Halides: Halite (salt)
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
The crystals of salt distinct cubic shape. At the bottom of the accumulation of crystals of the Salton Sea, Imperial City (USA)
Na Cl (sodium chloride)
Crystal system cubic
Hardness 2
The proportion of 2.1-2.2
Cleavage is perfect
fracture conchoidal
Colour colorless, raznookra- Weighted
Color white powder
Gloss glass
Rock salt or halite. Rock salt mineral called himself, and folded them to breed. Sodium chloride. Gloss glass, zhirnovat. Transparent. Colours: white, gray, yellow, blue, red; often colorless. The bar is white. Fracture conchoidal. Cleavage is perfect. Taste salty. Colors the flame yellow. Formed mainly in sedimentary rocks. The crystals (cubic system) have the shape of a cube. Often forms dense solid mass. Deposits: Stasfurt (Germany), Lower Saxony, Bavaria (Germany), Tyrol (Austria), Italy, Spain, CIS, USA.
 Usually it crystallizes in the form of a cube. On the faces of the crystals is often observed characteristic distortion in the form of depressions, which are called "square craters." This phenomenon - evidence of very rapid and uneven growth of the crystal, since the substance is deposited on the edges of a lot faster than on the faces of the plane. Galit can be massive or granular.
Usually it crystallizes in the form of a cube. On the faces of the crystals is often observed characteristic distortion in the form of depressions, which are called "square craters." This phenomenon - evidence of very rapid and uneven growth of the crystal, since the substance is deposited on the edges of a lot faster than on the faces of the plane. Galit can be massive or granular.
Table salt - typically allohromatichesky mineral. It can take very different color - from colorless to almost black because of the bituminous inclusions; sometimes reddish, red or gray-red due to the inclusion of tiny dendrites, hematite or iron hydroxide. Often it can be blue, unevenly distributed over the volume of the crystal, that is possibly connected with the manifestations of natural radioactivity. Similar to the glass, transparent and translucent, the salt is a soft, light and fragile mineral. She has a perfect cleavage on the cube.
Chemical composition. Sodium (Na) 39,4%, chlorine (Cl) was 60.6%. Form crystals. Cubic crystals, often grainy or shpatopodobnye aggregates (rock salt). The crystal structure. Typical ionic structure. Face-centered cubic lattice of sodium ions (Na +) and chlorine ions (Cl), alternating in the crystal lattice, are located at the corners of the small cubes (see Table 1..). Class symmetry. Geksaoktaedrichesky - m3m. Cleavage. It is very perfect for the cube; mineral splits in three directions; fluidity different. Aggregates. Granular or dense mass (rock salt).
Diagnostic features.
The main feature of salt - the ability to dissolve in water. Its solution has a pleasant salty taste incomparable with a bitter taste, which provide potassium and magnesium salts. It melts, turning the flame yellow. The water dissolves easily, has a pleasant salty taste, very different from similar sylvite, and is readily soluble in water, but has a pungent taste. You can not be confused with poisonous radioactive celestite !!
Although in itself "halite (table salt) in pure form" human needs, his illiterate ingestion can cause poisoning, disease and even death. In Galite there are two types of chemical impurities - surface that can be washed off or gently scrape off, and distributed in the thickness of the crystal. Before any chemical analysis of all the halite salt - especially blue and blue - are primary (!!) a rigorous test on a regular dosimeter without exception. This ensures the production of injury caused by radiation.


Blue and violet halite (table salt) with impurities hazardous to health - soluble


