Carbonates: Dolomite
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
Photo: dolomite crystals and pyrite. Below: dolomite mine of Traversella (Turin). Bowl of differently colored dolomite.
Ca Mg (CO 3)2
Crystal system trigonal
Hardness of 3.5-4
Specific gravity 2.85-2.95
Cleavage easily divided
fracture conchoidal
Colour colorless, raznookra- Weighted
Color white powder
Shine from glass to pearl
Dolomite mineral called and composed of his breed. Calcium and magnesium carbonate. Gloss glass. It shines through. Colours: white, yellow, brown; rarely is colorless and translucent. The bar is white. Fracture conchoidal. Fragile. Cleavage is perfect. In contact with warm dilute hydrochloric acid, "effervescence."
Rock-forming mineral sedimentary carbonate rocks. It formed in hydrothermal veins and fractures. It often occurs intergrown with calcite. The crystals (trigonal crystal system) usually curved saddle. Among them dominate rhombohedrons (same shape and have spines vykolki). Frequent granular aggregates, solid, large crystal blocks with a distinct cleavage, dense and porous cellular mass. Distributed everywhere.
Anchors, or brown spar. The iron dolomite. In rare large masses typically formed under hydrothermal conditions.
 Presented rhombohedrons formed by the planes of faces that represent the diamonds. Typical are also aggregates of crystals with curved surfaces faces, giving them the appearance "of a cavalry saddle."
Presented rhombohedrons formed by the planes of faces that represent the diamonds. Typical are also aggregates of crystals with curved surfaces faces, giving them the appearance "of a cavalry saddle."
The crystals having good cleavage along the rhombohedron can be colorless and transparent, sometimes light gray, yellowish, pinkish and then opaque. Sunblaze colorless crystal-glass, but more typical pearl, especially saddle units. Dolomite can be a solid mass or dense saccharoidal addition, sometimes cavernous.
Chemical composition. The double salt of CaCO 3 - MgSO3; calcium oxide (CaO) 30.4%, magnesium oxide (MgO) 21,7%, carbon dioxide (CO2) 47.9%; isomorphic impurities: iron, manganese (up to a few percent). Form crystals. rhombohedral; crystal faces often curved. The crystal structure. Characterized in that calcium ions (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) alternate along the threefold axis. Class symmetry. Rhombohedral - 3. Cleavage. Perfect for the rhombohedron (1011). Aggregates. Typically, granular, often porous, less kidney-shaped, hollow, spherical.
 Diagnostic features.
Diagnostic features.
Dolomite is scratched with a knife, and not too heavy. From calcite is characterized in that no effervescence in contact with cold dilute acids. Not melts and cracks. Behavior in acids. The cold HCl dissolves slowly and heated - faster (with a strong effervescence); calcite vigorous effervescence in the cold HCl.
Origin.
Dolomite - is a very common mineral, the main component of sedimentary carbonate rocks, dolomite and dolomitic limestone. They are formed mainly by the action of seawater, enriched with magnesium, to marine calcareous sediments. Thus there is the gradual replacement of the magnesium-calcium. Dolomite is also present in some of the low-temperature hydrothermal veins among the various metamorphic rocks.
Place of Birth.
In Italy it is very common. In the Piedmont crystalline dolomite is found in crevices among the dolomite saharoobraznyh Krevola d'Ossola. Gorgeous crystals known from mines Brosseau and Traversella near Turin. In the region of Lombardy in the form of saddle dolomite crystals found in quartz porphyry in Guasso al Monte (Province of Varese). It is abundant in the dolomite formation and often falls among Carrara marble. Excellent samples of dolomite crystals known in the region of Navarra (Spain).
Application.
Pure dolomite is an excellent raw material for extraction of magnesium metal, used mainly in the production of light alloys. Dolomite prepared from magnesium salts used in medicine. In the building materials industry dolomite used for the manufacture of special types of cement.

