ENERGY PHENOMENON OF VACUUM - 2

Kosinov NV, Garbaruk VI, Polyakov DV
 Welcome to the forum Welcome to the forum

In this paper, the ideas developed in the article "The Energy Phenomenon of Vacuum - 1" are developing . The nature of the physical vacuum is investigated and requirements are considered, with satisfaction of which the physical vacuum can be attributed to the most fundamental kind of physical reality. It is shown that a physical object, claiming a fundamental status, must have the property of continuity. In this case, it has the greatest generality and does not have limitations inherent in a multitude of objects and phenomena that have a secondary status. A physical vacuum possessing the property of continuity expands the class of known physical objects. Substance and vacuum correlate as mutually complementary and interrelated opposites, they are in complementarity relations, corresponding to the complementarity principle of N. Bohr.
New physical phenomena are presented which, in the opinion of their authors, do not have an explanation or demonstrate the possibilities of a physical vacuum. The authors of this article give the results of their experiments on single-wire and wireless energy transfer, on the vortex motion of an electrically conductive liquid in a magnetic field and on the unusual behavior of a plasma. In particular, the results of experiments showing the presence of regular structures in the plasma are shown.
1. The riddle of the nature of the physical vacuum.
The incentive of persistent interest in the physical vacuum is the hope of scientists that it will open access to an ocean of environmentally clean vacuum energy. Obviously, these hopes are not groundless. In the framework of quantum electrodynamics, the theory indicates the reality of the existence in the physical vacuum of the "ocean" of energy. The energy density of the vacuum W is determined by the relation [2]:
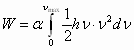 , ,
Where: h - Planck's constant, a - coefficient, ν - frequency.
It follows that the energy of the vacuum can be very large. However, due to the high symmetry of the vacuum, direct access to this energy is very difficult. As a result, being essentially in the midst of an ocean of energy, mankind is forced to use only traditional methods of obtaining it, based on the burning of natural energy carriers. Nevertheless, if the symmetry of the vacuum is violated, access to the ocean of energy is possible. Therefore, the attention of researchers is attracted to new physical effects and phenomena in the hope that they will allow to force a physical vacuum.
When the critical level of excitation is reached, the physical vacuum generates elementary particles - electrons and positrons. Therefore, many researchers are interested in the ability of a vacuum to generate electricity. The Casimir effect indicates the possibility of extracting mechanical energy from a vacuum. Achievement of real results, in terms of practical use of the energy of the physical vacuum, is hampered by a lack of understanding of its nature. The riddle of the nature of the physical vacuum remains one of the serious unsolved problems of fundamental physics.
According to modern concepts, quantized fields lie at the basis of all physical phenomena. The vacuum state is the ground state of any quantized field. Hence it follows that the physical vacuum is the most fundamental kind of physical reality [3]. At present, the concept prevails, within the framework of which it is believed that matter originates from a physical vacuum and its properties result from the properties of a physical vacuum. Ya. B. Zel'dovich investigated an even more ambitious problem - the origin of the entire universe from the vacuum [4]. He showed that the firmly established laws of Nature are not violated at the same time. The law of conservation of electric charge and the law of conservation of energy are strictly observed. The only law that is not fulfilled at the birth of the universe from the vacuum is the law of conservation of the baryon charge. It remains unclear where the huge amount of antimatter that was to come from the physical vacuum was. Therefore, the solution of the physical vacuum problem is of interest, both for fundamental science and applied research. Despite the great interest in it, the physical vacuum remains a mysterious object, to which, nevertheless, science determines the most fundamental status.
2. Philosophical problems of vacuum.
In a number of philosophical concepts, "nothing" or "content emptiness" is considered as the basis of the world. This implies that it is "relative nothing", devoid of specific properties and limitations inherent in ordinary physical objects, must have a special generality and fundamentality, and thus cover the entire variety of physical objects and phenomena. The philosophers of the ancient East argued that the most fundamental reality of the world can not have any specific characteristics and, thus, resembles non-existence [3]. Very similar signs of scientists impart a physical vacuum [3]. At the same time, the physical vacuum, being a relative non-existence and "substantial emptiness", is not the poorest, but, on the contrary, the most informative, most "rich" kind of physical reality [3]. It is believed that the physical vacuum, being a potential being, is capable of engendering the whole multitude of objects and phenomena of the observed world.
Despite the fact that the actual physical vacuum contains nothing, it contains everything potentially. Therefore, due to the greatest generality, it can act as the ontological basis of the whole variety of objects and phenomena in the world. In this sense, emptiness is the most substantial and most fundamental essence. This understanding of the physical vacuum forces us to recognize the reality of existence, not only in theory, but also in Nature and "nothing" and "something." The latter exists as manifested being - in the form of the observed real-field world, and "nothing" exists as an unmanifested being - in the form of a physical vacuum. Therefore, unmanifest being, when this concept is extended to a physical vacuum, should be regarded as an independent physical entity that must be studied.
The physical vacuum is not directly observed, but the manifestation of its properties is recorded in experiments. Vacuum effects include: the creation of an electron-positron pair, the Lamb-Rutherford effect, the Casimir effect. As a result of vacuum polarization, the electric field of a charged particle differs from the Coulomb one. This leads to the Lamb shift of the energy levels and to the appearance of an anomalous magnetic moment in the particles. When a high-energy photon is exposed to a physical vacuum, real particles appear in the nuclear field-the electron and the positron. The Casimir effect indicates the emergence of forces that bring together two plates that are in a vacuum. These effects indicate that the vacuum is a real physical object.
3. Physical phenomena.
3.1. Experimental observation of the violation of the second law of thermodynamics.
Scientists from the Australian National University published a report [5] on the experimental confirmation of the law of entropy decrease [6]. They found that at small time intervals the trajectories of micron-sized particles clearly indicate a decrease in entropy. In the experiment, the behavior of a system of micron-sized colloidal particles in water was studied in an optical trap created by a focused laser beam. At the same time, the position of the particles was monitored with high accuracy. When the laser was turned off, the particles made Brownian motion, but when the laser was switched on, the force directed to the region of maximum light intensity began to act on them. It was found that in short time intervals the trajectories of the particles correspond to a decrease in entropy, whereas on large time intervals, such trajectories are practically not observed. This is the first direct observation of the violation of the second law of thermodynamics [6]. In our opinion, this experiment is confirmed by Yu.L. Klimontovich established by him. Law of decreasing entropy for open systems [7].
3.2. The law of decreasing Klimontovich's entropy. S-theorem of Klimontovich.
In thermodynamics, the basic law is the law of increasing entropy. In an isolated system, there is an evolution to an equilibrium state. In this case, the entropy of the system increases monotonically and remains unchanged when the equilibrium state is reached. This result was established by Boltzmann on the example of a rarefied gas. It is called the Boltzmann H-theorem.
Klimontovich Yu.L. Showed that for the processes of self-organization, there is another law - the law of decreasing entropy. An analogue of the Boltzmann H-theorem for open systems is the Klimontovich S-theorem [8]. The essence of the new law amounts to the following: if the "equilibrium state" corresponding to zero values of the control parameters is taken as the origin of the randomness measure, then as the distance from the equilibrium state changes as a result of the change in the control parameter, the entropy values referred to the given value of the mean energy decrease [8] .
Klimontovich's theorem practically removes the ban on the occurrence of regular structures in the continuum. Within the framework of the physical vacuum theory, using Klimontovich's S-theorem, it becomes possible to rigorously justify the occurrence of not only regular structures in the continuum, but also the generation of discrete particles by a continuous vacuum. One of the consequences of Klimontovich's S-theorem is the conclusion that discreteness results from continuity. The law of decreasing Klimontovich's entropy provides the key to solving the fundamental conflict of continuity and discreteness, which has not yet been solved.
3.3. Screw structures in a lithium plasma.
A group of Ukrainian and Russian scientists at the Robotron installation [56] carried out a series of experiments with a turbulent lithium plasma in which discharges with heat fluxes to the wall of 13 kW / cm 2 were obtained [58]. Such flows can be carried by Li + and Li ++ ions. The electron concentration was 10 15 cm- 3 . It was found that the photon flux corresponding to the main resonance transition of the lithium atom is 10 4 10 5 times lower than the value expected for complete recombination of ions moving to the wall. At the same "Robotron" installation, helical structures were found in a strongly ionized turbulent lithium plasma. The structure of turbulence was measured from the fluctuations in the radiation of the resonance line of lithium and the hydrogen line. The left-handed structure of turbulence is accompanied by the motion of the plasma glow zone along the discharge [57]. In our opinion, the appearance of structures in the plasma indicates a decrease in the entropy of the plasma. One of the authors of the works (Mudretkova EV) in the book [9], to explain the origin of structures in the plasma, introduced and described the smallest particles (eleptino and electrically) existing in space [9].
