Carbonates: Roditsit
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
Cs B 12 Be 4 Al 4 O 28
Crystal system cubic
8.5 Hardness
Specific Gravity 3.44
Cleavage poorly expressed
fracture conchoidal
Colour colorless, differently colored
Shine from glass to diamond
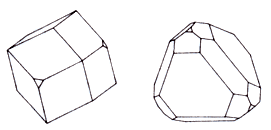
 Presented mainly rhombohedral crystals and tetrahedral shape. Translucent, colorless or white, often yellowish, with a bright glassy luster, tending to the diamond. Rich Cs cesium.
Presented mainly rhombohedral crystals and tetrahedral shape. Translucent, colorless or white, often yellowish, with a bright glassy luster, tending to the diamond. Rich Cs cesium.
Diagnostic features.
Roditsit insoluble in acids; a first flame colors green, and then red.
Origin.
This mineral genesis is associated with advanced stages of the formation of granitic pegmatites rich in boron.
Place of Birth.
In the field region in the Urals Murzinka miarolitovyh pegmatites crystals found in close association with rubellite and quartz. From Madagascar pegmatites come mainly yellow large crystals up to 2 cm. The hardness of a mineral pozovlyaet used as inserts (rare earth - possible radioactive minerals, can be dangerous for sensitive ratsiatsii).

Roditsit. Madagascar. The crystals 1-2 cm Photo:. © AA Evseev.

Roditsit. ITAS-Antsirabe, Madagascar. Photo: © AA Evseev.
Cesium relatively low toxicity, its biological role in humans is not fully understood, although it is assumed that it plays a role in maintaining the homeostasis of the human, it is effective in a sharp decrease in blood pressure (fainting, shock states, collapse) - similar to potassium in the body and has the ability to accumulate, replacing the item. The daily requirement of the human body - has not been established.
Getting into the body with food, cesium (as potassium basic element) is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood. Cesium is evenly distributed in organs and tissues, mainly enters the intestine and is reabsorbed back into it downstream departments. About 80% of the cesium that has entered into the body, accumulates in muscle, 8% - in the skeleton, the remaining 12% is distributed uniformly in other organs and tissues (heart, liver, blood content - up to 2,8 mg / l). The 137-Cs human body is distributed relatively evenly, and no significant adverse effects. Displayed cesium mainly through the kidneys and intestines (after his substitution of potassium ions).
The biological role in humans. Cesium is known role in certain physiological processes. It established the stimulating effect of this element on the circulatory function and effectiveness of its salts with hypotension of various origins. Based on the expressed hypertensive and vasoconstrictor action of cesium salt even in 1888 it has been adopted Russian doctor working in the laboratory of IP Pavlov - SS Botkin - in disorders of the cardiovascular system. He found that cesium chloride causes increased blood pressure for a long time, and this effect is associated primarily with increased cardiovascular activity and constriction of peripheral blood vessels.
Cesium, increasing and prolonging the action of endogenous vasomotor agents, it has a positive effect in hypotension of various origins. cesium salts in optimal doses promote rapid recovery dramatically reduced blood pressure in different types of shock and collapse (and their subsequent elimination from the body, and the substitution of potassium salts). Established adrenomimeticheskoe and sympathomimetic effects of cesium salts in the central and peripheral adrenergic structures, which is especially pronounced in the oppression of the tone of the sympathetic part of the central nervous system, and deficiency of catecholamines. Cesium salts peculiar mainly? -adrenostimuliruyuschy Effect.
cesium salts influence nonspecific indicators immunobiological resistance - they cause a significant increase in titer of complement, lysozyme activity, phagocytic activity of leukocytes. There are indications of cesium salts stimulating effect on the blood-forming organs. In microdozes they cause stimulation of red blood and leykopoeza (20-25%), significantly increases the resistance of red blood cells, increases the hemoglobin in them. Cesium chloride is involved in gas exchange, activating activity of oxidative enzymes, cesium salt increases the body's resistance to hypoxia.
Cesium synergists and antagonists. Synergist is cesium rubidium. Signs of cesium failure: loss of appetite; growth and developmental delay. Cesium is needed (as a temporary replacement of potassium in the body): the state of shock, fainting, collapse, hypotension, peptic ulcer disease, diphtheria. Food cesium sources: the accumulation of cesium in most tissues of freshwater algae and arctic terrestrial plants, especially lichens. High content of cesium is observed in lettuce (in the roots) and Honey fungus. In animal body cesium accumulates mainly in muscle and the liver. The highest rate of accumulation noted in his reindeer and the North American waterfowl. According to the materials: http://www.pharmacognosy.com.ua
Cesium-137. In the case of long-term radioactive contamination preventive measures are to control the food chain. In particular this applies to broadleaf plants (spinach, lettuce, burdock - a medicinal plant, roots) and milk (due to the use of herbs in food ruminants). Among the radioactive isotopes cesium first place belongs to the cesium-137. Its half-life is 30 years, which is considerably higher than that of iodine-131. It is extremely toxic and radioactive substances, which often accumulates in plants and fungi.
That is why the decades after the Chernobyl accident (Chernobyl, Ukraine, CIS) boars were found in the Vosges (and they are, by the way, are big fans eat mushrooms) with elevated levels of radiation in the body. Although in terms of cesium chemistry is quite close to potassium (the item is an integral part of the processes of cellular metabolism in the body) ways to get rid of it practically does not exist. Cesium can cause cancer of the digestive system, lungs or blood (leukemia). Last cleavage product, strontium-90, has a more significant half-life in their chemical properties similar to calcium in the body and may be in the milk in the food chain. According to the materials: http://inosmi.ru/fareast/20110329/167865529.html .
ADR 4.3


Substances that emit flammable gases in contact with water
The risk of fire and explosion on contact with water.
Goods that are scattered, you need to cover and keep dry
Blue diamond, the number of ADR, black or white flame
ADR 5.1
Substances which are oxidized
Risk of vigorous reaction, ignition and explosion in contact with combustible or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, the number of ADR, a black flame over a circle
ADR 8
Corrosive (corrosive) substances
Risk of burns by corrosion. May react violently with each other (component) with water and other substances. The substance that spilled / scattered, can release corrosive steam.
Constitutes a danger to the aquatic environment or the sewage system
White upper half of the lozenge, black - bottom, of equal, the number of ADR, tubes, hand
| Name of especially dangerous during transportation of cargo | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| CESIUM | 1407 | 4.3 |
| Caesium hydroxide | 2682 | 8 |
| Caesium hydroxide SOLUTION | 2681 | 8 |
| Caesium Nitrate | 1451 | 5.1 |
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.