Fluorite (crystals to 2 cm). Elmwood Mine, Tennessee, USA. It looks like halite. Photo: © AA Evseev.
 Physical features blue and blue halite.
Physical features blue and blue halite.
This mineral may contain radioactive components of the blue and blue (normal natural radiation - 17-24 mR / hr). Elevated levels of stones and minerals radiation yavlyaetsya radiation level from 29-32 mR / h and above. On the right - the sign of a potential radiation hazard (Ukraine, K.305).
Radioactive rocks and minerals during prolonged wearing on the neck can cause radiation damage shitovidnoy gland and cause its changes (including cancer). Similar local damage can be caused by prolonged wearing hazardous minerals directly at the chest or in the pockets of men's trousers. Because of the high background radiation, these hazardous minerals chosen by men, leading a solitary life - and that harm to health and the environment (lead unhealthy lifestyles).
Safely carry minerals with low levels of radiation, regardless of their type on the hands (in the rings and brasletah- "wristband") and on the legs - as far as possible from the thyroid gland, birthmarks, moles large (particularly convex) from the breast, superficial lymph nodes, etc. easily the targeted object radiation on the human body. In any case, for safety and environmental reasons, it is not recommended to wear a poisonous and potentially radioactive rocks and minerals constantly and keep in an apartment or the office of the major examples of such minerals (house and apartment - not a mineralogical museum with acceptable levels of radiation from 32 to 120 mR / h and above for mineralogical expositions and special depositories of state institutions).
The radiation from a point source and object decreases with the square of the distance to the object. Moving away 2 meters from a dangerous object, you can reduce the level of study of this object is 4 times. Stepping back 10 meters, you will reduce the radiation level of the object 100 times. If the object has a point source of radiation in 2000 mR / h with natural background ambient radiation 19 mR / hr (total of 2000 +19 = 2019 mR / h), moving away from a dangerous object at 10 meters, you will protect yourself until the radiation level of 20 mR / hr on the subject and 19 mR / hr from the environment (total overall level of radiation from the object and the environment will have 20 + 19 = 39 mR / hr).
Dangerous is the direct contact with the body and worn on the body point and diffuse sources of radiation and radioactive components (about 50% of the radiation is absorbed by contact with the outer surface of the body and about 100% of the radiation - ingestion of radioactive or contaminated object). The most dangerous is the direct ingestion of radioactive components, rocks and minerals, including comminuted into a powder and particularly soluble in the liquid. All unauthorized injection of radioactive drugs are strictly prohibited. It is not sapifry !! Unlike natural sapifrov not soluble in water, blue and blue halite dissolve easily and lose weight (their sale - fraud) !!! Halite - soluble mineral.



Remember, this is important - if chemical impurities distributed within the salt and form a detachable part with her friend of other components, such dyed salt (halite) is not used in foods under any circumstances. "Color" salt is not subject to any mechanical and chemical treatment, with a view to the subsequent eating of living creatures and treated exclusively as industrial production and raw material for non-food industries (even cleared of colored impurities !!) - it is not food and fertilizer.

Blue halite, almost perfect fake sapphire (dissolved).
Radioactive. Based on materials from the website http://www.catalogmineralov.ru/
Specific compounds of red can be suspected in these mineral salts aggregates red cinnabar - mercury poisonous salt. The photos above are obviously inedible halite samples with dangerous minerals. So look impurities to Galit not only blue salt, but also the most dangerous toxic soluble salts of mercury - red cinnabar, a favorite stone "black lithotherapists" (especially from Western Europe, and Spain, which revealed the largest deposits of red cinnabar - especially dangerous lake reservoir cinnabar open outputs to drinking water reservoirs), which grows very well not only in quartz and other host rocks and penetrates into these rocks, but also on aggregates white table salt - halite. The photographs are shown clearly inedible halite samples with dangerous minerals - blue, blue and red of foreign inclusions.
Origin.
It is found in the sediments of different ages, formed as a result of the evaporation of salt water in closed basins. Similar formations are diverse in scale and sometimes very significant. Small amounts halite can be formed by direct deposition of volcanic sublimation vapor and gases.