3.4. Fractals in plasma.
In [10], unusual physical phenomena in plasma were investigated, leading to the appearance of fractal structures in it. It was found that the quasineutral state of the plasma was replaced by an ordered state [10]. The regular structures formed had a fractal regularity, and the fractals in the plasma were manifested on a macroscopic scale. At a macro scale, the structured plasma consisted of two symmetrical systems resembling nested cones in shape (Fig. 1). In fractal structures, a characteristic dependence is constructed, constructed on the principle of period doubling. The universality of the period doubling scenario in systems with chaotic behavior was pointed out in his studies by Feigenbaum [11].
Thus, in plasma, instead of chaotic behavior, there was an absolutely definite type of organization and a very definite interconnection of the elements of the structure. The revealed high degree of order in the plasma, contradicts the traditional understanding of the processes in it. All this points to the processes in which the entropy of the plasma decreases.
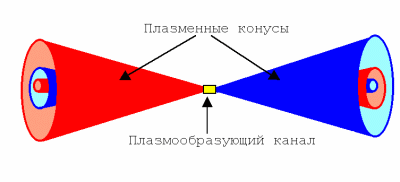
Fig. 1. Structure observed in plasma [10].
Using the example of plasma studies [10], it can be seen that regular structures arose and remained for a short time. If we assume that there was a violation of the second law of thermodynamics in these processes, then this could only occur at small intervals of time. At the same time, it should be noted that the concept of "small time intervals" makes sense if the estimation of time intervals occurs at the pace of macro-world processes. The same time intervals are very large intervals, if they are evaluated in the rate of processes in the world of elementary particles. On the example of the appearance of fractals in a plasma, we can conclude that in Nature there must be two processes - a decrease in entropy and an increase in entropy. In this case, the law of increasing entropy is satisfied only on the average for a large period of time, and at the initial stage a decrease in entropy is observed. The results of a study of the decrease in plasma entropy can contribute to an understanding of the most important process in the physical vacuum, leading to the creation of a discrete substance from the vacuum, since such a process must occur with a decrease in entropy.
3.5. Hubbard Generator
In [12], a description of the device invented by Alfred Hubbard is given. It includes a central core with a coil, around which are located eight peripheral coils. After the primary pulse in the coils, pulses are alternately generated, and a rotating magnetic field is created in the central coil. It is asserted that the power generated in it is sufficient for self-excitation of the entire system. The circuit of the generator is shown in Fig. A boat and an electric car were shown, powered by a Hubbard generator. A 25.7 kW electric motor was connected to a Hubbard transformer, 12-14 inches in diameter and 14 inches in length. This device produced enough energy for the boat to move at a good speed. It remains a mystery how to obtain high power in the "Hubbard generator" [12].
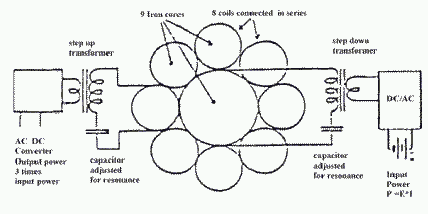
Fig. 2. The circuit of the Hubbard generator [12].
3.6. Generator of Hendershot
In [13], a device constructed by Lester J. Hendershot is described. The author of the device claimed that the system uses the "Earth current" for work. Hendershot found that the operation of the generator is affected by the orientation relative to the earth's magnetic field. The system works best north-south.
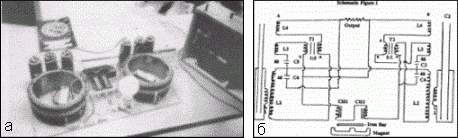
Fig. 3. The generator of Hendershot [13, 14].
Figure 3a shows a model of the Hendershot converter, shown at the "Gravitational Field Energy Congress" in November 1981 in Toronto [14]. Figure 3b illustrates the circuit diagram of the converter [13].
3.7. Generator Hansa Kohler
Hans Kohler invented a device, which he called the converter of the energy of the gravitational field [15].
The device consists of six permanent magnets, connected so that the magnets themselves enter the electrical circuit (Fig. 4a). On each of the magnets coils are wound. These coils are located hexagon (Fig. 4b). The circuit includes two capacitors, a key and two solenoids nested one in the other (Fig. 4c). The device is started by displacing the magnetic coils and solenoids relative to each other. The maximum voltage value obtained was 12V. In [15, 16], the results of testing the device designed by Kohler are described. The load was three incandescent lamps with a supply voltage of 8 V. The test results showed that the power consumed by the load is several times higher than the power consumed by the device from the batteries. The latter was 1.7 W, and the power in the load was about 8 W. Professor M. Koloss, who led the tests, stressed that the load current was 12 times higher than the current consumed by the batteries. In conclusion, Professor M. Koloss wrote: "The only suggestion that can be made is that the source of energy is the magnetic system [15].
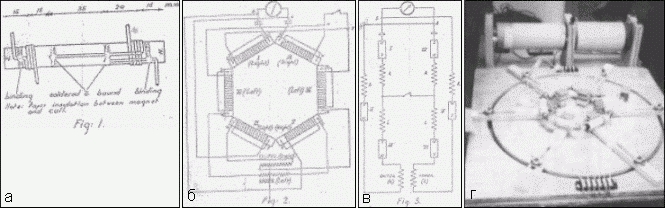
Fig. 4. The generator of Hansa Kohler [14, 15]
Figure 4d depicts the model of the device of Hansa Kohler, reconstructed by Jorge Hatavei, shown in November 1981 at the congress in Toronto [14].
3.8. Single-wire power transmission
In the Moscow scientific and research electrotechnical institute, SV Avramenko demonstrated the transmission of alternating current through a single wire without grounding [17].
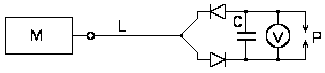
Fig. 5. The scheme of single-wire energy transfer according to Avramenko's scheme [17].
The basis of the device was the "Avramenko plug", which consists of two series-connected semiconductor diodes (Fig. 5). If the plug is connected to a wire under an alternating voltage of 10-10000 V, then a pulsating current circulates in the fork loop, and after a while a series of sparks is observed in the spark gap P.
The time interval from connection to discharge depends on the capacitance C , the ripple frequency and the gap size P.
The inclusion of a 2-5 MΩ resistor in the transmission line does not cause any significant changes in the operation of the circuit [17].
Investigating the transmission of energy via one Avramenko wire, Zaev and Lisin come to the conclusion that the phenomenon is due to the presence of a polarization current [17, 18]. In their opinion, the magnitude of the polarization current depends directly on the frequency, the diameter of the generator winding wire, the density of the wire material, the atomic number of the wire material and inversely proportional to the length of the winding wire, the mass number of the wire material. But the main dependence, according to the researchers - is inverse proportionality to the difference in the squares of the vibration frequencies - the resonant frequency of the atom of the winding material and the frequency of the generator.
The authors of [18] consider it necessary to verify the expediency of manufacturing the windings of the generator from wires of copper, nickel, iron, lead, etc.
The idea of a single-wire power transmission interested many researchers. So in [17] describes the experiment of Stefan Hartmann, based on the invention of Avramenko.
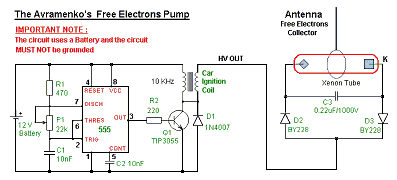
Fig. 6. Stefan Hartmann's scheme [17].
The generator uses a car ignition coil. The electronic generator operates at a frequency of 10 kHz. As a load, a xenon flash lamp is used, a copper wire is used as an antenna (Fig. 6). The generator of alternating voltage through a conductor, whose length is a multiple of the length of the standing wave of the electric field in it, is connected with the "Avramenko plug". In the case of resonance, the amplitude of the voltage at the "plug" connection point is maximal. The author claims that the capacitor is charged with a voltage that does not affect the primary energy source. The generator, in his opinion, is only a source of information. The energy released in the xenon lamp is determined by the frequency and amplitude of the oscillations. The lamp was set on fire by free electrons flowing through a copper antenna. If you remove the antenna, the xenon lamp does not light.
