musical compositions and the corresponding values of the numerical parameters obtained in the classification procedure and describing a wide range of possible psycho-emotional states of a person. When assigning musical compositions, the actual condition of the patient is taken into account, for which the patient is invited to conduct a self-assessment of his psycho-emotional state. With this in mind, the music composition closest to the diagnosed condition is selected and presented to the patient. Simultaneously with the musical composition, the patient is presented with a visual dynamic image simulating changes in the sound image in time. The change in the volume of the sound corresponds to a change in the brightness of the visual image. The method is implemented with the help of a software and hardware system based on a personal computer.
The disadvantage of the prototype method is the fact that it is based on subjective assessments of experts regarding the emotional impact of a music piece, as well as on the patient's assessments of his own condition. The effectiveness of the method, given the foregoing, is low. The method, in addition, requires for its implementation quite complex and expensive software and hardware, attracting a large number of highly qualified personnel, in particular experts.
It is an object of the present invention to increase the effectiveness of the method by eliminating subjective assessments of the means of influencing the patient, and the need for the constant presence and interaction with the patient of the therapist physician; In addition, the task is to simplify and reduce the cost of implementing the method.
According to the invention, this object is achieved due to the fact that in a method of regulating a person's psychophysiological state, including presentation to the patient of a visual dynamic image with varying brightness, the patient is presented with a visual dynamic image in the form of a set of separate alternating and switching light sources, the patient's attention being fixed on the subject , Immobile located between the patient and the set of light sources; After the patient starts to perceive a set of separate alternately switched on and off light sources as a single luminous field with unchanged brightness, the session continues for 10-60 minutes.
The Applicant has not identified sources containing information on technical solutions identical to the present invention, which makes it possible to conclude that it meets the criterion of "novelty".
The implementation of the distinctive features of the invention makes it possible to achieve important new properties of the object, which consist in the complete elimination of subjective assessments both by the personnel carrying out the method in relation to the images presented to the patient and by the patient with respect to his own psychophysiological state.
The applicant is not aware of any publications that contain information about the effect of the distinctive features of the invention on the technical result achieved. In this regard, according to the applicant, it can be concluded that the claimed technical solution meets the "inventive step" criterion.
The method is carried out as follows. The patient is laid on the couch. At a distance of 60-70 cm from the patient's head place a set of individual light bulbs. In a particular example, electric bulbs with a power of 0.5 W in the amount of 400 pieces were used. The combination of bulbs creates a single visual dynamic image, the brightness of which is randomly changed due to the alternate switching on and off of individual bulbs. Between the set of electric bulbs and the patient, approximately in the middle, place the object, in a specific example, a glass ball with a diameter of 5 mm. On this subject, the patient's attention is fixed. After 1-5 minutes the patient starts to perceive a set of separate alternately switched and switched off electric bulbs as a single luminous field with an unchanging brightness. After this, the session lasts for 10-60 minutes, depending on the patient's condition.
The proposed method causes the patient to have a trance condition. At the same time, excitation is removed, and the brain passes into a state of rest (calm response of the cortex). The maximum number of muscle groups is relaxed, a profound effect on the course of physiological and pathological processes in the body.
The proposed method can be realized, in particular, by means of a second invention, an apparatus for influencing a person's psychophysiological state.
A device is known for implementing a method for correcting a person's psycho-physiological state, comprising an actuator, a time-sequence generating unit for control signals, a memory unit, a random exponential pulse generation unit, an exponential pulse generator control unit, a converter, a comparison element, a reference signal unit and a mode selection unit Device. The fan is used as an actuating element, see Patent of the Russian Federation No. 42028081 for class A 61 B 5/16 of 14.10.92.
This device allows to improve the coordination of the human-machine interface, raises the level of human comfort in human-machine environment. However, this device can not be used with sufficient degree of efficiency for therapeutic purposes.
The device for effecting a person's psychophysiological condition, including a light stimulus display unit, a control unit, a shaping unit, a physiological sensor unit, a registration unit, is known. See Russian Patent No. 2046598, class A61B 5/16 of September 23, 1987.
