Earth puzzles from the height of a satellite

"Observatory of the Earth" (Earth Observatory) - the most important public project of NASA. Through this online resource, the US space agency makes images from satellites and other scientific information available to the public.
Annually visitors of a site vote for the best images of the Earth. Competition Tournament Earth is held in four categories: important events, scientific information, photographs and photography.
In 2015, Icelandic volcanoes and night darkness in North Korea, a planetary scale drop and windmills at the mouth of the Thames conquered the palm tree. The winner was recognized as a snapshot of the Pitsian Fracture in the northeast of China: a living illustration of the multi-million-dollar geological history of the Earth in several multicolored stripes.
Lava flows on the plateau of Holuhrein
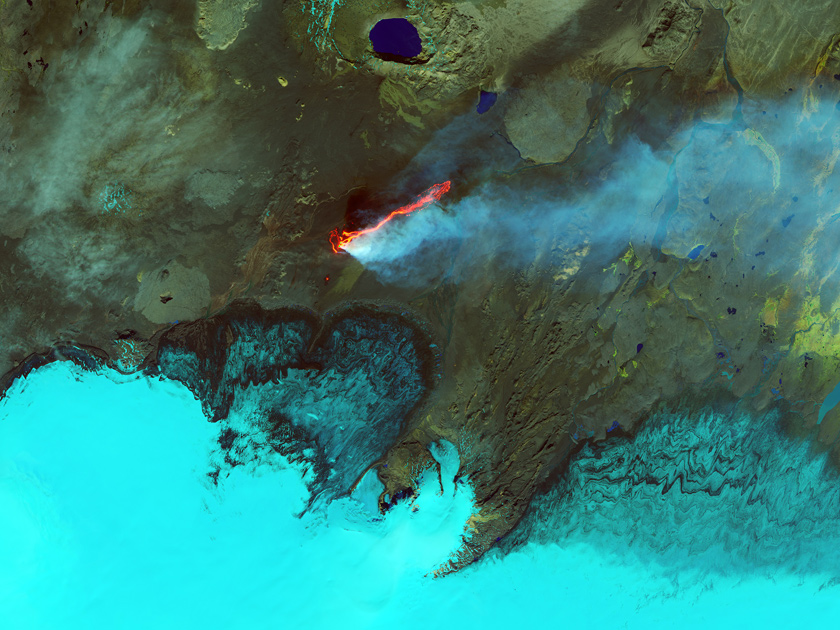

Photo: Jesse Allen / NASA Earth Observatory
The eruption of the Icelandic volcano Bardarbung began in August 2014. The Operational Land Imager tool on Landsat 8 satellite is shooting in infrared radiation of different wavelengths. On this pseudo-color image, the plume of steam and sulfur dioxide has a bright blue hue, water is blue. The rocks around the lava field are painted in shades of green and brown, and fresh lava - red and orange. In natural color, this landscape looks much more ascetic. Such heat-sensitive surveying methods allow scientists to estimate the area of lava flows, the rate of lava flow to the surface, and the sulfur dioxide content in the gas plume. In the presented picture, for example, you can see how the lava tongues break out onto the surface, then to merge into a single stream.
