Sulphides: Scutterudite
 Diagnostic card.
Diagnostic card.
(Co, Ni) As 3
Cubic amount of cubic zirconia
Hardness 6
Specific weight 6,5-6,8
Cleavage is poorly expressed
Fracture is conchoidal or irregular
Color light gray
Color in powder black
Glitter metal
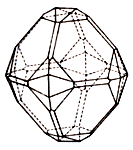
Scutterudite is a group of minerals with the general approximate formula (Co, Ni) As3 - cobalt and nickel arsenides. Metallic shine, opaque. The color is tin-white, areas with a pinkish touch. The line is gray-black. The fracture is uneven. Fragile. Cleavage is imperfect.
Formed in hydrothermal deposits, often in intergrowth with other ore minerals. Crystals (cubic syngony) are small, granular aggregates, dense, kidney-like secretions, interspersed grains. Important ores of cobalt and nickel. Deposits: in the Ore Mountains (Germany), Harz (Germany and Germany), England, Norway, CIS, Canada, Morocco.
Scutterudite is formed as a result of medium-temperature hydrothermal processes, found in cobalt ores with other cobalt and nickel arsenides (mixed kimberlite). The crystals are isometric, small, usually octahedral, collected in small druses; Granular aggregates, variegated aggregates with disseminated grains, dense, kidney-shaped crusts. It dissolves in nitric acid, staining the resulting solution in pink with a significant cobalt content, or greenish - with predominance of nickel. It melts well, melting into a magnetic queen with the release of the smell of garlic (arsenic). Electroconductive. In appearance, the mineral can be confused with arsenopyrite, lellingite.
Scutterudite is an ore of cobalt, nickel and arsenic. Collectors appreciate beautiful large crystals (1-2 cm), mined in Germany, Norway, Morocco (killer stone - poisonous). The group includes the actual scutterudite CoAs3 and its variety of smaltine (spike cobalt), nickel cotterudite (chlorantite, nickel pyrite (NiAs2? 3), ferroscutterudite [1], safflorite (Fe, Co) As2 (CoAs2) .The maximum amount of cobalt contains smaltine (shmaltin CoAs2 or CoAs3? 2, up to 24%), nickel-chlorantite (NiAs3-2, up to 21%), and rimmelsbergite-NiAs2 The general theoretical chemical formula for the minerals of the (Co, Ni) As3 (CoAs3) group.









Scutterudite forms dense, fine-grained masses, very rarely cube-octahedral crystals. The latter can be modified due to the development of smaller facets (dodecahedron, etc.). Color light gray. The species in which nickel predominates is called nickel-scutterudite. Scutterudite, he's also a cobalt, he's smaltin. The site of mineral finds Scutterud (Norway, EU) gave him the name - skutterudit. The name comes from Skutterud (Norwegian Skutterud) in Norway, where the mineral was first discovered in 1845.
 Class of symmetry. The diododecahedral one is m3. Form of crystalline precipitates. Dense, coarse-grained masses. Crystal structure. Atoms of arsenic form in the lattice of the As4 group. Elementary cell contains 8 cobalt atoms, which are located in the centers of small cubes, and 6 groups of As4 Cleavage. Clear by the cube (100). Aggregates. Dense, coarse-grained. Minerals of the scutterudite group: smaltine, CoAs3-2, a synonym: spike cobalt (smalt - blue cobalt paint); Chlorantite, NiAs3-2, synonyms: white nickel pyrite, nickel-cetuditite (Greek "chlonates" - green).
Class of symmetry. The diododecahedral one is m3. Form of crystalline precipitates. Dense, coarse-grained masses. Crystal structure. Atoms of arsenic form in the lattice of the As4 group. Elementary cell contains 8 cobalt atoms, which are located in the centers of small cubes, and 6 groups of As4 Cleavage. Clear by the cube (100). Aggregates. Dense, coarse-grained. Minerals of the scutterudite group: smaltine, CoAs3-2, a synonym: spike cobalt (smalt - blue cobalt paint); Chlorantite, NiAs3-2, synonyms: white nickel pyrite, nickel-cetuditite (Greek "chlonates" - green).
Diagnostic signs.
It dissolves in nitric acid, staining the solution in red. It melts at low temperature. Fused into a magnetic queen (with a strong smell of garlic).
Origin.
Mineral of medium-temperature hydrothermal veins. It occurs together with minerals of cobalt, nickel, silver, as well as bismuth and uranium.
Deposits and applications.
Scutterudite is found in Scutherder and Kongsberg in Norway, in Vittichenel-Baden and many other places in Saxony in Germany; In the form of crystals with siderite and arsenopyrite in Turtmanthal in Valais, Switzerland. Beautiful and quite large crystals are known from Alt-Ahman (BuAzer) in Morocco. Used to extract the elements that make up its composition - cobalt, nickel and arsenic.
ADR 4.1

Highly flammable solids , self-reactive substances and solid desensitized explosives
Risk of fire. Flammable or combustible substances can ignite from sparks or flames. May contain self-reactive substances capable of exothermic decomposition in the case of heating, contact with other substances (such as: acids, heavy metal compounds or amines), friction or impact.
This can lead to the emission of harmful or flammable gases or vapor or spontaneous combustion. Containers can explode when heated (over-dangerous - practically do not burn).
Risk of explosion of desensitized explosives after loss of desensitizer
Seven vertical red stripes on a white background, equal in number, ADR number, black flame
ADR 5.1
Substances that are oxidized
Risk of violent reaction, ignition or explosion if exposed to flammable or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, ADR number, black flame above the circle
ADR 6.1
Toxic substances (poison)
Risk of poisoning by inhalation, in contact with skin or if swallowed. Dangerous to aquatic environment or sewer system
Use a mask for emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, ADR number, black skull and crossbones
| The name of a cargo that is particularly dangerous for transportation | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| COBALT RUBBER DEPOSITED | 1318 | 4.1 |
| COBALT NAPHTHENATES - POWDER | 2001 | 4.1 |
| Nickel Nitrite NICKEL (II) NITRITE | 2726 | 5.1. |
| Nickel nitrate NICKEL (II) NITRATE | 2725 | 5.1. |
| NICKEL (II) NITRATE | 2725 | 5.1. |
| NICKEL (II) NITRITE | 2726 | 5.1. |
| NICKEL CARBONYL | 1259 | 6.1. |
| NICKEL CYANID | 1653 | 6.1. |
- Ghetchellit - "New Almaden blend" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulfosol)
- Antimony is a toxic metal (semimetal) , widely used in metallurgy, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and undiscovered metal and the most dangerous precious stone in oxide and salt
- Gold - yellow dangerous and poisonous metal of modern accurate digital and cable technologies
- Sulfur is a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of active volcanic activity
- Cadmium is an undisputed toxic silvery metal unknown to a wide range of people
- Lead - a toxic gray imitator of metallic silver and toxic metal blende
- Arsenic is a classic poison of medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity)
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in case of radioactivity exceeding 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection)
Catalog of minerals and semi-precious stones of the world by groups
** - poisonous stones and minerals
** - radioactive stones and minerals


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.