home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
4.2. Determination chislennostiotdelnyh categories of workers
Outlining the goals and directions of development of the company, its management should identify the necessary resources for their implementation, including labor.
Manpower planning at the operating enterprise begins with an assessment of their presence. The latter provides an inventory of jobs, identifying the number of those who work on each transaction, providing the ultimate goal (the creation of products, services). Analysis and further calculations are carried out by employee category (workers, executives, professionals, employees), and in each of them - in occupations, professions, ranks. When it comes to knowledge workers, in this case, you can use the system inventory of skills or trades, t. E. Registration of professional skills of employees with fixing the number of employees who own them.
Numerical calculations are based not only on the quantitative assessment of own labor resources, but also on the possible level of their use and to analyze the factors affecting the level of - technical, organizational, social and economic.
Objects of analysis in this case are:
- Nomenclature of manufactured products and services;
- Loss of working time and the reasons thereof;
- The nature and the comparative level of technological processes and equipment;
- Progressiveness and the contemporary requirements of the organization of labor and production;
- The level of motivation of labor activity;
- Standards of service and production, the level of actual implementation of standards, etc.
Determination of the planned number of staff depends on the specific production features of its functioning. In particular:
1. estimates the number of personnel in connection with the production volume will be different for the enterprises of mass and serial production in comparison with the single enterprises and pilot production;
2. The company, which radically diversifies its activities, will face significantly greater problems with the calculations, the number of personnel, compared to now, only increases the volume of production or services;
3. The company, which has a production at the seasonal nature will always have trouble with the definition of the number of personnel in periods of sharp increase and decrease of production during the year.
Provided significant organizational changes (for example, the creation of new businesses) assessment of future needs in the labor force is quite a challenge. In this case, use a typical structure model counterparts.
In the process of determining the number for the foreseeable future environmental factors need to be considered, namely:
- market conditions associated with the one or the other activity;
- cyclical nature of economic development, prediction of possible general economic downturn;
- regional labor market characteristics (moving production facilities to regions with lower labor costs);
- the state (government) programs, purchase orders, contracts (according to the latest enterprise is obliged to create new jobs);
- legal aspects (laws, agreements with unions, etc.), regulating labor relations, protect the interests of certain categories of the population and workers;
- the possibility of using the temporary hiring of workers, home-based work.
Engineering calculations planned number of specific categories of employees is determined by the specific characteristics of their profession and industry features of the functioning of an enterprise. But in any case it should be based on the account of possible factors for saving labor costs.
Consider the system required (basic) calculations on the example of an industrial enterprise.
First of all, to identify the total (hypothetical) number of industrial personnel for the planning period using the method of adjusting the number of the base:
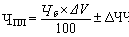
where the ELA - the number of industrial personnel necessary to ensure the planned volume of production, people .;
BW - basic (expected) number, people .;
D V - the planned rate of growth of volume of production,%;
DCH - total change in the number of payment options at factor productivity growth, people.
A more accurate method is to calculate the number of planned on the basis of the full complexity of manufacturing products:
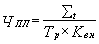
where St - the complexity of the planned full year production program (including the complexity of technology, the complexity of services and production management), labor hours;
Tr - the estimated effective fund-time per employee, hours (Table 4.3.);
Kv.n - expected rate of implementation rules.
Table. 4.3
The number of workers employed in the standardized work  , Calculated by the formula
, Calculated by the formula
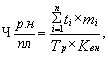
where ti - planned unit labor input i-th type of product, labor hours;
mi - the number of products i-th kind of units;
n - number of types of manufactured products.
The number of main workers at work Norm ( 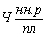 ) - Control process, control devices, machines and other equipment, is calculated according to service standards, namely:
) - Control process, control devices, machines and other equipment, is calculated according to service standards, namely:
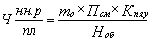
where mo - number of served objects (units, vehicles and other.);
PSM - the number of shifts of work per day;
Kp.ya.u- conversion factor into your safe house number, which is calculated according to the formula Kp.ya.u = 100 / (100 - f), where f - planned percentage of absenteeism of workers at work;
Knob - normal maintenance of the machine (car) - the number of objects in one operation.
The number of workers (mostly auxiliary), for which it is impossible to establish service standards and calculate the volume of work ( 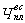 ) Is determined by the formula
) Is determined by the formula
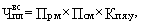
where Pr.m - the number of jobs.
The number of management employees, professionals, employees is calculated for each function by direct regulation, if the complexity of the data is sufficiently reliable.
Due to lack of information or excessive complexity of the calculations can be used the number of valuation method for these categories of staff using the correlation type
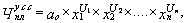
or
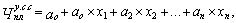
Where 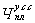 - Normative (planned) number of management employees in a specific function;
- Normative (planned) number of management employees in a specific function;
X1X2 ... xn - an important factor determining the number of employees for this function;
U1 U2 ... Un - exponents of the numerical value of the factor;
Common - a constant factor depending on the regulatory equation;
a1 a2 ... AN - regression coefficients (the exponents or coefficients) determine the extent of influence of each factor on the number of employees.
In determining the number of managerial staff are usually guided by the typical full-time schedules (charts, models), developed by the management of science and practice in a particular field of activity. Additional need for personnel for the foreseeable future states based on a comparison of its actual availability and need for planned period on separate professions and qualifications.
It is calculated as the expected increase in view of reducing the compensation (retirement, conscription, etc.), Replace the practitioners, etc.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.