Native Elements: Silver

 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
On the picture. One can see the typical forms of native silver in the form of procrastination.
Ag
Crystal system cubic
Hardness of 2.5-3
The share of 9,6-12
Cleavage is absent
The break in the wrong
Color white gray
Colour gray metallic powder
shine metal
For noble metals include silver, gold, platinum and platinum group metals. Silver in native form is found in ores of gold, as well as polymetallic (Pb-Zn), nickel-cobalt and some tin ores. It is produced mainly as a component passing in the processing of ores of other metals. Along with native silver ore minerals of this metal are argentite, Freyberg (faded silver ore) and Proust-pyrargyrite. Silver is widely used in electrical and radio engineering and electronics. Jewellery and utensils made mainly of silver with copper alloys.
Shine metal, opaque. Color silvery white, gray or black coating. The bar silver and white. Fracture hooked, well drawn into wire, malleable. Cleavage is absent. It occurs in the form of slots or impregnation. The crystals of the cubic system, usually irregular, often in the form of wire or thin hairs, frequent dendrites. Places of manifestation: Freiberg (Saxony, Germany), Kongsberg (Novergiya), Cobalt (Canada), Nevada (USA), Mexico, the CIS.
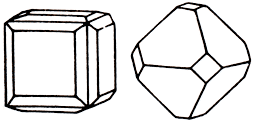
Rarely forms crystalline cubic form and an octahedral shape (as shown on the left). Usually they are deformed and very small size; sometimes form intergrowths dendritic appearance. Records are commonly observed, ribbons and wire may also present the masses of different sizes. Gloss is usually usually a metal; mineral darkens in air in the presence of even small amounts of ozone and hydrogen sulfide.
Form crystalline precipitates. Most of the dense clusters, are also characteristic of the wire, hairlike form small flakes, leaves, flat feathery dendrites, grains of irregular shape. The crystal structure. Face-centered cubic lattice. Class symmetry. Geksaoktaedrichesky - mZm
Due to its unique natural qualities of silver occupies a special place in the cultural heritage of different peoples. The history of the use of silver has the millennium, although it became known much later gold. During this time, I accumulated a lot of silverware in the world. Small amounts of silver were found in the cementation zone or sometimes - in the hydrothermal veins of silver oxidation zone.
Diagnostic features.
Furthermore colors and shapes, is recognized native silver with nitric acid and blackening in the sulfuric acid vapors. It is a good conductor of electricity and heat.
Origin.
May have either primary origin (directly from the magma during its solidification) or be the result of decomposition of other minerals (argentite, various sulphosalts, galena containing silver).
Place of Birth.
Native silver has economic value only in Copiapo (Chile), as well as in Batopilas and Guanajuato (Mexico). In small quantities observed in Butte (Montana), Silver City (Idaho), Silver King Mine (Arizona). The block of nine quintals was discovered in Cobalt City (Ontario, Canada).
Application.
For the most part used for the production of coins, glassware, artwork, etc. The main mass of silver is mined as a byproduct of the smelting of lead and zinc. Making art - a very ancient tradition. Major museums withdrawn silverware special departments. On the territory of Ukraine it has been very popular manufacturer of jewelry from silver wire - ancient art of filigree and filigree.

Amalgam is silver. Dendritic plate thickness of 2 mm of cracks in the claystone. The sample size of 21 cm. Hachakchanskoe ore occurrence, Tomponsky District. Photo: © AA Evseev.



Silver. Sarbaisky district to, Kazakhstan. Height 6 cm. Silver. Germany. Munich-show-2007. The dendrites of native silver from Mexico.


Silver. Bear on., White Sea, Russia. Silver. Skeletal crystals. Bostanitos, Mexico. Photo: © AA Evseev.