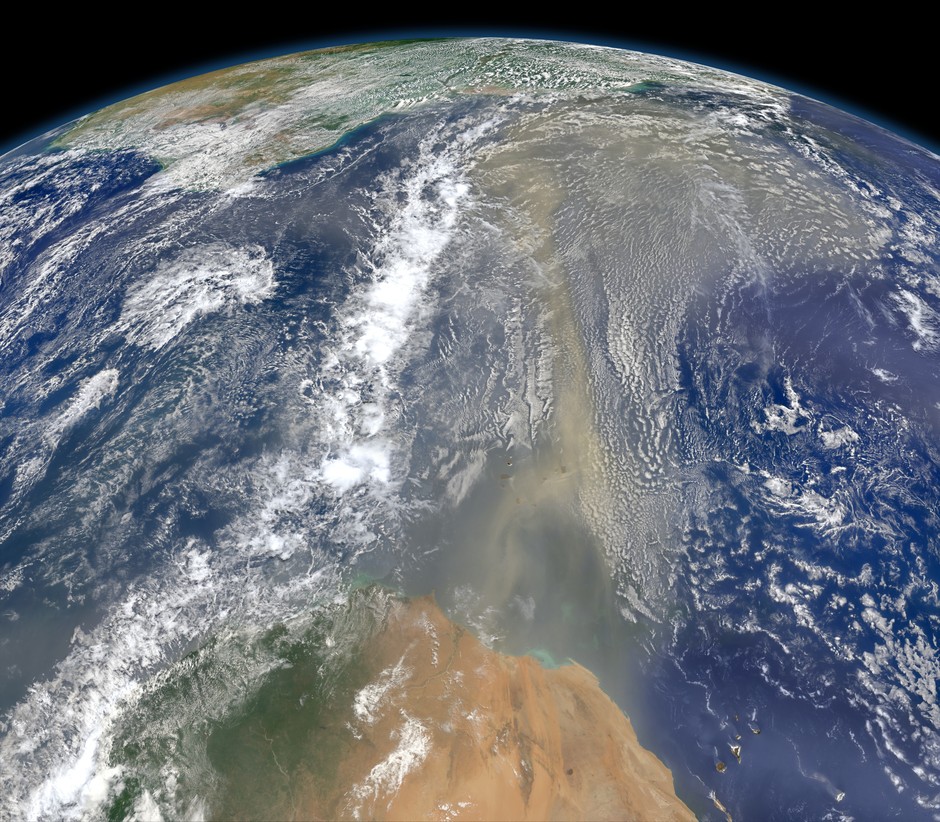
Particles of Africa fly to America
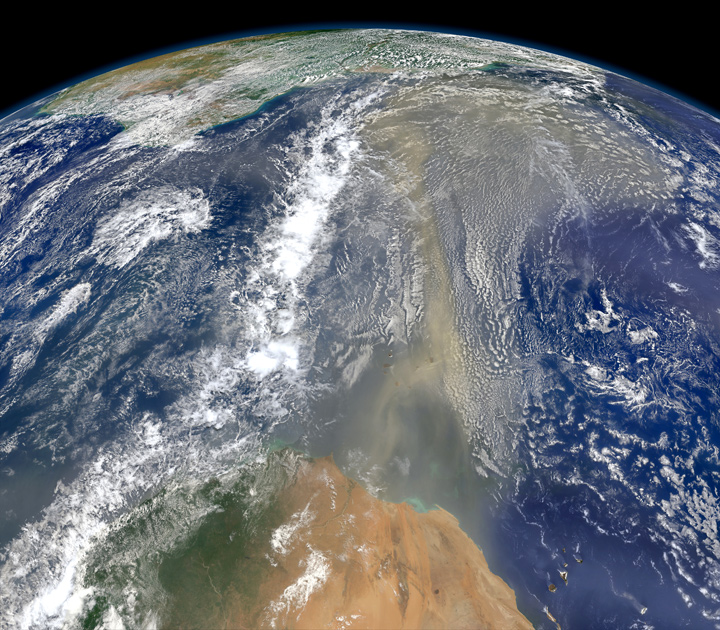
Photo: Norman Kuring / NASA Earth Observatory
The east wind carries America's clouds of Sahara to America, June 2014. A composite image was created using the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite from the meteorological satellite Suomi NPP. Recently, scientists have found that nutrients from the Sahara provide the fertility of the Amazon jungle. The wind raises a plume of dust and sand over the Sahara, which then moves thousands of kilometers to the west, settling in South America. This dusty plume contains several thousand tons of phosphorus (from the bottom of the dried up Lake Chad), which is extremely poor in the basin of the great river.