3.9. Our experiments on single-wire energy transfer.
The authors of this article conducted experiments on the transmission of electricity by one wire. In our scheme, the "Avramenko plug" was not used. Instead of "fork Avramenko" was used the usual bridge scheme. In addition, we made a number of other changes to Avramenko's scheme, which increased its effectiveness. The diagram is shown in Figure 7.
The general view of the device is shown in Figure 8a. The device provides a DC power supply B5-47. The load is an incandescent lamp 220V 25W. In the electrical circuit shown in Fig. 7, the digits indicate: 1 - generator, 2 - spectrum expander, 3 - "antenna". The generator and transformer are housed in a dielectric casing (Fig. 8b, 8c), diodes, a capacitor, a lamp, elements 2 and 3 that make up the energy receiver - in a white-blue casing under the lamp (Fig.
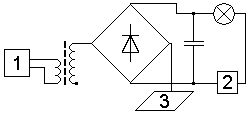 Fig. 7. Schematic diagram of the device for single-wire power transmission Fig.
8. Photographs of experiments on single-wire energy transfer.
In the experiments, various incandescent lamps were used, the best result was achieved when using lamps 220V, 25W (Fig. 8d, 8d). The key point in increasing efficiency, in comparison with the Avramenko scheme, is the use of a standard bridge circuit, not half of it, but also the presence of a spectrum expander. The presence in the circuit of the spectrum expander leads to the fact that the load does not interfere with the full charge of the capacitor. As a consequence, all incoming energy is spent on charging a high-voltage capacitor with a low leakage current. The circuit is then closed by the bias currents to the free end of the secondary winding of the transformer through antenna 3 (Fig. 7).
3.10. Experiments with burnt out incandescent lamps.
In our experiments described above, single-wire energy transfer burns both serviceable lamps and burned-out lamps.
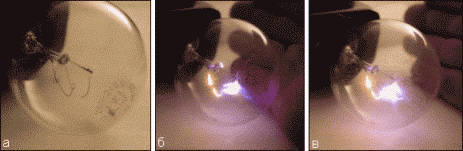
Fig. 9. Photos of experiments with burnt out incandescent lamps.
Figure 9a shows the rupture of the filament of the incandescent lamp. Figures 9b and 9b - photographs of experiments. A glow of the spiral and a bright spark at the point of the spiral break are visible.
With the glow of burnt out incandescent lamps, without suspecting, almost every one of us is facing. To do this, it is enough to take a close look at the burned-out lamps. You can see that the lamps often burn out in several places. The probability of simultaneous burnout of a lamp in several places is very small. This means that the lamp, having lost the integrity of the spiral, continued to shine until the chain exploded in yet another place. This phenomenon occurs in most cases of burnout of incandescent lamps, powered by a 220V 50Hz network.
We conducted such an experiment: we connected standard 60W incandescent lamps to the secondary winding of the step-up transformer. At idle, the transformer produced a voltage of about 300V. In the experiment, 20 incandescent lamps were used. It turns out that most often incandescent lamps burn out in two or more places, and not only the spiral burns out, but also the current-carrying wires. In this case, after the first break of the chain, the lamp continues to shine more brightly until another section is burnt. One lamp in our experiment burned out in four places, namely, in two places a spiral burned out, and both electrodes burned out! The results of the experiment are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Number of lamps used in the experiment |
Number of lamps burned in one place |
Number of lamps burned in two places |
Number of lamps burned in three places |
Number of lamps burned in four places |
Number of lamps burned in five places |
20 |
8 |
8 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
3.11. Experiments on wireless transmission of energy.
We give information about our experiments on the implementation of wireless (without grounding) transmission of electricity. Fig.
10. Frames of videotaping experiments on wireless power transmission.
In our experiments, the energy source was a complex consisting of a power supply unit B5-47, a generator and a transformer, it is clearly visible in frames 10a and 10b, and the receiver is a direct current electric motor IDR-6. The electric motor is mounted on an electrically conductive platform, which, in turn, is mounted on the body of an insulating material. Inside this case is an electronic node. The receiver scheme in this case differs somewhat from that used in the previous experiments described in Section 3.9. The interior of the receiver is shown in the photos 10g and 10d. On the frame 10d with a circle, the electronic node of the receiver is allocated directly.
In experiments, rotation of the electric motor rotor in the hands of a person was observed. The engine was installed on a platform on which there were no power supplies. An increase in the transmission coefficient with decreasing distance was observed (Fig. 10c). As the distance was reduced, the rotational speed of the motor shaft increased. On (Fig. 10b) is shown a video frame where the shaft rotation frequency increased sharply if the electric motor was in the hands of two people.
The problem of wireless power transmission remains relevant. Scientists from different countries continue to work on it.
3.12. Our experiments showing the glow of an incandescent lamp in the hand.
It is known that Nikola Tesla demonstrated a luminous lamp in his hand. We were not able to find descriptions of this experiment, so we developed our experimental design. Below are the results of our experiments, demonstrating the glow in the hand of the incandescent lamp. Figure 11 shows that the lamp 220V, 25W glows in the operator's hand, being connected by one contact to one wire. The photographs (Fig. 11) show a conductor from the generator, supplying energy to one contact of the lamp cap. These experiments are the continuation of a series of experiments with a single-wire energy transfer. Picture 11a shows a fragment of the preparation for the experiment. The photographs of 11b, 11c show the fragments of the experiment.

Fig. 11. Photos of experiments showing the glow of an incandescent lamp in the hand.
3.13. Experiments demonstrating the behavior of electrically conductive liquids in a magnetic field [20].
We carried out experiments showing that when a current flows through an electrically conductive liquid in a magnetic field, the liquid comes into a vortex motion. This physical effect, in its appearance, has a great analogy with the rotation of the Earth, and with some other manifestations in its interior and on the surface [20]. The effect of the vortex motion and the temperature effects observed in the laboratory conditions, in our opinion, can be extended to a large number of natural phenomena. Fig.
12. Vortex motion of molten tin in a magnetic field [20].
We shall describe the effect of the vortex motion of the medium on the example of molten tin. The cuvette with tin is placed in a magnetic field, the vector of magnetic induction of which is directed vertically (Fig. 12a). The figure shows: 1 - vessel, 2 - molten metal, 3 - spiral coil, 4 - metal ring, 5 - electrode, "S" - south magnetic pole, "N" - north magnetic pole. Four straight arrows in the figure show the position of the compass needle during the experiment. In the central part of the vessel, an electrode is lowered into the molten metal. The second electrode is made annular. It is installed along the perimeter of the vessel and is lowered into the liquid. When a current flows through an electrically conductive liquid, the latter comes into a vortex motion, observed in the zone between the central and peripheral electrodes with the center of the vortex at the central electrode. The direction of movement of the molten metal is indicated by an arrow. The effect is clearly visible on the video footage of the experiment (Fig. 12b and 12c). The frequency of rotation is maximum at the center and decreases toward the periphery. The vortex motion of the molten metal appears even with a slight current. Starting from a current of several amperes, it is confidently observed visually. With a further increase in the current, the intensity of the vortex motion increases sharply, which leads to the formation of a deep funnel in the center of the vessel (Fig. 12b). When the direction of the magnetic field changes or when the polarity of the applied voltage changes, the direction of the vortex motion changes to the opposite direction. We believe that a similar effect is manifested in Nature and leads to the formation of vortices, tornadoes, cyclones [20].
The vortex motion of a liquid in a magnetic field is accompanied by a temperature effect. Its essence lies in the fact that a temperature gradient appears in the vortex medium. An increase in the temperature of the medium at one electrode is accompanied by a decrease in the temperature of the medium at the other electrode. We describe the effect on the example of an electrically conducting liquid. A cuvette with an electrically conductive liquid is placed in a magnetic field, the induction vector of which is directed vertically. In the central part of the cuvette, an electrode is lowered into the liquid. The second peripheral electrode is made annular and installed along the perimeter of the cell (Fig. 13a). When the current flows, vortex motion of the liquid is observed, which is accompanied by an increase in the temperature of the medium at one electrode and a decrease in the temperature of the medium at the other electrode. This is manifested in the experiment as the formation of a solid phase of the metal at one of the electrodes (Fig. 13b and 13c). When the experimental conditions change, the solid phase is formed not in the central region, but near the peripheral electrode.
Fig.
13. The temperature effect accompanying the vortex motion in a magnetic field [20].
In our opinion, this temperature effect manifests itself in Nature. Perhaps, it contributes to the occurrence of low temperatures in the polar zones of the Earth.