Magnesium - component enzymes in the human body is contained in bones, teeth, is a regulator of the nervous system. Magnesium - macrocell, which is suffering from the disease to 90% of people. The human body contains approximately 140 g of magnesium (0.2% by weight), and accounts for 2/3 of the bone tissue. The main "depot" magnesium is in the bones and muscles in the form of phosphates and bicarbonates. Magnesium comes into contact with food (in particular the sodium salt - bitter "Artyomsol") and water.
Depletion of blood magnesium noted in rickets. Symptoms of magnesium deficiency: the deterioration of the transmission of nerve and muscle impulses, causing irritability and nervousness, increased excitability, spasms and cramps, disorientation in time and space, insomnia, migraine, chronic fatigue, digestive disorders, heart palpitations, seizures, fits of anger or irritation. The first sign of magnesium deficiency are twitching and convulsions, especially the calf muscles. Psychiatric mineral.
Magnesium deficiency underlies the cardiovascular diseases. Against the background of continuous magnesium deficiency increases the risk of atherosclerosis of the heart arteries, heart attacks and heart rhythm changes. It can be a cause of fatal cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, cardiac arrest, asthma (particularly on the basis of inhalation cinnabar), chronic pain syndrome (PTSD), depression, insomnia, irritable bowel syndrome and pulmonary diseases. Develop arthritis and osteoporosis. Most magnesium is contained in wheat bran and sprouts of cereals (520 and 270 mg per 100 g).
Magnesium is essential: for hypertension, symptomatic hypertension, atherosclerosis, liver disease and biliary tract, depression, dizziness, muscle weakness and twitching, in psoriasis, scleroderma, lupus erythematosus, premenstrual syndrome, to maintain the body's normal pH balance, calcification of soft warning tissues. It provides protection from arterial endothelial stress caused by sudden drops in blood pressure, necessary for the formation of bone and mineral metabolism of carbohydrate, to dissolve kidney stones formed from oxalates and phosphates. Magnesium enhances the effectiveness of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), important for the prevention of atherosclerosis.
Increased magnesium level (gipermagniemiya) may occur in the blood while taking antacids or laxatives containing magnesium, in patients with chronic renal failure. For parenteral administration of magnesium sulphate may experience symptoms of intoxication in the form of a general depression, weakness and drowsiness (brain involved), cardiac failure. The use of magnesium sulfate solution in pregnancy and childbirth in a 4-fold increased risk of cerebral palsy in the newborn (weak mother's birth). Anesthesia (coma) occurs when the concentration of magnesium in the blood of 15-18 mg%.
Magnesium afraid of even the doctors, it is a dangerous "comatose" ( "sleepy") drug depressing brain - almost 100% of the hospital (for the treatment of medical magnesia). The mineral ions which are "working" on the junction of the neurons (axons). In acute renal failure with oliguria, especially in combination with metabolic acidosis, gipermagniemiya possible. calcium infusion (antagonist) may counteract the toxicity of magnesium.
ADR 4.1

Flammable solids, self-reactive substances and solid desensitized explosives
Risk of fire. Flammable or combustible materials can be ignited by sparks or flames. May contain self-reactive substances that are liable to exothermic decomposition in the case of heating, contact with other substances (such as acids, heavy-metal compounds or amines), friction or shock.
This may result in the evolution of harmful and flammable gases or vapors or self-ignition. Containers may explode when heated (ultra-hazardous - practically do not burn).
Risk of explosion of desensitized explosives after loss of desensitizer
Seven vertical red stripes on a white background, of equal, the number of ADR, the black flame
ADR 4.2

Substances capable of autoignition
Risk of fire as a result of self-ignition if packages are damaged or there is the source of the content.
May react vigorously with water
White upper half of the rhombus, red - the lower, equal size, number of ADR, the black flame
ADR 4.3


Substances that emit flammable gases in contact with water
The risk of fire and explosion on contact with water.
Goods that are scattered, you need to cover and keep dry
Blue diamond, the number of ADR, black or white flame
ADR 5.1
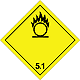
Substances which are oxidized
Risk of vigorous reaction, ignition and explosion in contact with combustible or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, the number of ADR, a black flame over a circle
ADR 6.1
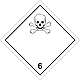
Toxic (Poison)
Risk of intoxication by inhalation, skin contact or ingestion. Constitutes a danger to the aquatic environment or the sewage system
Use a mask for the emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, the number of ADR, black skull and crossbones
| Name of especially dangerous during transportation of cargo | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| Magnesium nitrate cm. Magnesium nitrate | 1474 | 5.1 |
| Magnesium - Magnesium alloy powder or - POWDER | 1418 | 4.3 |
| Magnesium or magnesium alloys containing more than 50% of magnesium (pellets, chips or strips) | 1869 | 4.1 |
| Magnesium silikatnoftoristy see. Magnesium fluorosilicate | 2853 | 6.1 |
| MAGNESIUM COATED GRANULES The particle size of at least 149 microns | 2950 | 4.3 |
| Magnesium phosphide (Mg3 (PO3) 2) cm. Magnesium phosphide (Mg3P2) | 2011 | 4.3 |
| Magnesium diamide | 2004 | 4.2 |
| magnesium arsenate | 1622 | 6.1 |
| Magnesium BROMATE | 1473 | 5.1 |
| of magnesium hydride | 2010 | 4.3 |
| Magnesium methyl bromide in diethyl ether cm. Methyl magnesium bromide in ethyl ether | 1928 | 4.3 |
| magnesium nitrate | 1474 | 5.1 |
| Magnesium peroxide (peroxide) | 1476 | 5.1 |
| magnesium perchlorate | 1475 | 5.1 |
| Magnesium silikatftorid see. Magnesium fluorosilicate | 2853 | 6.1 |
| magnesium silicide | 2624 | 4.3 |
| Magnesium phosphide | 2011 | 4.3 |
| Magnesium fluorosilicate | 2853 | 6.1 |
| Magnesium chlorate | 2723 | 5.1 |
| Magnesium chloride solution | - | - |
| Magnesium-aluminum phosphide | 1419 | 4.3 |
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.