Halite. Artemovsk, Donbass, Ukraine. Photo: © AA Evseev.
Place of Birth.
In Italy, there are deposits of salt Wol-Terra (Pisa), as well as in many places the region of Sicily, mainly in the provinces of Agrigento (Racalmuto) and Enna (Kalachibetta). Huge deposits of halite crystals developed in Stassfurte (Saxony); near Salzburg (Austria); in Wieliczka (Poland). Deposits of its known in Switzerland (Beke, Vaud), France (Lorraine) and Spain (Catalonia). In addition to the European ones, the most important are the American salt-bearing basins in the states of Louisiana, Kansas, Arizona and California. In addition, there are deposits in Peru and Argentina, and the largest - Ukraine.
 "Artemsol" - production association for salt production in the Donetsk region of Ukraine. Established in 1976. Includes operated 6 mines (Mine N 1 - the oldest, in operation since 1898), and other processing plants.
"Artemsol" - production association for salt production in the Donetsk region of Ukraine. Established in 1976. Includes operated 6 mines (Mine N 1 - the oldest, in operation since 1898), and other processing plants.
The main industrial and administrative center - Soledar Armemovsk and was Donetsk region. "Artemsol" develops Artemovskoye field, salt-bearing section which is confined to the Permian and has 19 reservoirs with a total capacity of up to 180 m, the angle of incidence of 2-5 o. Best food salt in the world.
Industrial layers - Nadbryantsevsky, Bryantsevsky and Podbryantsevsky capacity 29-40 m Content prmyshlennogo halite NaCl -. 97,7% -98,7%, the insoluble residue 0.2% -0.5% (0.7% - very low) hardness factor of salt - 2.
Tectonics deposit - relatively calm, there are outputs of native chlorine (a very dangerous poisonous gas, burns lungs, trachea and larynx), hydro-geological conditions for underground works relatively favorable (water is). The average depth of development - 260 m (maximum - 320 m to 400 m - the type of Fergana mine rkasnoy cinnabar "Khaidarkan" in Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia, CIS), layers of mineral deposits uncovered vertical shafts (industrial occurrence - the type of bedrock formation Industry red cinnabar in Almadén, Spain, the European continent, the EU west).
 The prevailing system of development - chamber (horizontal seams of halite) leaving interchamber pillar along strike. Camera width of 17 m, a height of 25-36 m (depending on the power of layers), the length of 1500-1800 m. Preliminary production (upper and lower chambers and transport undercutting drifts) are roadheader type "Ural-20, the KC" and "4PP- 2 "; to work in the mine blasting used method of breaking, rope, chain and circular saws.
The prevailing system of development - chamber (horizontal seams of halite) leaving interchamber pillar along strike. Camera width of 17 m, a height of 25-36 m (depending on the power of layers), the length of 1500-1800 m. Preliminary production (upper and lower chambers and transport undercutting drifts) are roadheader type "Ural-20, the KC" and "4PP- 2 "; to work in the mine blasting used method of breaking, rope, chain and circular saws.
Loading salt - excavators and rock-loading machines. Underground transport gorizonralnoy penetration - the conveyor; used self-propelled trains and electric cars (slaughter like a subway in Kharkov, st. m., "Historical Museum" saltivska line). Power shafts - 780-2300 thousand tons per year. The average load on the working face - 1500 m, average productivity for the production of salt - 684-1200 tons (1981).
Salt is processed on special solefabrikah - crushed crusher and roller mill. The product is packaged in packs of 1.5 kg (1 liter) for sale to the public, and in bags weighing 50-75 kg for deliveries of food and other (flavoring) industries.
Agricultural enterprises and farms in the hunting salt is sent in the form of lumps (2-40 kg - for animal feed) and briquettes with mineral additives (5-10 kg), including: Feeding fish in especially fresh waters (p. Uda, right tributary of the river. Seversky Donets, Chuguev, Kharkiv region.) and artificially-freshened, including Distilled water (fish tanks, aquariums, swimming pools for content and other coral reefs).
Application.
Sodium chloride, which is extracted from salt water and extract in the development of deposits of salt - an indispensable component of nutrition for humans. In the chemical industry uses to produce substances such as baking soda, caustic soda and hydrochloric acid.

Halite. Kalush, Carpathians, Ukraine. Photo: © AA Evseev.

Galit, accrued on a branch. Oz. Saki, Crimea, Ukraine. Photo: © AA Evseev.
ADR 4.3


