HEMATITIS (BLOODWOOD)


 Characteristics of the mineral.
Characteristics of the mineral.
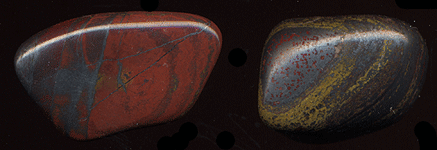
Hematite is a stable modification of iron oxide. Cleavage is absent. The chemical formula is Fe2O3. Specific gravity 5.3 g / cm3. Color from black in large-crystal aggregates to bright red in dense varieties. Hardness 5. It has been known since ancient times as an ornamental stone. His other name is a bloodstone and since ancient times he is a powerful talisman, amulet and amulet simultaneously. Often hematite is forged in the form of cheap bracelets, beads or rings "for three rubles." This is not natural hematite, but a special ceramic fake. In order to distinguish hematite from a fake or other stone, you need to force them to carry on unglazed porcelain (faience), and hematite will leave a red trail.
In order to reliably, surely and very simply distinguish natural hematite from a very similar to it cheap ceramics (imitation), it is enough to remember two diagnostic features. First, ceramics are light enough, and hematite is a much heavier iron-containing material. The weight of even a small piece of hematite is felt on the palm as a weft. Secondly, natural hematite is attracted by a strong magnet, and ceramics is not (does not react at all). In the rock, veins of hematite can be found with a magnet. Not without reason deposits of hematite mark strong magnetic anomalies in the earth's crust. This is enough to distinguish hematite from imitation. Similar to hematite is a mineral magnetite, which in this case has magnetic properties.
When processing hematite on the machine, the sparks are red due to iron oxide. Hematite is also called by its red color "iron wool" and is used as a natural mineral paint. In ancient times it was called predominantly a blood-colored powder and was considered curative in wounds, bleeding, inflammation and outbursts of anger. Named from the Greek. "Game" - the blood. Synonyms: Alaskan black diamond or diamond black, bloodstone. The radial-fibrous variety of hematite (the "red glass head") is formed in low-temperature hydrothermal processes, often under near-surface conditions. It is possible to form aggregates of hematite and multi-colored jasper, both hematite-cut jasper masses, and solid hematite with dot-colored inclusions or layers, called hematite jasmoids (a beautiful and original ornamental mineral), which usually speaks of the natural origin of the mineral. Hematitis can be associated with the tiger's eye.
Hematite varieties: iron shine - with a strong semimetallic luster; Iron mica - scaly aggregates of hematite; Red iron ore - dense, cryptocrystalline; Red glass head - large kidney-shaped forms with radial-radiant structure. Treated hematite is similar to morion, black agate, obsidian, goethite, from which it is distinguished by strong metallic luster, high density, reddish color and firmness. Fragile. Hematite is used not only in jewelry - in the first place today it is an important iron ore.
Magic properties of stones.
Its main advantage is to save the owner from bouts of anger and rash actions, to feel confident and secure because hematite gives an opportunity to influence other people, events and many processes. It helps to accumulate and use energy as the owner wants. However, we must remember that a person who wants to harm others, the stone itself can do a lot of trouble: hematite does not like to work for evil, although it is misinformed about him that the stone is almost an obligatory part of black magicians, sorcerers, etc. On the contrary, Hematite is a stone of soothsayers, allowing you to penetrate into the secrets of nature in order to help a person, and about its medicinal properties you can write volumes. Bloodworm was widely used in medieval magic. The magician did not dare to summon spirits, not having a finger ring with a blood on his finger. A stone of magicians and spellcasters, protects from evil power. It contains the power of Mars and the tremendous energy that allows this stone to affect other people.


Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity).
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in the case of radioactivity over 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection).
All rare stones are subject to mandatory inspection at the standard dosimeter for the permissible level of radiation and in the chemical laboratory for the absence of poisonous and evaporating components that are dangerous to humans and the environment.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.