This device is adopted as a prototype of the present invention. With its help, the person's psycho-physiological state is influenced, mainly with a diagnostic purpose or with professional selection. The use of the device with therapeutic purposes is slightly effective; In addition, the device is quite difficult both in terms of design and management, when the device is in operation, the constant presence of the operator is necessary.
The invention is based on the solution of a simple device design problem, which would provide an effective therapeutic effect on a person's psychophysiological condition.
According to the invention, this object is achieved due to the fact that in the device for influencing a person's psychophysiological state, including a light stimulation display unit provided with a control unit, and a power source, the light stimulus display unit is a screen on which separate light sources are placed, Connected to the power supply via controllable contacts, alternately closing and opening of which is carried out by the control unit, while an element for fixing the person's attention, which is located between the screen and the person, is connected to the screen by means of communication; Light sources are grouped together, and in each group they are connected in parallel; The screen is provided with a light diffuser, for example a frosted glass; The screen is equipped with a tripod and is interfaced with it by means of a mechanism with three degrees of freedom.
The Applicant does not know of any devices for carrying out psychophysiological effects on a person's condition identical to the present invention. This allows us to conclude that it corresponds to the criterion of "novelty".
The applicant did not identify any sources of information that would contain information about the effect of the distinctive features of the invention on the technical result achieved. The device has an extremely simple, reliable design, it is not difficult to operate and does not require the constant presence of medical personnel. At the same time, despite the simplicity, the device provides a pronounced therapeutic effect in the treatment of a wide range of psychosomatic and somatic pathologies. These considerations confirm, in the opinion of the applicant, that the claimed technical solution meets the criterion of "inventive step".
The essence of the invention is illustrated by the drawings, which show:
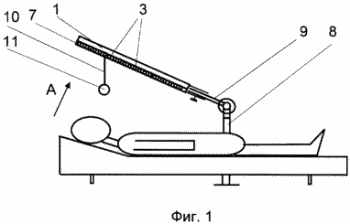 FIG. 1 - general view of the device in the working position |
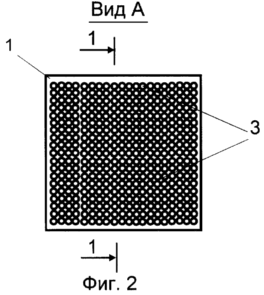 FIG. 2 is a view along arrow "A" in FIG. 1 on the screen |
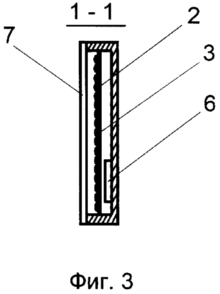 FIG. 3 is a section along 1-1 in Fig. 2 |
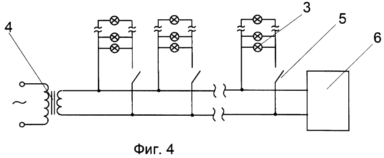 FIG. 4 - basic electrical |
The device includes a light stimulus display unit made in the form of a screen 1. In the case of the screen 1 on the panel 2, light sources are fixed, in a specific example, light bulbs 3, with a power of 0.5 W, a voltage of 6 V in the amount of 400 pieces. Lamps 3 are placed in 20 rows of 20 light bulbs in each. The light bulbs of each row form, in this example, a separate group, with each group of lamps connected in parallel and connected to a power source - a step-down transformer 4 via controllable contacts 5. Alternately, the control contacts of each group of light bulbs are alternately closed and opened by means of unit 6 Control, in this case it is a conventional electronic relay. The time for the lamps of each group to remain on is 0.25 seconds. The screen can be provided with a light diffuser, in particular a frosted glass 7, which reduces the load on the patient's vision. With a tripod 8, the screen is paired with a hinge mechanism 9 having three degrees of freedom and providing the necessary spatial position of the screen relative to the patient. A shiny glass ball 11 is suspended from the screen on the flexible connection 10.