Substances that emit flammable gases in contact with water
The risk of fire and explosion on contact with water.
Goods that are scattered, you need to cover and keep dry
Blue diamond, the number of ADR, black or white flame
ADR 5.1
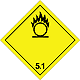
Substances which are oxidized
Risk of vigorous reaction, ignition and explosion in contact with combustible or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, the number of ADR, a black flame over a circle
ADR 6.1
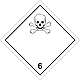
Toxic (Poison)
Risk of intoxication by inhalation, skin contact or ingestion. Constitutes a danger to the aquatic environment or the sewage system
Use a mask for the emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, the number of ADR, black skull and crossbones
Sodium - vital intercellular and intracellular element that the human body is involved in the creation of the necessary buffer capacity of blood, regulating blood pressure, water metabolism (sodium ions contribute to the swelling of colloids tissues to retain water in the body and contribute to its accumulation), activate digestive enzymes, food nervous and muscular tissue. Accumulating water in the body, prevents dehydration (water deficiency when cells cease to function, and in the body of accumulated toxins). It is required for cardiac muscle.
Signs of deficiency of sodium: spasms of the muscles of the abdomen, loss of appetite (anorexia), nausea, vomiting, disorientation, loss of coordination of movements, dehydration, depression, dizziness, fatigue, hallucinations, headache, heart palpitations, decreased the threshold of taste, drowsiness, low blood pressure, memory loss, muscle weakness, recurrent infections, weight loss.
Excess sodium leads to the development of hypertension and excess water in the body. Excessive sodium consumption overloads the heart and the kidneys (in the formation of urine, they are processed with increased blood sodium content), swollen feet and face. In diseases of the kidneys and the heart it is recommended to limit salt intake.
sodium chloride human toxicity mounted on the minimum lethal (lethal) dose of 8.2 g / kg body weight when administered orally (through the mouth and digestive tract). The mechanism of the toxic effect at the injection site due to the high osmotic pressure. As a result, there is an intensive flow of water from the surrounding tissue, which leads to dehydration and impaired cell function. The epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract and the renal tubular inflammation develops, resulting in tissue necrosis.
Permanent excess sodium and potassium accompanied by an increase in blood insulin level. There have been other hormonal disorders. The introduction of large amounts of sodium chloride causes the breakdown of protein and weight loss. For parenteral administration of isotonic solution may increase the body temperature, which is observed in children. People with excess sodium excitable, vulnerable, are hyperactive, they appear thirst and sweating, urinary frequency increased. The main manifestations of excess sodium - fatigue, agitation; neuroses; adrenal dysfunction, renal dysfunction; kidney stones; thirst, swelling; hypertension, osteoporosis.
Sodium is needed: with heavy physical labor, high ambient temperature, sweating (normal sodium intake increased almost 2-fold), sports on hot days or in hot climates, working in hot shops, vomiting, diarrhea, as well as in the use of foods rich in potassium (sodium - potassium antagonist). The main source of sodium - salt. Person in need day 5.7 g of salt. But actually we eat it anymore because the salt found in meat and fish, and vegetables. For taking mineral baths and therapeutic sea salt may be used since it contains other trace elements.
ADR 2.3
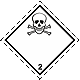
Toxic gases.
Skull and Crossbones
Risk of poisoning. May be under pressure. May cause burns and / or frostbite. Containers may explode when heated (ultra-hazardous - instantaneous dissemination gases vicinity)
Use a mask for the emergency leaving the vehicle. Use cover. Avoid low areas of the surface (holes, depressions, trenches)
White diamond, the number of ADR, black skull and crossbones
Chloro, as well as the sodium salt is halite element and is vital for the human body. This is one of the basic elements of water-salt metabolism of living organisms (food - in the digestive tract). Excess chlorine as the accumulation of the products of its interaction with other substances can cause an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, allergic reactions and miscarriage in pregnant women. Studies show that consumption of chlorine in the water associated increase in bladder cancer.
Chlorine and its compounds are highly toxic (a poison). The main manifestation of an excess of chlorine - inhibition of growth. Free chlorine in the water oxidizes and kills microorganisms, but it also cooperates with other substances, forming toxic compounds. Chlorine is a synergist of sodium.
Children who use an indoor chlorinated pool for swimming, may be more likely to develop asthma - Chlorine is used in water purification basins. The by-products of chlorination contaminate the indoor air pools, irritating the airways and lungs, making them more vulnerable to allergens. Chloro absorbed mainly in the colon. The effect of water sulfur springs and sulfur inhalation.
In the human body (body weight - 70 kg) contains 95 g of chlorine. About 85% of the chlorine is in the extracellular space. Muscle tissue contains human 0,20-0,52% chlorine; Bone - 0.09%; blood plasma - 0.35%. Chlorine is accumulated in the visceral tissues, skin, and skeletal muscle. In gastric glands (GI) and the human skeleton chlorine three times higher than in other organs and tissues. Chlorine is excreted in the urine (90-95%), feces (4-8%) and through the skin (2%).
Chloride ions are involved in the maintenance of osmotic equilibrium, chloride ion has an optimum range for the penetration of cells through the membrane. This explains its joint participation with sodium and potassium ions in the establishment of a permanent osmotic (chemistry) and pressure regulation of water-salt metabolism. Chloride ions have inhibitory effect on neurons by reducing the action potential (not metal). Chloride channels present in many cell types, and mitochondrial membranes of skeletal muscle. These channels perform functions in the regulation of fluid volume transepithelial transport of ions and stabilizing membrane potentials, are involved in maintaining the pH (acid level) cells.
In the stomach, the chlorine ions create an environment for the action of proteolytic enzymes of the gastric juice, it is part of hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach, necessary to digest food. Chlorine is important for the formation of a blood plasma, an activator of enzymes plays an important role in maintaining the blood acid balance. He participates in all biochemical reactions that occur when sodium participation. Chloro plays an important role in the body, maintaining a normal balance of fluids.
Chlorine deficiency can occur in diseases of the stomach and duodenum, in which the chlorine content is reduced. Also chlorine failure may occur, subject to salt-free diet, which is prescribed for hypertension, kidney disease and other illnesses. The symptoms of chlorine deficiency: loss of taste and appetite, nausea, lethargy, muscle weakness.
Most mistaken belief that the recommended sodium intake automatically norm is consumed and the rate of chlorine - not all the minerals and sodium salts have chlorine. Sodium chloride - a salt (halite). There are other chlorides. Natural sources of chlorine. With food chloro usually supplied as sodium chloride and potassium chloride. Especially chlorine rich in bread (it is further halite salt), meat and dairy products, vegetable products - black radish, kelp (seaweed).
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.