Let all the flowers blossom ... electricity
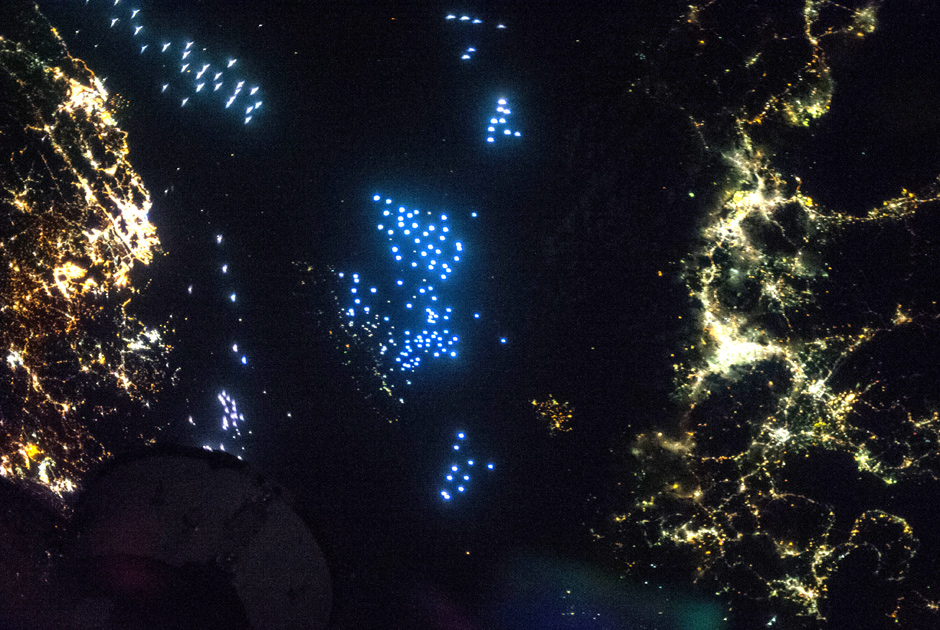

Photo: JSC / NASA
A peaceful struggle between different types of light bulbs (LED and incandescent, for example) is visible even from outer space. In the photo of the Tsushima Strait separating Japan from South Korea, we see a fleet of fishing vessels. Sailors lure the Pacific squid with xenon bright blue lights. The lights of Korean cities have an orange tinge - there they use sodium gas-discharge lamps for street lighting. In Japan, they prefer greenish mercury. The photo was taken by one of the crew members of the 37th expedition to the International Space Station on October 11, 2013.
Border of Kazakhstan and China
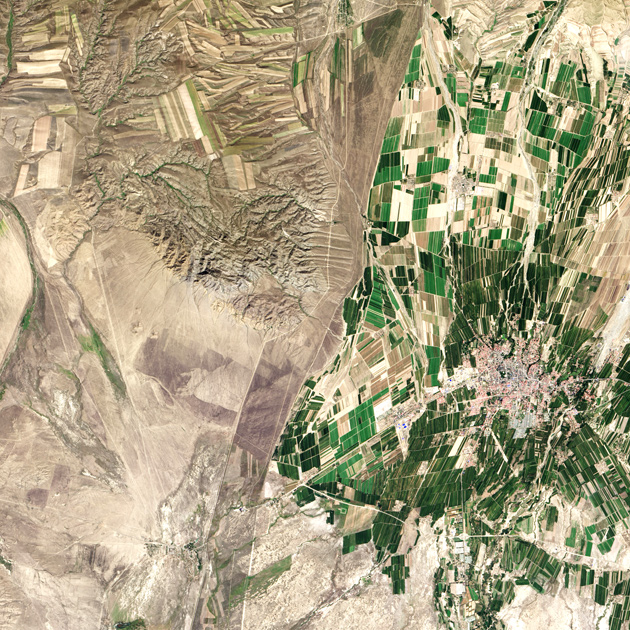

Photo: Robert Simmon / NASA Earth Observatory
A vivid illustration of the contrast of the socio-economic structure is the border between Kazakhstan and China in the vicinity of the town of Chuguchak. The Chinese lands are intensively cultivated and irrigated (green color), otherwise the country's half-billion-strong population, where only 11.62 percent of the territory is suitable for cultivation, does not feed. Fields in a few Kazakhstani farms (heirs of Soviet collective and state farms) are irrigated only by rain and hardly stand out against the background of the surrounding landscape. The image was taken at NASA on September 9, 2013, based on data from the Landsat satellites.