The appearance of a temperature gradient was also observed in the experiment, the scheme of which is shown in Fig. 14a. Frames of videotaping 14b and 14b demonstrate the formation of two differently directed vortices. You can see video of experiments with the vortex motion of molten tin on the site http://www.unitron.com.ua

Fig. 14. Double vortex [20].
One-sided temperature effect is also observed in the effect discovered by the French metallurgical engineer J. Rank. In turbulent tornado spontaneously there is a powerful heat current from the axis to the periphery: the core of the flow is always colder than the periphery. The Rank's vortex tube (Fig. 15) is the same cyclone, but reconstructed to obtain the maximum amount of cold in the axial part of the vortex flow and, accordingly, heat - in the peripheral.
The temperature difference between the hottest and coldest layers in the vortex tube can be significant. These layers in the field of centrifugal forces coexist at a distance of several millimeters from each other [21].
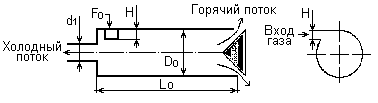
Fig. 15. Vortex tube [21].
It should be noted that, in contrast to the temperature effect observed in our experiments, the Ranke effect always flows from the vortex axis to the periphery, regardless of the direction of the vortex. In our experiments, cooling of tin was observed under certain conditions at the center, while in others - at the periphery.
3.14. New physical effects in plasma.
We conducted a series of experiments on the Unitron unit, in which unusual plasma behavior was revealed [10]. In the experiments we observed simultaneously two plasma formations symmetrically disposed relative to the plasma-forming channel.
Below are the footage from the filming of the experiments. Fig.
16. Shots of video shooting experiments with plasma.
Plasma clots are visible in the frames in various phases of their existence. Fig. 16a and Fig. 16b show the initial phases of the existence of plasma in the form of fireballs and spindles.
At a certain distance from the plasma-forming channel, outside the plasma generation zone, we placed targets. The targets were sheets of paper, cardboard and metals. On the third frame (Fig. 16c), a fractal plasma formation freely moving in the air is visible. In addition, this frame shows a certain formation, which has a reddish hue, hanging at the edge of the table on which the installation is located. On the fourth frame (Fig. 16d) both conical plasma formations are immediately visible. In this experiment the targets were not established. Figure 16d depicts the final stage of the existence of the plasma. It shows the expanding molten fragments of the target.
The photo (Fig.17) shows the targets after the action of plasma.

Fig.17. Targets after exposure to plasma.
During the experiments we observed explosive melting and sublimation of metals, even such refractory as tungsten. This can be seen from the holes formed in the metal sheets. In Fig. 17, there are targets on top and on the right, which are a complex of aluminum foil and paper. In some experiments, we established these complexes with the paper side to the plasma generation zone. The target in this case remained unaffected. In other experiments, we installed the complexes with foil to the generation zone. As a result, the foil in some area evaporated, while the layer of paper behind it remained unaffected. The result of one of these experiments is shown in close-up in Fig. 18a. When installing strips of tissue paper without any coatings as a target, the latter was not flammable. Paper targets remained intact, they did not light up, although they were inside a fiery plasma ball. In the course of the experiments, it was found out that the plasma produced by our setup affects only the conductors. Dielectrics have a strong mechanical effect, similar to electrostatic repulsion. These facts indicate that the factor acting on the target is not the temperature of the plasma.
By definition, plasma is an ionized gas in which the densities of space charges created by positively and negatively charged particles are the same or almost identical (quasi-neutrality), and the chaotic thermal motion of these particles predominates over their directional displacement under the action of an external electric field [22]. The results of our experiments show some features of the plasma. We came to the conclusion that there is practically no chaotic thermal motion in the plasma generated by our setup, as a result of which a clear, regular, fractal structure in the form of embedded cones is observed in the plasma. This is confirmed by the results of inspection of samples of materials serving as a target for plasma. Figure 18 shows the front and back sides of five different targets after exposure to them by plasma. In the first column (Fig. 18a) there are images of the above-mentioned complex, consisting of aluminum foil and strips of writing paper. In the second - (Fig.18b) there are photographs of the hole formed in tungsten. They clearly visible structures formed by alternating light and dark rings. The melting point of tungsten is 3370 ° C, the boiling point is 5900 ° C.
In one of the experiments, conditions were created under which, as a result of the contact of the plasma with the target from tungsten, there was no hole in the latter (Fig. 18c). In the photographs of this target, ring structures of different sizes are seen showing a self-similar structure. It can be seen from these photographs that some of the rings occupy an area approximately equal to the area of the holes formed under other experimental conditions. The photographs (fig.18g) depict a strip of tantalum foil on both sides. In a detailed study of these "prints," they found a clear, regular, fractal structure formed by a large number of alternating dark and light rings. In the photographs located in the fifth column (Fig. 18d), a copper target is shown. On it, and clearly visible ring structures. Fig.
18. Photos of targets close-up.
It should be noted that in our experiments we did not affect the plasma by artificial magnetic fields.
3.15. The converter of energy of a gravitational field on the basis of electric
Equivalent of the Mobius band
Japanese scientist Shinichi Seik investigated a dual solenoidal 3-phase generator based on the electrical equivalent of the Mobius band [23]. The device includes a coil made in the form of a double solenoid, containing 1000 turns, 3 condensers, a special alloy disk and a ferrite block. Near the double solenoid there is a generator coil consisting of 40 turns of wire (Fig. 19a).
A 3-phase voltage is applied to the generator to produce a rotating electromagnetic field. There is a constant increase in the output potential, which the converter writer explains by the gradual, continuous absorption of the energy of the gravitational field. The initial potential - 3V gradually increases, reaching 40V for 3 months (Fig.19b). According to the scientist, this result shows a gradual influx of energy. A constant decrease in frequency is observed. For three days the frequency decreases from 100 kHz to 1.5 kHz.
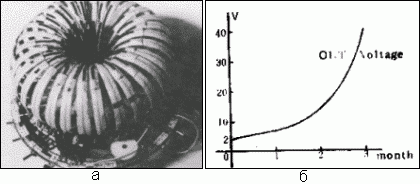
Fig. 19. Research scientist Shinichi Sake [23].
3.16. Generator Vilenkin
The generator is called "Vilenkin's energy-generating battery" [24]. In the photo (Fig. 20a) it is shown that his generator produces 2.191 Volts. It is claimed that no primary capacity is required to operate the device.
"Zametron", another name for the device, consists of coils wound around the left or right-handed Möbius circuit, forming a magnetic Klein bottle. Alexander Vilenkin argues that in his device "works" time. The researchers found several modes of operation, one of them is presented on an oscillogram (Fig. 20b), an amplitude of 0.1 V at a frequency of 85.1 kHz.
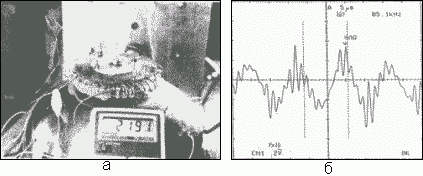
Fig. 20. The generator of Vilenkin [24].
3.17. Phenomena accompanying the operation of devices containing non-oriented contours.
At present, in many countries experiments are being conducted to obtain ball lightning with the help of unoriented circuits such as electric analogues of the Möbius sheet, Klein bottles and their combinations. IM Shakhparonov, the leading investigator of unoriented contours, believes that the radiation discovered by Kozyrev and the radiation of unoriented contours is one and the same phenomenon. This radiation Shakhparonov called: "Radiation Kozyrev-Dirac" [25].
In [26], the experiments of IM Shakhparonov with unoriented contours are described. The goal was to create a generator of gravitational waves, which, supposedly, should have been a strip of aluminum foil, folded into a Mobius strip. The Mobius strip is made of a dielectric strip, and a metal layer is deposited on its surface on both sides. An unoriented circuit with a dielectric core was obtained, which was connected to a 220V power socket. At the same time, a short circuit occurred. In fact, every time there were ball lightning of various colors, a bright blue electric discharge resembling a flower with 3, 5 or 7 petals, this discharge occurring before a short circuit.
It was noted that the radiation of Kozyrev-Dirac, interacting with matter, cools it. In [25], information is given that a beam of focused radiation from Kozyrev-Dirac along the path of its motion destroys the crystal lattice of matter. However, within two weeks, the substance restores it without defects inherent in natural crystal structures. A series of experiments on animals is described, the purpose of which was to identify the effects of focused radiation from Kozyrev-Dirac on the mammalian organism. In experiments with animals, it was found that this radiation reduces the amount of glucose in the blood, reduces its viscosity, promotes an increase in immunity and the number of cells in the bone marrow.
