home
 Finance Finance
 Books Books
 Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М. Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
|
Finance and Statistics - Ковалева А.М.
Analysis of coefficients of financial results
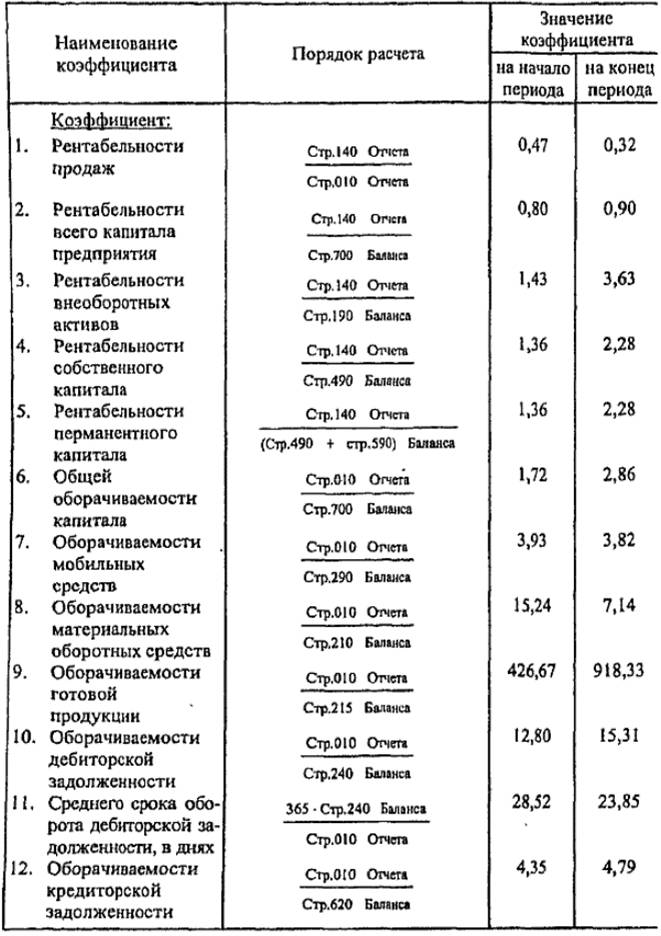
The analysis of the coefficients of financial results consists of two parts: the analysis of profitability and analysis of business activity (turnover). Their analysis is preceded by preliminary calculations, the results of which are summarized in Table. 11.12.
When analyzing the coefficients of financial performance of the enterprise, the characteristics of the coefficients presented in Table 1 are used. 11.2.
The coefficient of profitability of sales decreased (from 0.47 to 0.32) -the decrease in profit per ruble of sold products indicates a decrease in demand for the enterprise's products.
The coefficient of profitability of the whole capital increased (from 0.80 to 0.90), which indicates a certain increase in the efficiency of the use of the property of the enterprise.
The coefficient of turnover of mobile means decreased (from 3.93 to 3.82) - the efficiency of using mobile means decreased.
At the same time, the efficiency of using material current assets decreased (the turnover ratio of material circulating assets at the beginning of the period was 15.24, and at the end of -7.14) due to an increase in costs in work in process.
Despite the increase in the turnover rate of the accounts receivable (from 12.80 to 15.31) and creditor (from 4.35 to 4.79) debts, the "debts" of the enterprise significantly exceed their "credits". The enterprise pays for its obligations several times slower than it receives money on "loans": the average period of the turnover of accounts receivable is 28.52 days at the beginning of the period and 23.85 days at the end of the period, while the average period of turnover of accounts payable is 83, 84 and 76.18 days respectively. '
The growth of individual coefficients, characterizing the profitability and business activity of the enterprise, does not reflect the actual rate of turnover of funds. Thus, the growth of the profitability index of non-current assets (from 1.43 to 3.63) is explained by a decrease in the share of non-current assets, rather than growth in profit.
Accordingly, the growth in the coefficient of return on equity (from 1.36 to 2.29) is due not to growth in profits, but to a decrease in the share of own capital.
The coefficient of profitability of permanent capital increased (from 1.36 to 2.28) due to the practical absence of long-term loans and a decrease in the share of equity.
The coefficient of total capital turnover increased (from 1.72 to 2.86) due to the relative decrease in the capital of the enterprise in the analyzed period.
The turnover ratio of finished goods increased (from 426.67 to 918.33) due to a reduction in the share of finished goods in the assets of the enterprise.
Table 11.12
The results of calculations of the financial performance of a contingent enterprise
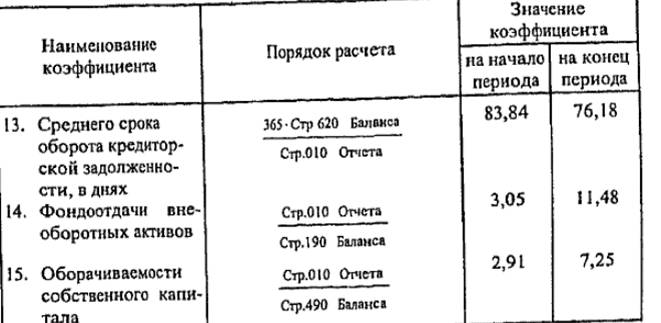
Growth in the return on assets (from 3.05 to 11.48) was caused by a relative decrease in non-current assets in the total value of the company's assets.
The increase in the coefficient of turnover of own capital (from 2.91 to 7.25) is associated with a decrease in the share of equity.
Analysis of business activity and profitability indicates a general decline in profitability and business activity of the enterprise,
General conclusions on the financial analysis of the enterprise. The enterprise is in crisis, this is due to the non-optimal structure of assets and liabilities of the enterprise, the creditworthiness is also decreasing, the dependence of the enterprise on borrowed capital is growing, the financial performance of the activity for the analyzed period has worsened, profitability and business activity have decreased. All this suggests that in order to avoid worsening of the financial situation, the enterprise must take urgent measures to improve financial activities, change the financial strategy.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.