Lightning: top view
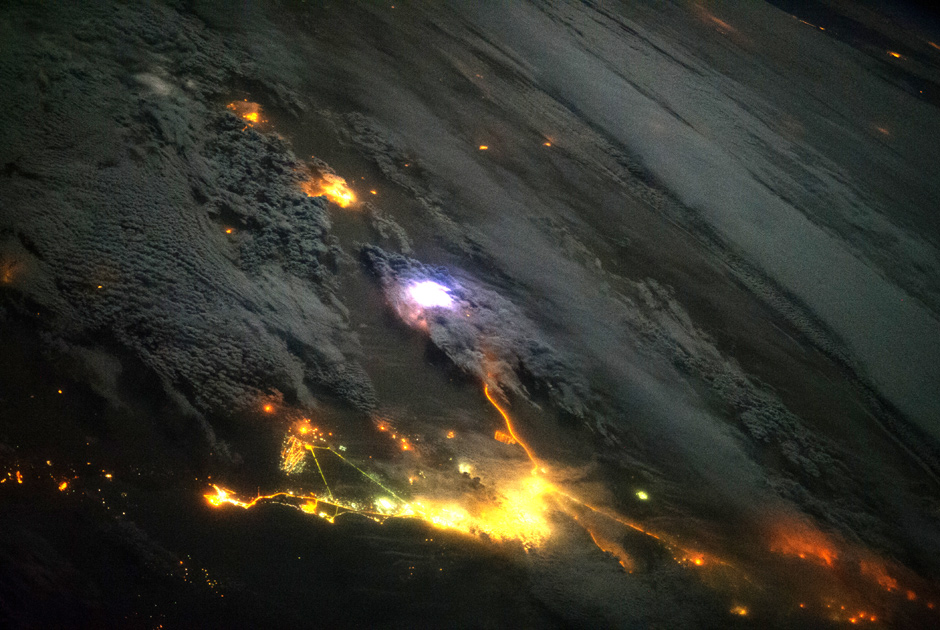

Photo: ISS / NASA
Lightning arises on Earth approximately 50 times per second, that is, 4.3 million times a day and 1.5 billion times a year. In order to observe this phenomenon in all details, in August 2013 the scientists installed the instrument Firestation on board the ISS. There are also photometers for measuring lightning flashes, and radio antennas for measuring the strength of atmospheric discharges, and finally a gamma-ray detector. It is by flashes of gamma rays in the upper layers of the atmosphere that Firestation finds lightning. This picture was taken on board the ISS on December 12, 2013: a bright flash of lightning is visible in the desert, between the cities of Kuwait and Saudi Arabia.
The Aral Sea in 2000
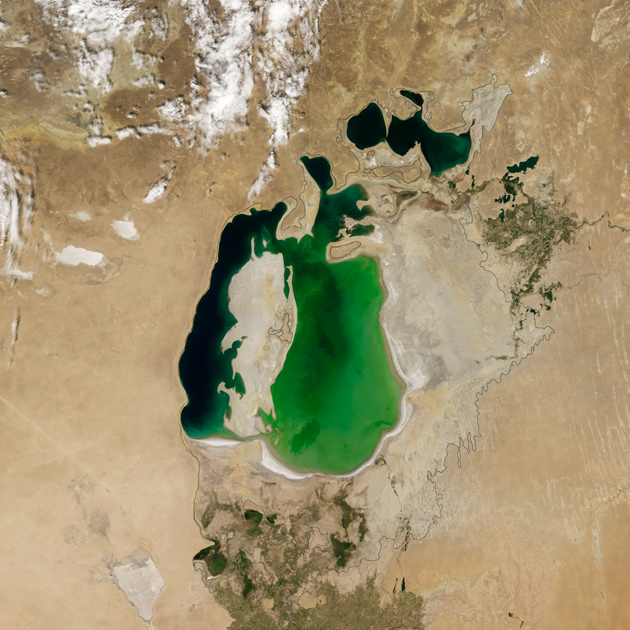

Photo: Jesse Allen / NASA Earth Observatory
The Aral Sea in 2000.
The Aral Sea in 2014
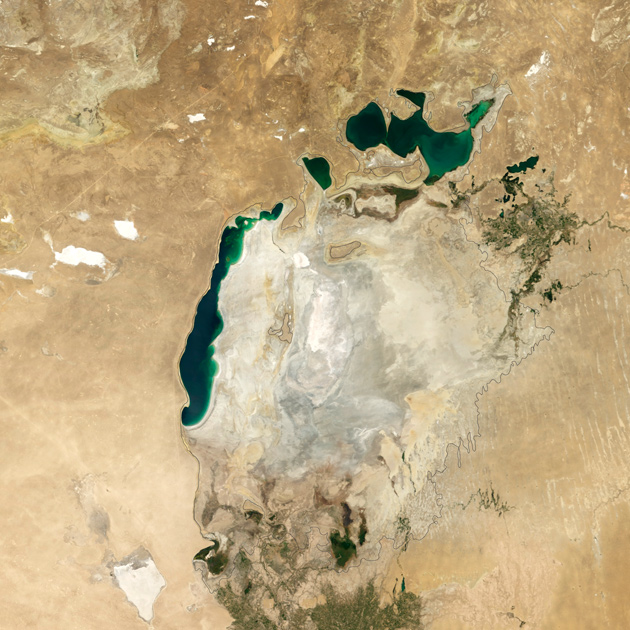

Photo: Jesse Allen / NASA Earth Observatory
The summer of 2014 was marked by another tragic stage of the drying of the Aral Sea: for the first time in modern history, the eastern basin of the southern part of the reservoir completely evaporated. The images were obtained by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer tool from Terra satellite in 2000 and 2014. The black outline indicates the coastline of the 1960s. The Aral was dried up because in the second half of the 20th century the water flow, which was formed mainly due to the Syr Darya and Amu Darya rivers, was actually "reset" - water was taken for agricultural needs. As a result, the Aral decreased by a factor of four, and by the volume of water - by a factor of ten, disintegrating into three bodies of water. By 2010, the state of the Aral Sea has stabilized somewhat. Moreover, the eastern part of the southern Aral Sea strongly depends on seasonal fluctuations. So, in 2010 it was actively restored in volume. And in 2014, the Amu Darya almost did not bring water there because of the scarcity of winter precipitation in the Pamir mountains.