3.18. Experiments demonstrating levitation of electrostatic systems
Thomas Brown (Thomas Townsend Brown) investigated the problem of creating unsupported thrust only due to electric forces [27]. One of his patents [28] describes ways of obtaining a driving force due to an electric power source. Initially, in a simple flat capacitor consisting of two plates, Brown discovered the presence of a force moving the capacitor toward the positively charged plate. The patent [29] describes the idea of creating an asymmetry of electrostatic forces in a system of charged bodies due to a special surface shape. As the inventor noted, the efficiency of the system can be "one million to one" [27].
Today the development of Thomas Brown's ideas is carried out by a group of researchers in France [30]. In Fig. 21 shows one of their developments. The power source of the electrostatic system is a high-voltage horizontal scan unit, from a computer monitor. In the foreground of the photograph is a levitating electrostatic system, which is a set of triangular frames. Aluminum foil, glued along their perimeter serves as a negative electrode. The positive electrode is a thin copper wire stretched along the perimeter of the frames above the foil.

Fig. 21. Levitation electrostatic system [30].
3.19.Experimental detection of "strange" radiation and transformation of chemical elements
In [31, 32] experiments on the study of the electric explosion of foils in water are described. The appearance of new chemical elements, which are detected both by spectrometric measurements in the process of discharge, and by mass-spectrometric analysis of precipitation left after the discharge. "Strange" radiation is registered, accompanied by the transformation of chemical elements.
The blasting chamber was a torus, with eight holes drilled evenly along the circumference into which liquid was poured. During the experiments, there was an intense luminescence appearing above the dielectric cover at the time of current rupture. The duration of the resulting luminescence exceeds the duration of the current pulse by more than 10 times.
Based on the results of the experiments, the authors describe the typical dynamics of spherical luminescence. At the time of current rupture, a very bright diffuse glow appears above the installation (Fig. 22a). Then the glow becomes less bright and on the next frame (Fig. 22b) the spherical glow is clearly visible. In the next 3-4ms there is no any dynamics, and then the glowing sphere begins to crumble into many small "balls". In a number of experiments it was noted that the "ball" first rises 15-30 cm above the surface of the dielectric cover, and then crumbles (Fig. 22c).
Figure 22b shows that the glow arises at the center between the electrodes above the dielectric cover and has a spherical shape.
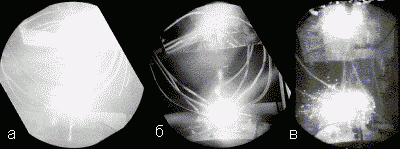
Fig. 22. "Strange" radiation that occurs during a current break [31].
Long-lived plasma formations in air were observed in a number of experiments in various laboratories [33, 34]. A distinctive feature of the described experiments are spectral measurements. The identification of the ruled portion of the spectrum led to two unexpected results. Firstly, the presence of nitrogen and oxygen lines was not recorded, while these lines should always be visible when an electric discharge is in the air. Secondly, the abundance of lines (more than 1000 lines in separate "shots"), and, accordingly, a significant number of chemical elements to which they correspond. Analysis of the spectra indicated that the basis of the plasma was Ti, Fe, Cu, Zn, Cr, Ni, Ca, Na. If the presence of the Cu and Zn lines in the spectrum can be explained by a sliding discharge along the structural elements of the installation and the supplying power cables, the presence of the remaining elements in the plasma could not be interpreted. A change in the experimental conditions, in particular a change in the mass of the exploding foil, led only to a redistribution of the intensity of the spectral lines, while its elemental composition changed insignificantly.
In the experiments, a change in the effective magnetic field was observed in ferromagnetic foils. The authors of [32] believe that this is due to the accumulation of magnetic monopoles, the existence of which was predicted by the English physicist P. Dirac.
3.20. Seven discoveries of a group of Russian scientists
In July 2001, a group of Russian scientists, led by the director of the Volgograd Institute of Materials Science, RAEN professor Valerian Sobolev, announced a series of fundamental discoveries [35].
The depletion process, a new state of matter, a new class of materials, a magnetic charge, a new energy source, a low-temperature plasma generation method, and a superconductor are discovered.
3.20.1. The process of impoverishment.
The process of impoverishment is opened, which is the main discovery. This process is similar to electrolysis. Its products are metals and monolithic substances with a melting point ranging from 1500 to 3000 ° C, with a chemical composition such as silica (quartz glass), aluminum oxide, titanium oxide, iron oxide, and the like.
A device was created in the form of a special electrochemical column (Fig. 23). "Sobolev's column" consists of two melt volumes, containing electrodes and dielectrically separated by a gas gap.
In the device, when an electric field of the upper volume is applied, which together with the electrode is an anode, the process of breaking (the terminology of the authors of the discovery) of the electron from the melt of the lower volume occurs, in which a ground electrode is in contact with the melt [36]. The volume of the melt, from which the electron is torn, acquires a positive charge. Under the action of the electrostatic field, the metal ions in the melt are moved to the grounded electrode and converted into atoms. This is how the process of depletion of the melt by the chemical elements of metals occurs.
Based on the discovery, a method has been developed and patented for the production of monolithic materials [37]. The method makes it possible to obtain these materials from glass-forming melts having a temperature much lower than those mentioned.
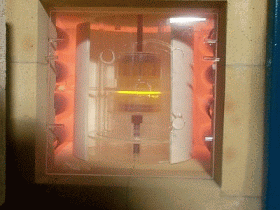
Fig. 23. The column of Sobolev [36].
3.20.2. New state of matter.
The consequence of the depletion process is a change in the combination of chemical elements in the melt, which generates a new, characterized by non-stoichiometry of the chemical composition, the state of the medium [36].
3.20.3 A new class of materials.
The multielement chemical compounds obtained during depletion differ in the variety of chemical compositions and form a vast new class of materials [36].
3.20.4. Magnetic charge.
The substance in the new modified state contains ordered structures that radiate a time-varying magnetic flux. In the opinion of the authors of the discovery, these ordered structures, as a whole, are a magnetic charge. The discovery was that the magnetic charge belongs to a continuous medium, and not to an individual particle [36].
3.20.5. A new energy source
Materials containing magnetic charge are a new source of energy. Emitting a magnetic flux, they create an EMF in the conducting circuits, together with which these materials constitute a new physical source of current. The average of the recorded EMF values is approximately 1500 volts, referred to 100 cm 3 of the melt volume. The phenomenon of EMF generation is explained by the ability of the substance to convert the energy of external natural fields into electric power. On the basis of the new autonomous device, the source of EMF, it is planned to manufacture an autonomous device - a self-governing safe power station for domestic and industrial use, in the form of a current source with a power of 3 kW capable of giving energy in any climatic conditions of the Earth [36].
3.20.6. Method of generation of low-temperature plasma.
The device is a generator of a spatial gas-like charge-a cold plasma-of one (positive) sign. The system is suitable for obtaining an intense magnetic field, ion beams carrying a powerful charge, the volume distribution of ions relative to the surface to obtain strong directed electrostatic fields with adjustable field strength [36].
3.20.7. Superconductor.
In the process of generation of a space gas-like charge, it is possible to focus the ions of the gas into a hollow vacuum cylinder, the axis, which serves as a superconducting channel.
Researchers assume the use of their inventions as elements that increase the efficiency of primary energy sources, elements of electrical engineering, the driving force of vehicles, including flying devices, devices that put electrostatic charge on objects with a density that removes objects or electrical circuits of objects from the working state [36].
3.21. Studentnikov Hydrogen Generator
Many scientists consider water as an energy carrier of the future [39]. The Russian patent [38] describes a simple high-performance device for the decomposition of water and production of cheap hydrogen from it by gravitational electrolysis of an electrolyte solution, called the "hydrogen-hydrogen generator". The generator is driven by a mechanical drive and operates at an ordinary temperature in the heat pump mode, absorbing through its heat exchanger the necessary heat from the environment or utilizing the thermal losses of industrial or transport power plants. In the process of water decomposition, the excess mechanical energy supplied to the generator drive can be converted into electricity by 80%, which can then be used by an external consumer. In this case, from 20 to 88 energy units of low-potential heat are absorbed for each unit of power expended by the generator drive, depending on the set operating mode. Since the process mainly uses free heat and cheap water, the cost of production of a cubic meter of hydrogen is reduced and becomes 1.5-2 times lower than the total cost of extraction and transportation of natural gas [38].