The device works as follows. The patient is laid on the couch. Next, the device is placed and by means of the mechanism 9, the screen 1 is oriented in the space in such a way that the line of sight of the patient passes through the ball 11 perpendicular to the plane of the screen 1. The device is connected to the AC network, alternating switching on and off of groups of light bulbs. Initially, the patient perceives the screen in the form of a flickering light field. After a few minutes the screen begins to be perceived by the patient as a single luminous field with a constant brightness throughout its area (the "fiery square"). From this moment the session lasts for 10-60 minutes. The first sessions, as a rule, last 10-20 minutes, and the subsequent sessions - 30-60 minutes. The total number of sessions for the course of treatment is 10-15.
Example 1
Patient P., 37, a teacher, received complaints of an uncertain nature. She considers herself ill about a year after her mother's death. There were palpitations, shortness of breath, abdominal pain. After anxiety, tachycardia, loss of appetite, constipation, and sometimes nausea. Arterial pressure and pulse are unstable (blood pressure 130/85 - 100/65, mm Hg, pulse - 70-88 per minute). Sweating of the palms, acrocyanosis; With Aschner's sample, the pulse slows by 14-16 strokes, then sharply increases by 20-24 beats per minute. Diagnosis: vegetative neurosis on the background of constitutional features and overwork.
Two sessions of treatment for 15 minutes, then another 12 sessions of 45 minutes. The patient's condition improved, BP stabilized at 110/70 mm Hg. Ceased to disturb tachycardia, dyspnea, pain in the abdomen. Examination after 4 months: the condition is satisfactory, vegetative disorders almost do not bother. Systematically engaged in gymnastics and jogging. BP 115/75 mmHg, pulse 70 per minute, rhythmic. Aschner's test is within normal limits.
Example 2
Patient F., 55 years old, is a disabled person of the II group, he complained of general stiffness. He got sick at the age of 45 years, when a few months after the minor trauma of the skull appeared awkwardness in his right hand during the writing and during the meal. He was treated with anticholinergic drugs (cyclodol, bellazone, ridinol) without visible improvement. Muscle tone is increased by extrapyramidal type, a little more in the left extremities. Tremor of the tongue and outstretched hands. Analyzes of blood and urine without deviation from the norm. Diagnosis: tremor paralysis (Parkinson's disease).
Preliminary 5 treatment sessions for 10 minutes, then 10 sessions for 30 minutes. Treatment is supplemented by coniferous baths, massage and therapeutic gymnastics. The patient's condition improved significantly - the tone in the extremities, especially the right ones, decreased, he became more free to walk and perform movements of the upper extremities, including writing.
The proposed method and device can be realized in the usual clinical conditions for the treatment of various psychosomatic and somatic disorders, but also at the initial stages of mastering the skills of integral yoga. Special training of medical personnel is not required. In the implementation of the invention, a conventional element base is used. These considerations enable us to conclude that the invention conforms to the criterion of "industrial applicability".
CLAIM
A method for influencing a person's psychoemotional state, comprising presenting to the patient a visual dynamic image with varying brightness, characterized in that the patient is presented with a visual dynamic image in the form of a set of separate alternating and switching light sources, the patient's attention being fixed on an object immovably placed between the patient and Set of light sources.
The method according to claim 1, characterized in that after the patient starts to perceive a plurality of separate alternately switched on and off light sources as a single luminous field with an unchanging brightness, the session is continued for 10 to 60 minutes.
An apparatus for influencing a person's psychoemotional state, comprising a light stimulus display unit provided with a control unit, and a power source, characterized in that the light stimulus display unit is a screen on which separate light sources are connected to the power supply via controlled contacts , Which are connected to the output of the control unit, while an element for fixing the person's attention, which is placed between the screen and the person, is connected to the screen by means of communication.
The device according to claim 3, characterized in that the light sources are grouped together, and in each group they are connected together in parallel.
The device according to claims 3 and 4, characterized in that the screen is provided with a light diffuser, for example a frosted glass.
The device according to claim 3, characterized in that the screen is provided with a tripod and is coupled to it by means of a mechanism with three degrees of freedom.
print version
Date of publication 11/21/2006




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.