Peninsula of contrasts
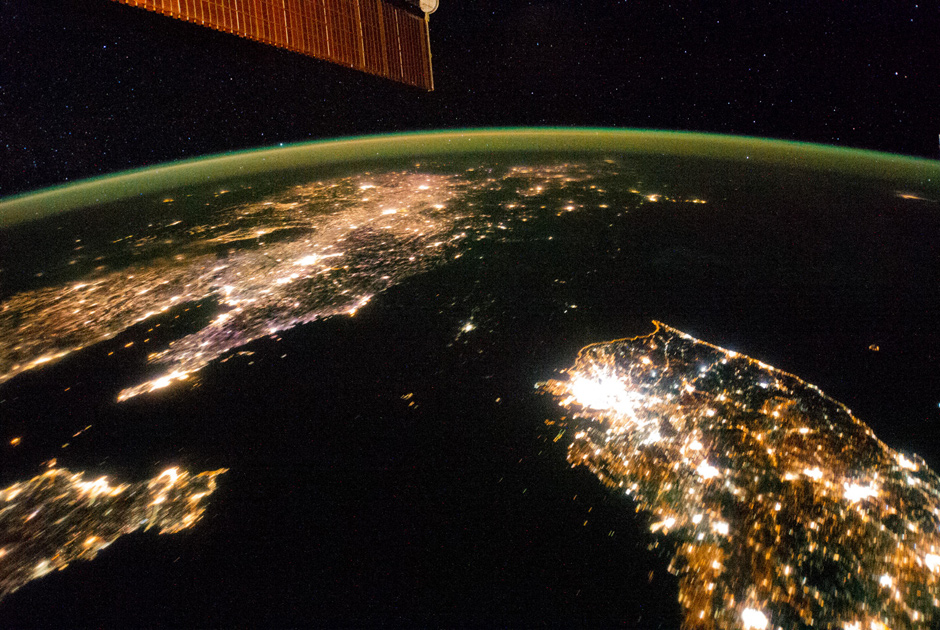

Photo: ISS / NASA
Night shots from space perfectly illustrate economic realities: look, for example, on North and South Korea. It is immediately noticeable what metropolis Seoul became and how the port city of Kunsan lags behind it. However, most of all, the darkness reigning in the DPRK is striking: the country resembles the sea strait that connects the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. The capital is like a small island. Recall that electricity consumption in the north is 739 kilowatt hours per capita, in the south - 10162. The picture was taken with the ISS on January 30, 2014.