3.22. Macroscopic fluctuations in processes of different nature
The paper [40] describes the results of the work of researchers with preparations of muscle proteins, during which an unusually large scatter of the measurement results was observed. This spread of results significantly exceeded possible methodological errors.
In 1981, investigating macroscopic fluctuations during the solar eclipse, the researchers came to the conclusion that the observed phenomena are related to the direct "visibility" of the Sun. The basis for this conclusion was significant changes in the processes under study at sunset and eclipse of the Sun. The diurnal variation of the rate of some reactions in different geographical latitudes was observed. Macroscopic fluctuations occur in different ways in different years, seasons, months, days and at different geographical latitudes [40]. In 1982, fluctuations were detected in measurements of such different processes as the electrophoretic mobility of cells and latex particles, the spin-spin relaxation time of water protons, fluctuations in the spectral sensitivity of the eye, the discharge time of the RC generator on a neon lamp, the measurements of radioactive decay and, finally, In the electrical and magnetic properties of various objects.
In the search for the cause of macroscopic fluctuations, a consistent transition was made from the notions of the special properties of muscle proteins, chemical and physico-chemical processes to processes of radioactive decay and further to the fundamental characteristics: the masses of microworld objects and universal constants. In [40], the authors state that, despite the long period of research of macroscopic fluctuations in processes of various nature, today there is no understanding of their essence. The observed effects can not be explained within the framework of electromagnetism. Since these fluctuations were observed simultaneously in different points of the Earth from different points of view, the researchers assume that the cause of the fluctuations has a global, cosmic scale.
3.23. Experiments demonstrating the phenomenon of remote drug exposure
Lupichev NL described experiments on unicellular organisms (bacteria, lymphocytes) objectively proving that chemical substances act on biological objects not only with molecular contact, but also remotely [41]. The essence of the experiments is as follows. In a test tube with a suspension of unicellular organisms, a sealed ampoule with a substance whose action on the cells is known is placed. After 30 minutes. After the incubation in the thermostat, the biochemical properties of the cells are examined, and comparisons are made with control samples that are a suspension of cells in another tube with an empty ampoule placed in it, and a suspension of cells with directly added substance (Fig. 24). The figure shows: 1- a test tube with a sealed ampoule containing the substance, a 2-tube with an empty ampoule, a 3- tube, into which the substance was directly added.
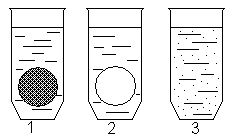 Fig. 24. Remote action of a chemical substance on unicellular organisms [42].
As a result, changes in the biochemical properties of cells were detected under the action of a chemical substance in a sealed ampoule, analogous to the action when it was directly added. In a test tube with an empty ampoule, no changes were found.
Experiments were carried out showing that the effect is carried out at a distance by means of conductors and by means of antennas [42]. The cell suspension and the substance were placed in separate tubes, and then an acupuncture needle was placed in each of them as an antenna. Control samples served without antennas, samples with directly added substance, and samples with antennas in shielding chambers from various materials (Fig. 25). The figure shows: 1- a test tube with a substance, a 2-screened tube with a suspension of cells, 3- a tube with a suspension of cells without an antenna needle, a 4-tube with an antenna needle containing a suspension of cells, a 5-tube with a suspension of cells and directly added Into it with matter.
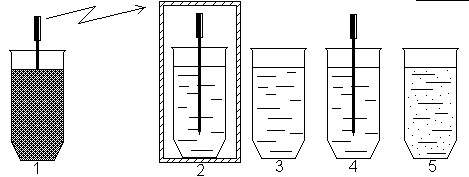
Fig. 25. Experiments showing remote effects [42].
More than a thousand experiments showed that the interaction occurs when there is an antenna connection between the reagents, and this did not require additional devices or energy sources [40]. Investigation of the shielding properties of bronze, steel, aluminum and plastic showed that only aluminum is an effective shield [41].
During the experiments, it was found that when the drug was exposed to water, the latter acquired new qualities and acted on biological objects identical to this drug [42]. Experiments were carried out, during which the slide of the picture was projected onto an aluminum screen, and the electrodes coming from it were applied to the necessary acupuncture points of the patient [42]. It turned out that the pictures of different artists have different effects on the human body. Pictures of Botticelli well relieve pain syndrome, Matisse pictures help with kidney diseases, Picasso - with violations in the cerebral cortex, etc.
The author [42] comes to the conclusion that remote interactions of real objects without mass transfer possess many properties of electromagnetic waves of the classical theory, properties of wave-particles of quantum mechanics, and properties that have no explanations.
3.24. Macroscopic nonlocality - a new physical phenomenon
A group of scientists led by SM Korotaev experimentally discovered a phenomenon called "macroscopic nonlocality". Macroscopic nonlocality represents a new physical effect, consisting in the correlation of dissipative processes without the means of local interaction carriers [43]. There is no complete theory of the effect. The researchers suggest that the basis is the phenomenon of quantum nonlocality, which under certain conditions remains in a strong macro limit [44].
The researchers performed experiments, the purpose of which was to measure the effect of a nonlocal source action on the detector signal. As processes-sources in these experiments, the processes of geomagnetic, ionospheric, synoptic and solar activity were studied, for which quantitative characteristics of nonlocal influence on trial processes were obtained. The principal independence of the results from a particular type of trial process was shown. In the main series of experiments, the source was the boiling of water with a known production of entropy. Two identical electrode detectors were used, including a process of known nature. Detectors were placed at distances of 0.5 and 4 meters from the source. The detectors were shielded from all known local impact types known from their theory.
The main qualitative result of the experiment [43] is that the nonlocal response of the detector is reliably recorded. The local thermal effect of the source on the detector was recorded, but it was three orders of magnitude smaller than the nonlocal one. The qualitative results of the experiment on measuring the effect of nonlocality of artificially excited dissipative processes confirm its universal character.
3.25. Experiments by Jiang Kanzhen
Jiang Kangzheng conducted a series of experiments that showed the possibility of direct transmission of information from one biological object to another using radio waves [45]. Jiang Kangzheng created the installation [46], which includes a hollow, regular polyhedron and hollow cones located on its faces. The biological object that carries out the action is placed in the cavity of the polyhedron, its radiation amplifies and is transmitted to another living object in the form of microwave radio waves.
In experiments with cereal crops, Jiang Kangzheng put green mass of wheat into his plant and exposed radio waves to germinating corn seeds. "Processed" corn had many side stems. In place of panicles, peculiar ears with grains, similar to corn, and wheat were formed (Fig. 26a). Acquired new qualities were steadily passed on to succeeding generations.
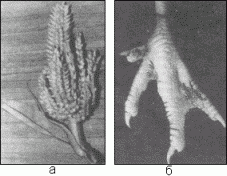 Fig. 26. The results of Jiang Kangzhen's experiments [45].
Using this technique, Jiang Kangzhen conducted experiments on animals. He put a duck in the installation and irradiated 500 eggs of chicken. Hatching 480 chickens, whose paws appeared on the legs (Fig. 26b), the position of the eyes changed and there was a flat duck shape of the head [45].
Jiang Kangzhen believes that when young organisms are exposed to old ones, they can rehabilitate the DNA of the latter and thus rejuvenate them. Experiments were carried out on old mice. They were exposed to the radiation of young germs of plants and embryos of animals. As a result, the mice improved their reactions, mobility, appetite. Some have recovered their sexual functions and reproductive capacity. For most of the experimental group, life expectancy increased by 1.5 years compared with the control group [45].
3.26. The Wave Genome
PP Garyaev advanced the idea that the genetic apparatus builds an organism with the help of acoustic and electromagnetic waves of a wide range [47]. The results of the following experiment are given in [47]. In a chamber made of permalloy, a material that does not allow the passage of electromagnetic waves, all the conditions necessary for the appearance of tadpoles from the frog's calf were created-temperature, humidity, the change of day and night, the composition of water and the atmosphere. The same conditions were created in another chamber - from ordinary material without shielding. Both fertilized frog eggs were placed in both chambers. In a normal chamber, development was normal, and the hatched tadpoles turned into frogs. All the tadpoles hatched from the caviar in the permaloe chamber died.
Pyotr Garyayev explains such results of the experiment by the fact that not all the information necessary for building an organism is stored in a fertilized sex cell, but only information on the synthesis of various proteins. The rest of the information comes through several external channels [47].
3. 25. A new method of obtaining energy, based on the decay of a proton
In the second half of the 20th century, scientists came to the conclusion about the possibility of proton decay [48,49].