Silver. Kongsberg, Norway. Length 16 cm, weight 2770 Nugget Peter I received as a gift when you visit the museum in Copenhagen. Silver. Kongsberg, Norway. Photo: © AA Evseev.
Silver in the body has a bactericidal, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, astringent. However tuj not considered to be vital for the body ultramicroelements. Poisonous. Bioavailability of silver, which is determined by the magnitude of absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, is 5%. In the body, silver forms complexes with plasma proteins (globulins, albumin, fibrinogen, hemoglobin, etc.), Blocking the sulfhydryl group (HS-) enzyme, inhibiting its activity, inhibits tissue respiration (oxygen - active oxidized silver and beologicheski "lit" effect of phosphorus in the body). Under the influence of myosin silver - protein human muscle tissue - loses its ability to break down ATP. Fabric "Silver" - "burns" (necrosis).
Manifestations of excess silver: central nervous system; visual impairment as a result of deposits of silver in the retina of the eye, lowering blood pressure, brown or grayish tinge to the skin and mucous membranes (argyria), right upper quadrant pain, enlargement of the liver; gastritis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; argyria - formation of silver deposition in the skin. Drink water with ions of silver or gold is not necessary. Silver, like gold - cellular poison xenobiotic. In contact with the silver accumulates in the liver, kidney, skin and mucous membranes.
silver ions replace micronutrient ions in enzymes, such as cobalt ions, responsible for the metabolism and reproduction. This leads to disruption of cell function and to its death. The constant use of silver, even in small doses, can cause disease associated with a high content of silver in the body - Argir (argentoz). Harmless to humans is the total cumulative dose a person can receive in a lifetime (70 years) - 10 g of silver, a single toxic dose - 60 mg, the lethal (brain death) - 1,3-6,2 was due to the accumulation of the brain and nervous tissue of silver - "black brain" (electric breakdowns between the brain and nerve cells, retinal cells, receptors and their destruction of biological and other electric shock, stroke).
Symptoms silver failure. By reducing the concentration of silver in the body being observed deterioration, headaches, fatigue, low immunity, disrupted the cardiovascular system, expanding the veins and arteries ( "bodybuilder's disease and computer operator", valves suffer), increases the concentration of cholesterol in the blood. Silver plays an important role in the processes associated with the higher nervous activity (Computing 32-bit human brain) and peripheral nervous system functions (contact the central brain "processor" and conducting nerve cells of the brain similar to the wire).
Silver is known for its bactericidal, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, astringent. Silver - the basis of antibiotics. Penicillin fungi assimilate this particular metal (self-preservation of fungi in a biological antagonism). Silver - a conductor of electric current. Silver - copper antagonist.
Available silver resorption through the skin and mucous membranes. Silver contained in small amounts in all organs and tissues; the average content of the element in the mammalian body reaches 20 g per 100 g dry mass. The richest silver cord (main depot of silver), lungs, liver, red blood cells, pigment of the eye and the pituitary gland. Displayed silver from the body through the intestines.
Silver requires at erosions, ulcers, excessive granulation, fractures, acute conjunctivitis, trachoma, chronic hyperplastic laryngitis, inflammation of the urethra and bladder (as an antiseptic), nervous diseases (neuralgia and epilepsy, as a conductor of electric current). Food sources of silver: watermelons, cucumbers, fennel, pine nuts, mushrooms, mushrooms, salmon, sardines, shrimp.
ADR 4.1

Flammable solids, self-reactive substances and solid desensitized explosives
Risk of fire. Flammable or combustible materials can be ignited by sparks or flames. May contain self-reactive substances that are liable to exothermic decomposition in the case of heating, contact with other substances (such as acids, heavy-metal compounds or amines), friction or shock.
This may result in the evolution of harmful and flammable gases or vapors or self-ignition. Containers may explode when heated (ultra-hazardous - practically do not burn).
Risk of explosion of desensitized explosives after loss of desensitizer
Seven vertical red stripes on a white background, of equal, the number of ADR, the black flame
ADR 5.1
Substances which are oxidized
Risk of vigorous reaction, ignition and explosion in contact with combustible or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, the number of ADR, a black flame over a circle
ADR 6.1
Toxic (Poison)
Risk of intoxication by inhalation, skin contact or ingestion. Constitutes a danger to the aquatic environment or the sewage system
Use a mask for the emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, the number of ADR, black skull and crossbones
| Name of especially dangerous during transportation of cargo | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| SILVER arsenite | 1683 | 6.1 |
| silver nitrate | 1493 | 5.1 |
| SILVER picrates WETTED with a mass of water of not less than 30% | 1347 | 4.1 |
| silver cyanide | 1684 | 6.1 |
| Silver nitrate cm. Silver nitrate | 1493 | 5.1 |
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.