The history of the Earth in a section
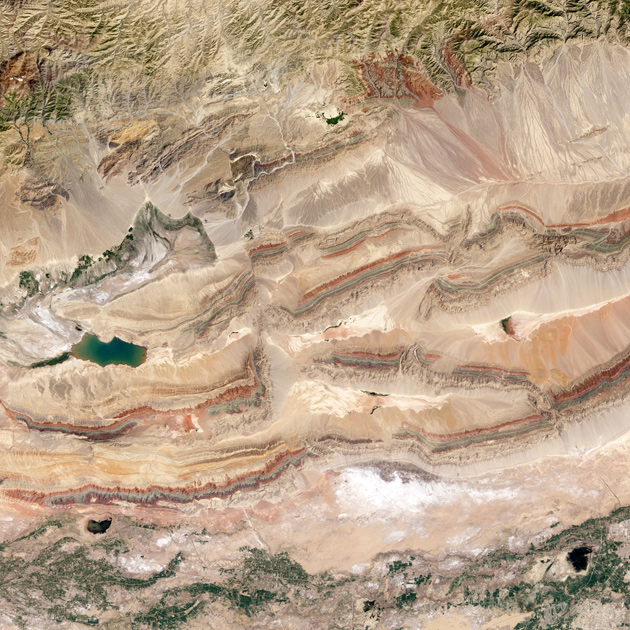

Photo: Jesse Allen / NASA Earth Observatory
And here is the winner of the 2014 competition - a picture of the Pitsian break in the northeast of China. Horizontal strips are the geological layers that crush and squeeze the Hindustan plate that "enters" the Eurasian plate. In the "bundles" of strips are visible multi-colored layers: each of them is responsible for approximately 50 million years. The lower green layer is the mosses of the Silurian period. A thin blue stripe - the early Devonian (400 million years ago), when on land appeared ferns and shrubs. And towards the middle of the Devonian (a large red band), shrubs firmly planted roots in the soil, and the first trees appeared next. A deep vertical fault line crushed the mountains in two. Those in the right half of the photo move north at a speed of 5-10 centimeters per year - with the same one with which the nails of a person grow. The image was received on July 30, 2013 by the Operational Land Imager tool of the Landsat 8 satellite.
Venetian dregs
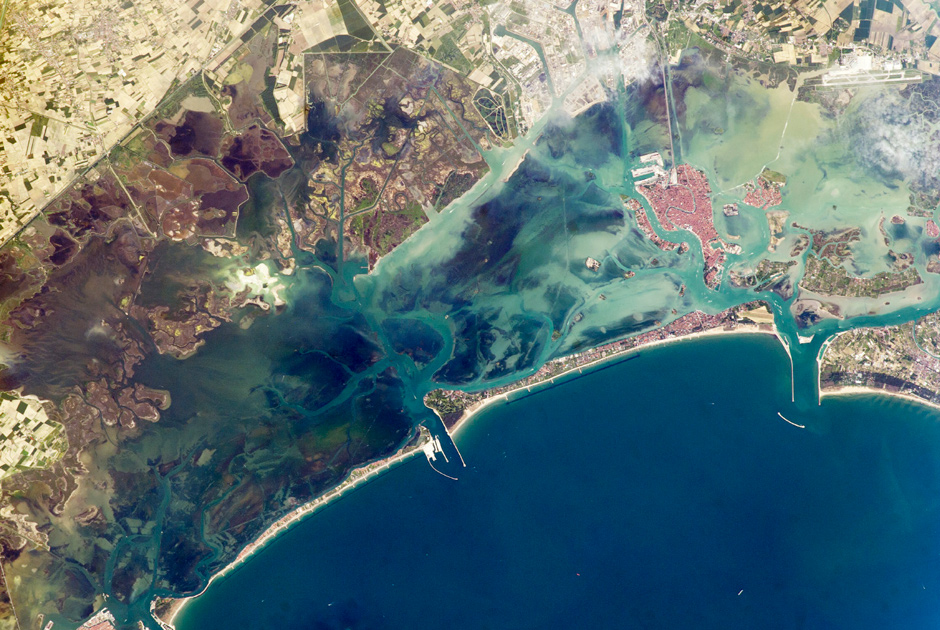

Photo: ISS / NASA
This image of the Venetian lagoon was made with the ISS on May 9, 2014. The great ancient city in the Adriatic Sea is constantly under threat of floods. A narrow barrier island protects the lagoon from storm waves, and breakwaters protect its bays. Red tile on the roofs of Venice is very different from the gray roofs of the satellite town of Mestre. The city is connected by a powerful dam. The same jumper, it would seem, Venice is connected to the airport (the upper right corner of the picture), but in fact it is the wake of the numerous boats and water taxis that cruise along this route. More and more turbid water in the lagoon (especially in the northern part of it) inspired the Venetians in 2002 to create the "Atlas della laguna", where the ecological situation and all its changes are recorded.