In [50], the conditions under which a new method of obtaining energy based on proton decay can be realized. If the proton is given additional energy, such that it exceeds the energy of ≈108 MeV, then it must lose stability and decay into light particles having a very short lifetime. This is the basis for a new way of obtaining energy. In Fig. 27 shows the scheme of energy transformations in a new way of obtaining energy.
Since all elementary particles that are lighter than a proton are unstable, such a scheme will not lead to the appearance of a residual substance at the final stage of energy transformations [51, 52]. This makes the method of obtaining energy environmentally friendly.
The impact on the substance with the aim of destructuring it can become a universal and effective tool for ensuring the environmental safety of production and transforming production waste into thermal energy. This fundamentally changes the view of existing types and classes of energy carriers and will allow to consider even hazardous wastes as potential energy carriers.
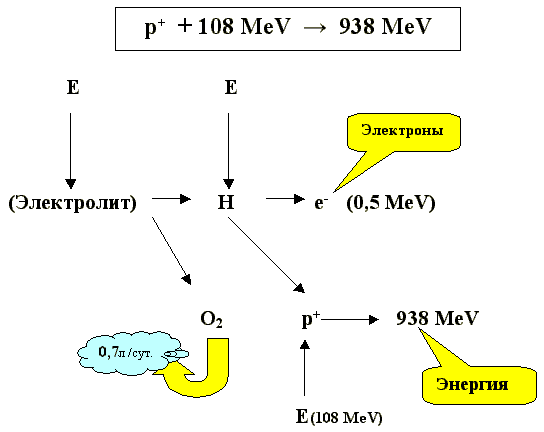
Fig. 27. Scheme of energy transformations in a new way of obtaining energy [50].
4. A new understanding of the essence of the physical vacuum
In the problem of the physical vacuum, the important point is the definition of the requirements, upon satisfaction of which the physical vacuum can be attributed to the most fundamental kind of physical reality. Modern physical theories demonstrate the tendency of the transition from particles - three-dimensional objects, to objects of a new species, having a smaller dimension. For example, in superstring theory, the dimension of superstring objects is much smaller than the dimension of space. It is believed that physical objects that have a smaller dimension have more grounds for claiming a fundamental status. In this respect, the approach of V.Zhvirblis [53] can be considered breakthrough. Zhvirblis argues that the physical vacuum is a continuous material medium. By analogy with the "Peano thread", infinitely densely filling a two-dimensional space, conditionally divided into squares, the author suggests his model of a physical vacuum - the "Zvirblis thread", infinitely densely filling a three-dimensional space conditionally divided into tetrahedra. In our opinion, this is a huge breakthrough in understanding the essence of the physical vacuum. Zhvirblis as a model of physical vacuum considers a one-dimensional mathematical object - "the thread of Zvirblisa". Unlike all known models, in its model of discretion the most minimal place is allocated. And in the limit it is understood that in the case of super-dense filling of space, the medium becomes continuous.
As noted above, in connection with the fact that the physical vacuum claims a fundamental status, even on the ontological basis of matter, it must have the greatest generality and it should not have particular characteristics characteristic of the set of observable objects and phenomena. It is known that assigning an object to an object reduces the universality of this object. For example, the pen is a universal concept. Adding a feature narrows the circle of objects covered by this concept (door handle, ball-point pen, etc.). Thus, we come to the conclusion that on the ontological status one can claim that essence which is devoid of any features, measures, structure and which can not be fundamentally modeled, since any simulation involves the use of discrete objects and description by means of signs and measures. The physical entity claiming a fundamental status should not be compound, because the composite entity has a secondary status in relation to its constituents.
Thus, the requirement of fundamentality and primacy for some entity entails the fulfillment of the following basic conditions:
- Do not be compound.
- To have the least quantity of attributes, properties and characteristics.
- To have the greatest commonness for the whole variety of objects and phenomena.
- Be potentially everything, but nothing.
- Do not have any measures.
Do not be compound - it means not to contain anything but yourself. Relatively fewest features, properties and characteristics should be ideal - not to have them at all. To have the greatest commonality for the whole variety of objects and phenomena is to not have the attributes of private objects, since any concretization narrows the community. To be potentially everything, and actually nothing - this means to remain unobservable, but at the same time to maintain the status of a physical object. To have no measures is to be zero-dimensional.
These five conditions are extremely consonant with the philosophy of the ancient philosophers, in particular, representatives of the school of Plato. They believed that the world emerged from the fundamental essence - from the original Chaos. In their views, Chaos spawned all existing structures of the Cosmos. In this case, they considered Chaos to be a state of the system that remains at the final stage as some conditional elimination of all possibilities for the manifestation of its properties and attributes [8].
The above five requirements are not satisfied by any discrete object of the real world and not a single quantum field object. Hence it follows that only a continuous entity can satisfy these requirements. Therefore, the physical vacuum, if it is considered to be the most fundamental state of matter, must be continuous (continual). In addition, by extending the achievements of mathematics to the field of physics (the continuum hypothesis of Cantor [55]), we come to the conclusion that the multiple structure of the physical vacuum is inconsistent. This means that the physical vacuum can not be identified with the ether, with a quantized object, or considered it as consisting of any discrete particles, even if these particles are virtual.
In our opinion, the physical vacuum should be considered as an antipode of matter. In the language of Eastern philosophy, this means that matter and vacuum are correlated as mutually complementary and interconnected opposites of the type "YIN" and "YAN". Thus, we regard matter and the physical vacuum as dialectical opposites. A holistic world is represented jointly by matter and physical vacuum. Such an approach to these entities corresponds to the physical principle of Bohr's complementarity. In such a complementarity relationship, physical vacuum and matter should be considered.
With such a physical object - unobservable, in which it is impossible to indicate any measures, physics has not yet come across. It is necessary to recognize the existence of a new physical reality - a physical vacuum possessing the property of continuity. The physical vacuum, endowed with the property of continuity, expands the class of known physical objects [54]. Despite the fact that the physical vacuum is such a paradoxical object, it becomes more and more confident in the study of physics. At the same time, because of its continuity, the traditional approach, based on model concepts, is not applicable to vacuum. Therefore, science has to find fundamentally new methods for its study. The elucidation of the nature of the physical vacuum allows a different look at many physical phenomena in the physics of elementary particles and in astrophysics. The whole visible universe and dark matter are in an unobservable, continuous physical vacuum. The physical vacuum genetically precedes the physical fields and substance, it generates them, so the whole universe lives according to the laws of physical vacuum, which science still has to discover.
In a chain of problems connected with the knowledge of the nature of the physical vacuum, there is a key link relating to the evaluation of the entropy of the physical vacuum. We believe that the physical vacuum has the largest entropy among all known physical objects and systems, and therefore the Boltzmann H-theorem is inapplicable for it.
The above five criteria of primacy and fundamentality indicate that such an object can be satisfied by an object having the highest entropy. We believe that the vacuum-substance phase transition refers to the processes of self-organization. In exactly the same way as the Boltzmann H-theorem and Gibbs' theorem became the basic tool in thermodynamics, for the theory of physical vacuum it is necessary to search for our tool on the basis of a generalization of the H-theorem to the processes of self-organization. Such a breakthrough approach has already emerged. A fundamentally new approach, applicable to the study of physical vacuum, opens the law of entropy decrease, established by Yu. L. Klimontovich [7].
5. Conclusions
- The clarification of the essence of the physical vacuum is the most important task of modern physics, its solution will provide the key to the creation of a new physical theory.
- A physical object claiming a fundamental status must have the greatest generality and it should not have particular characteristics characteristic of the set of observable objects and phenomena.
- The most common is an object that has the property of continuity, so a physical vacuum claiming a fundamental status must have the property of continuity.
- A physical vacuum possessing the property of continuity expands the class of known physical objects.
- A continuous physical vacuum and a discrete substance are correlated as interrelated and complementary opposites, they are in complementarity relations, corresponding to the complementarity principle of N. Bohr.
- The physical vacuum has the greatest entropy among all known physical objects and systems.
- For the theory of physical vacuum, it is necessary to search for a new research tool on the basis of a generalization of the Boltzmann H-theorem to the processes of self-organization.
- A new approach to the study of the physical vacuum is opened by Klimontovich's S-theorem. The law of decreasing Klimontovich's entropy provides the key to resolving a fundamental conflict of continuity and discreteness that has not yet been solved in philosophy, in mathematics, or in physics.
The source of information
- Kosinov NV, Garbaruk V.I. "Energy phenomenon of vacuum."
