RUBY



 Characteristics of the mineral.
Characteristics of the mineral.
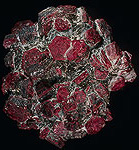
Ruby - one of the most expensive jewelry stones. This is a kind of corundum, aluminum oxide. Takes second place in hardness after diamond. The color of the stone is associated with an admixture of chromium. Corundums, painted in other colors, are called sapphires. It can be confused with less hard zircons, grenades and spinel (the latter is a precious but less expensive stone). In Russia all the red stones were called jacons. Today, artificial rubies from dark pink to red and densely red (corundums) are very popular, having, unlike natural rubies, perfect transparency, even color, large size, absence of cracks and foreign impurities. Like natural sapphire, natural ruby is star-like: mineral inclusions of rutile parallel to the faces of the crystal, sometimes intersect at an angle of 60 degrees, forming a 6-ray star (pure rubies with a star very expensive, opaque cheaper).
From the point of view of mineralogists, ruby is a red variety of corundum mineral, a widespread natural compound of aluminum oxide (Al2O3). Nature has created a very perfect design in the crystal lattice of corundum. It is built from aluminum and oxygen ions so that the oxygen ions are layered in a dense hexagonal package, like billiard balls in a box, and between the layers of oxygen - in voids - aluminum ions are filled, filling two-thirds of all the voids. This is one of the most perfect and dense structures of minerals. And it is no accident that the properties of pure precious corundum are so close to the properties of diamond. The famous color of the candle flame color appears when chromium enters the lattice of the mineral in place of a portion of the trivalent aluminum ions. The content of Cr2O3 is about 2% in red rubies, about 4% in red and black rubies. Ultraviolet and infrared rays "excite" trivalent chromium ions, charge them with energy, and they begin to emit visible light-luminescence. Their red color is really glowing.
Large rubies are found less often than diamonds and today are more expensive. For the years 1870-1970. More than 300 diamond crystals with a mass of more than 200 carats were found, and only a few pieces of the same optically pure rubies. Very large rarity - pure rubies with a mass of more than 30 carats. In the world market, a two-carat ruby costs twice as much as an equal-sized diamond. With increasing magnitude, the price divergence is even stronger. In the East, ruby from ancient times was considered the most valuable jewelry stone. Prior to 1800 rubies were also called some other red stones: Cappuccino rubies - grenades from South Africa, rubies-balet - Burmese spinel, Colorado and Arizona rubies - grenades from pcs. Colorado and Arizona (USA), Brazilian rubies - pink topazes of Brazil, Siberian rubies - rubellite (tourmaline) of Siberia.
The red color of ruby is determined mainly by the admixture of chromium ions, the content of Cr2O3 in densely stained samples can reach 4%. Pink stones are not rubies, as these are tinted corundums (sapphires). The shades of color are affected by impurities: a brownish tinge is associated with an increase in the content of iron ion impurities, violet - vanadium, etc. The intensity and shades of ruby color can vary greatly. Burmese rubies have a blood-red color. The best rubies of this variety are found only in Burma. The color of Siamese rubies from violet to brownish red, Ceylon rubies from light to violet red. The most valuable stones are red with a light purple hue. Strengthening the violet and the presence of orange shades reduce the cost of the stone. The stones with a brown tint are least valuable. According to the intensity of any color, the average tone has the greatest value, followed by a light and dark tone. Uneven coloring also reduces the cost of the stone.
Ruby processing uses facet cut. To identify the most beautiful violet-red color, the ruby is oriented perpendicularly to the optical axis during cutting. The most important thing in ruby is not brilliance, but depth and color saturation. The cost of a stone is less affected by its defects (cracks, opacities, inclusions) and the quality of the cut itself. From stones with the effect of asterism (running on the surface of the star) or a cat's eye, cabochons make such stones in nature are usually not transparent (excessive transparency and high contrast of the star on the surface of the stone may indicate the origin of this ruby or sapphire).
The deposits of rubies of Burma are confined to skarned marbles, which are in contact with dikes of granites or granite-pegmatites (the frozen outlets of red-hot magma of extinct volcanoes). The Mogoka area of Burma, with an area of about 400 km2, is the most ancient area for mining precious stones. Rubies are found in the form of granular, nest-shaped clusters or individual crystals interspersed in the main soft rock - marble. Industrial extraction of rubies is conducted from placers formed during the destruction of ruby-bearing marbles. The crystals of a prismatic or barrel-shaped ruby are fairly large. Coloration is red, pink, often uneven. There are rubies with asterism (quite often).
Diagnosis of noble corundum is complicated by the fact that there is a significant number of minerals used as their imitations or simply very reminiscent of them. Of all these minerals, the ruby is distinguished by its high hardness. It is the hardness caused by the defect of "fire signs", sometimes formed during its processing and faceting, which is formed by small uneven cracks in the near-surface part of the stone. A natural ruby is usually difficult to confuse with its ideal synthetic analog. Diagnosis of them is done by physical properties and inclusions.
Magic properties of stones.
It allows the owner to be in complete safety even among enemies, rewards invulnerability, but for this, the stone must be worn under clothing on the body and it is desirable never to part with it. He manages love desires, settles disputes, protects from harmful magic, corrects a bad mood, relieves grief and sadness. A stone of saturated tones relieves nightmares. Rubin increases responsibility in man and promotes leadership aspirations, relieving the owner of complexes of inferiority and uncertainty. He gives birth to love and gravitation to the great, whether it be science, art, military affairs, etc. It is generally said of the ruby that he gives the lion's strength, fearlessness of the eagle and wisdom of the serpent. The stone can change color, that the owner will serve as a warning about the danger, but for this ruby skill you need to watch long enough, if only because the color does not change too much. Ruby is the stone of those who want to achieve much in life, and he supports the master in this if he does not have vanity and understands that great goals are the goals of achieving happiness for other people. With usurpers ruby lives extremely reluctantly and, as a rule, does not give them their energy. A bad person ruby will try to de-energize, pump out energy from it.
Ruby is a stone of passionate and passionate love. It was believed that if you wear a ruby in a suspended form - it means being great among people, worthy of their respect. Ruby is a stone of power, strength and turbulent energy associated with the karma of other people, strong and bright. Scarlet, pure ruby water, strengthens strength, chases depression and protects from evil spells, changing shades of color warns its owner of imminent danger. Irritant and unrestrained people as a talisman ruby is dangerous, because. Its influence can push on a rash act, plunge into the irreparable, intensify the natural cruelty. For people who are unkind by nature - this is an evil demon, whose influence becomes fatal. On the contrary, the ruby is shown to the person timid, shy, for developing a choleric temperament, gives the will to victory, drives sadness. Ruby gives rise to the attraction to the great. It is a mystical stone associated with the mysteries of the beyond world.






Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity).
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in the case of radioactivity over 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection).
All rare stones are subject to mandatory inspection at the standard dosimeter for the permissible level of radiation and in the chemical laboratory for the absence of poisonous and evaporating components that are dangerous to humans and the environment.


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.