Megadians and desert lakes
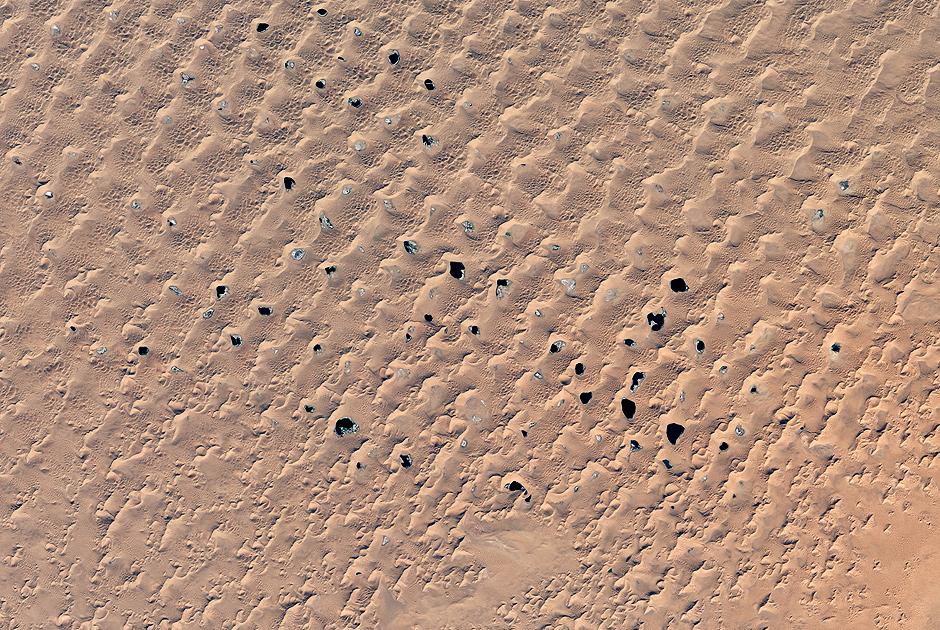

Photo: Jesse Allen / NASA Earth Observatory
The Badyn-Jaran desert in Inner Mongolia (PRC) is famous for the highest sand dunes on the planet - up to 460 meters (like the Empire State Building skyscraper). Among them are scattered about a hundred lakes, fed by groundwater. These lakes and gave the desert name, which in Mongolian means "mysterious lake". In recent years, because of increased consumption of water in cities and agriculture, the lake began to grow thin. The image was received on October 5, 2014 by the Operational Land Imager tool of the Landsat 8 satellite.
Windmills at the mouth of the Thames
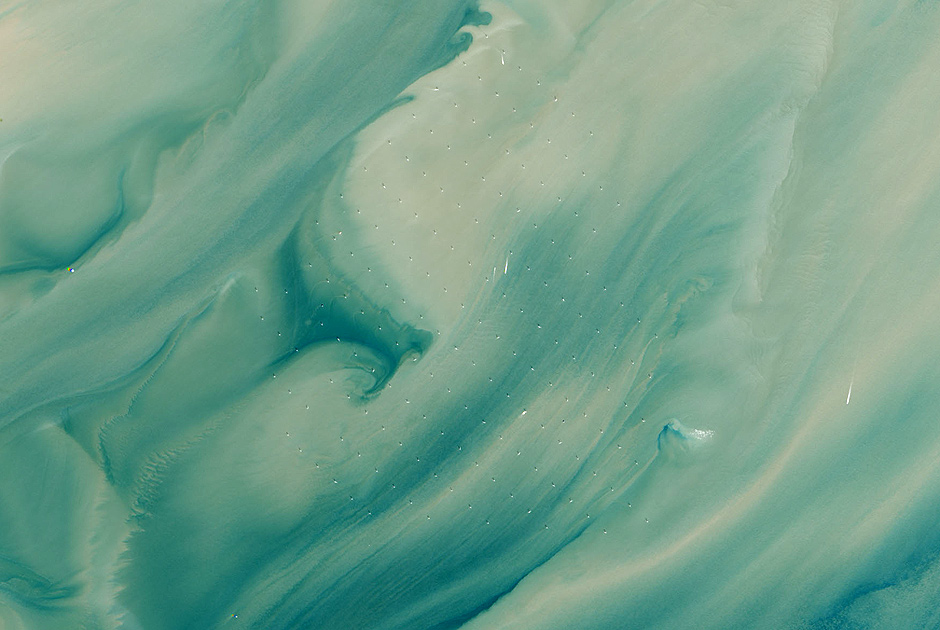

Photo: Robert Simmon, Jesse Allen / NASA Earth Observatory
At a distance of 20 kilometers from the coast of the counties of Kent and Essex, at the mouth of the Thames, on April 8, 2013 the world's largest sea wind power plant began to catch a sea breeze. London Array is capable of delivering up to 630 megawatts - this is enough to supply half a million households with electricity. 175 windmills London Array are located on an area of 100 square kilometers at a distance of 650 to 1200 meters from each other. The power station was built on two natural sand banks, far from the main maritime communications of the British capital. The photo was taken by the Operational Land Imager (OLI) tool on the Landsat 8 satellite in 2013.