Http://www.nt.org/tp/ie/efv.shtml
Http://rusnauka.narod.ru/lib/author/kosinov_n/1/
Http://www.sciteclibrary.com/eng/catalog/pages/2646.shtmll
Http://www.eprussia.ru/lib/elektro/nit_001.shtml
- Ya.B. Zeldovich. The theory of vacuum, perhaps, solves the problem of cosmology. UFN, Vol. 133, no. 3, 1981.
- Mostepanenko AM, Mostepanenko V.М. The concept of vacuum in physics and philosophy. Nature, 1985, №3, p.88-95.
- Zeldovich Ya.B. Is the formation of the Universe "out of nothing"? Nature, 1988, №4, p.16-27.
- GWWang, EMSevick, Emil Mittag et al. Phys.Rev.Lett., V.89, 050601 (2002).
- E.Onishchenko. Experimental observation of the violation of the second law of thermodynamics.
Http://www.scientific.ru/journal/news/0802/n300802.shtmll
- VIArshinov, Yu.L. Klimontovich, and Yu.V. Sachkov. NATURAL SCIENCES AND DEVELOPMENT:
DIALOGUE WITH THE PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE. Http://dr-gng.dp.ua/library/xaos/posl.shtml
- Klimontovich Yu. L. Decrease in entropy in the process of self-organization. S-theorem. Letters to the Technical Journal
Physics 1983, v. 8, p. 1412.
- Mudretskaya E.V. Earth physics and reality: A glance from the outside. - К .: Zadruga, 2000. - 176 with.
- Kosinov NV, Garbaruk V.Ifractals in plasma. Physical vacuum and nature, N5, 2002.
- Feigenbaum M. Universality in the behavior of nonlinear systems. Successes nat. Sciences. , 1983. T.141, N2, C. 343-374.
- "Generator of Hubbard" http://www.skif.vrn.ru/energy/arhiv2-3.shtml
- T. Brown "The Hendershot Motor Mystery", Extraordinary Science, v.2, 1992
- Niper, Hans. A. Revolution in Technik, Medizin, Gesellschaft. 1983.
- "The invention of Hans Coler, relating to an alleged new source of power," International Congress of Gravity Field Energy, March 20-21, 1987,
P.361-400
- Niper, Hans. A. Revolution in Technik, Medizin, Gesellschaft. 1983. "The Coler Converter of the German Navy", p. 132-133.
- "Resonance of Avramenko" http://www.skif.vrn.ru/energy/arhiv1-3.shtml
- Zaev NE, Avramenko SV, Lisin VN, "Measurement of the conduction current excited by a polarizing current".
Journal of Russian Physical Thought No. 2, 1991
- PECULIARITIES OF ENERGY TRANSFER IN THE FRONT AREA OF DISCHARGES IN THE PARTIES OF LITHIUM. Http://www.fpl.gpi.ru/Zvenigorod/XXVIII/PP/ru/u3/05-Pavlov.doc
- Kosinov NV, Garbaruk VI, Kosinov L.V. "PHYSICAL EFFECTS EXPLAINING THE ROTATION MECHANISM
EARTH "http://www.sciteclibrary.com/eng/catalog/pages/2406.shtmll
- "Azarov's micro-conditioning" http://www.skif.vrn.ru/energy/arhiv5-4.shtml
- Plasma. TSB т.33
- Niper, Hans. A. Revolution in Technik, Medizin, Gesellschaft. 1983. "Gravitational Field Energy Research in Japan" p. 68-71
- Sur la piste de l`energie libre http://quanthomme.free.fr
- Shakhparonov I.M. "RADIATION OF KOZYREV - DIRAK AND ITS INFLUENCE ON ANIMALS" http://www.physical-congress.spb.ru/russian/shahparonov/shahparonov.asp
- Technique of Youth, 10/1996.
- A.Frolov "Free energy" http://prometheus.al.ru/phisik/frolov.shtml
- Patent United Kingdom, number 300, 311 of August 15, 1927
- US Patent No. 3187206, filed June 1, 1965, filed May 9, 1956
- Jean-Louis Naudin "Lifters experiments" http://go.to/jlnlabs
- L.I. Urutskoev, V.I. Liksonov, V.G. Tsinoyev "EXPERIMENTAL DETECTION OF" STRANGE "RADIATION AND
TRANSFORMATION OF CHEMICAL ELEMENTS " http://jre.cplire.ru/jre/mar00/4/text.shtmll
- L.I. Urutskoev, V.I. Liksonov, V.G. Tsinoev "Observation of the transformation of chemical elements in the discharge" Applied Physics, no. 4,
Pp. 83-100, 2000.
- Stakhanov IP On the physical nature of a lightning bolt. - M., "Scientific World", 1996, p.262.
- Ball lightning in the laboratory. - M., "Chemistry", 1994, p. 255.
- Http://vesti.ru/2001/07/26/996163684.shtmll
- Http://www.grus.ru
- US Patent No. 5,964,913
- Patent Russia, number 2174162 dated 27.09.01
- Hydrogen Generator Studennikov http://www.skif.biz/energy/arhiv3-3.shtml
- N. V. Udaltsova, V. A. Kolombet, S. E. Schönol "Possible Cosmophysical Distinctness
MACROSCOPIC FLUCTUATIONS IN PROCESSES OF DIFFERENT NATURE " http://www.mvu.narod.ru/Schnol.shtmll
- Lupichev NL, Marchenko VG "The role of superweak radiations in biological processes". "Bulletin of the experimental
Biology and medicine "of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR .- М., 1989.-8с., Dep., VINITI № 5712-В.
- Lupichev N.L. "Electro-puncture diagnostics, homeotherapy and long-range phenomenon". Moscow, 1990.
- Korotaev SM, Serdyuk VO, Sorokin MO, Machinin VA "Experimental study of non-locality of controlled
Dissipative processes " http://www.chronos.msu.ru/Public/korotaev_eksperimentalnoe.shtmll
- Home D., Majumbar AS, Phis. Rev. A52, (1995), p. 4959
- Sergey Demkin "Miracles and adventures", "TM" N4, 1996
- Patent of Russia No. 2044550, 1995
- Teleportation? Elementary! Http://www.skyzone.al.ru/tech/garjaev07.shtmll
- Ya.B. Zeldovich. The theory of vacuum, perhaps, solves the problem of cosmology. UFN, Vol. 133, no. 3, 1981.
- A.D. Sakharov. Violation of CP invariance. C-symmetry and baryon asymmetry of the universe. Letters to the ZhETF, Vol.5, 1967, p. 33-35.
- Kosinov NV, Garbaruk V.I. "INTERNAL PROTON STRUCTURE AND A NEW METHOD OF OBTAINING ENERGY"
Http://www.sciteclibrary.com/eng/catalog/pages/2264.shtmll
- N.V. Kosinov, V.I. Garbaruk. Vacuum origin of the electron. Physical vacuum and nature, N1, 1999.
- N.Kosinov, V.Garbaruk "Vacuum origin of Electron and Positron". Physical Vacuum and Nature, N4, 2000.
- V. Zhvirblis "NOT" THE WORLD ETHER ", AND PHYSICAL VACUUM" http://re-tech.narod.ru/fizique/teor/vacuum.shtml
- Kosinov N.V. Electrodynamics of physical vacuum. Physical vacuum and nature, No. 1, 1999, p. 24-59.
- Cohen P.J. Theory of sets and the continuum hypothesis. Trans. With English., M.: 1969.
- Nedospasov AV, Mudretskaya EV, Zhmendak AV Strongly ionized turbulent lithium plasma // DAN-200-t.374.-P.754-756.
- Mudretskaya EV, Pavlov SN, Kvitsinsky VA, Verco VF, Sergienko GV, Huber A. Investigation of the structure of turbulence in lithium plasma. The fourth meeting on magnetoplasma aerodynamics in aerospace applications (annotations to reports), Moscow, April 9-11, 2002, p. 92.
- V.F. Virko, V.A. Kvitsinsky, E.V. Mudretskaya, S.N. Pavlov, S.A. Perevoznikov. FEATURES OF ENERGY TRANSFER IN THE FRONT AREA OF DISCHARGES IN THE PARTIES OF LITHIUM.
Http://www.fpl.gpi.ru/Zvenigorod/XXVIII/P.shtmll
print version
Authors: Kosinov NV, Garbaruk VI, Polyakov DV
PS The material is protected.
Date of publication 04.02.2004гг


Liked? Subscribe to RSS news! You can also support shram.kiev.ua, press:
It will not be superfluous for your friends to learn this information, share their article with them!
|



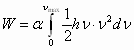 ,
, 





















Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.