Greenery in June
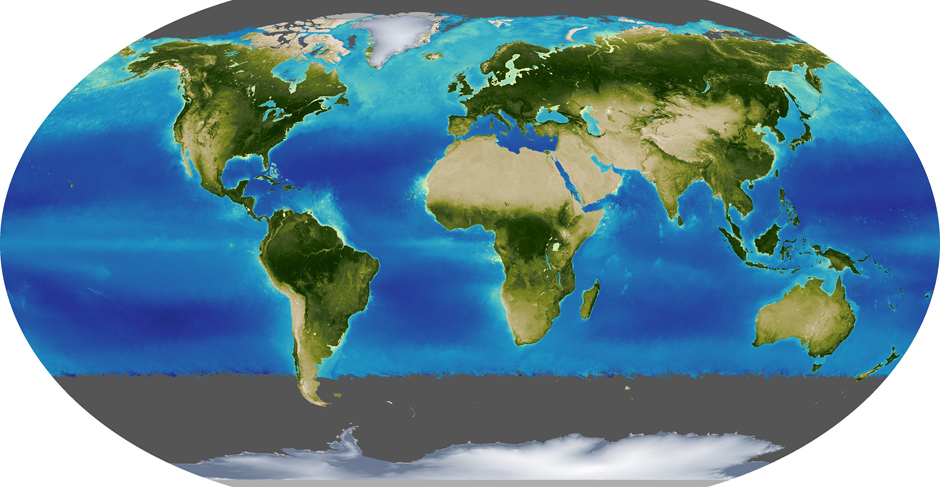
Image: Kevin Ward / NASA Earth Observatory
Scientists and ecologists are very interested in how during the year the vegetation of the planet changes, where the leaves most often fall and spread. In seas and oceans, plants are mimicked by phytoplankton. The averaged data for June and December 2000 to 2014 were obtained by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer tool from the Terra satellite. Gray areas of the polar night are shown, which were not collected any information. Visible is the turbulent vegetation of the Northern Hemisphere, as well as the flowering of phytoplankton in the North Atlantic.
Greenery in December
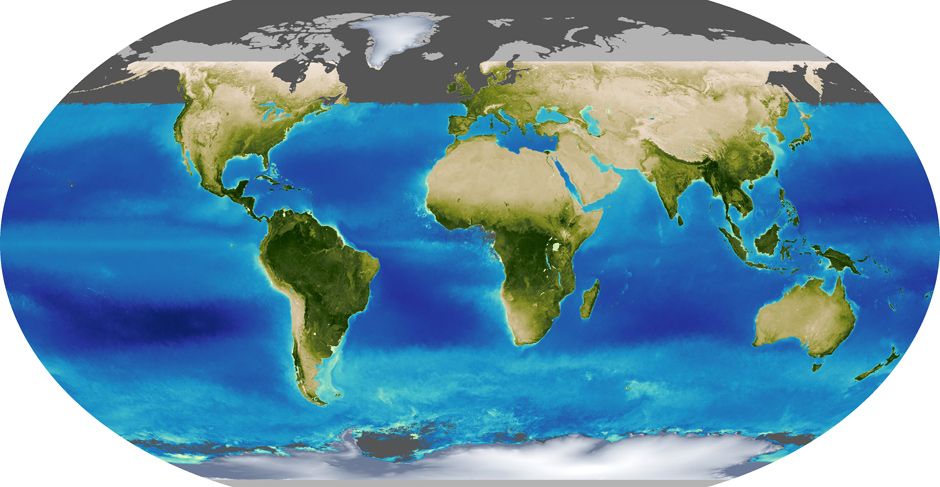
Image: Kevin Ward / NASA Earth Observatory
In December, the flowering of life moved to the south, although summer in the Southern Hemisphere is not so much different from winter, as in the North. At the equator, both terrestrial plants and phytoplankton are much less dependent on the season.
Via lenta.ru


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.