home
 Economy Economy
 Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
|
Economy of the enterprise - Pokropivny SF
Chapter 7. Circulating assets
Key concepts and terms
Revolving funds; Structure (elemental composition); Normalized working capital; Methods of rationing; The norm of circulating assets in production reserves; The norm of circulating assets in work in progress; Coefficient of increase in costs; Performance indicators .
7.1. General characteristics and rationing
Concept and structure . At the enterprises there are current expenditures of financial (monetary) funds, which are involved in a certain cycle during the economic process (they are in the money, production and commodity stages). At the first stage of the circuit, the funds are spent on the acquisition of raw materials, materials and other resources, that is, they pass from the monetary form to the material and commodity, forming certain production reserves, and then enter the second stage - the production stage. At this stage, workers are included in the production process, who receive wages for their work. Then material and commodity values materialize in the form of finished products. At the last stage of the circuit, the manufactured products are sold (sold) and the enterprise receives the appropriate revenue (a certain amount of money), which should not only fully recover the previously incurred costs, but also give a certain profit.
Circulating assets - this is a set of cash assets of the enterprise, which are necessary for the formation and provision of circulation of production revolving funds and circulation funds.
Formation and regulation of individual elements of working capital has its own characteristics. With this in mind, they allocate working capital in the spheres of production and circulation, and also subdivide them into normalized and unregulated ones (Figure 7.1).
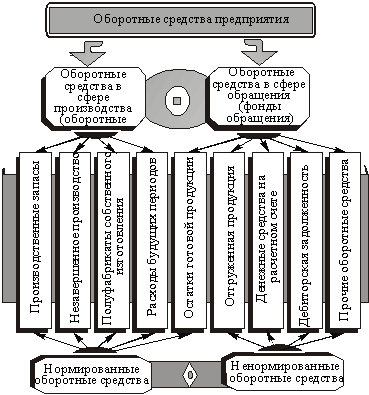
Fig. 7.1. Elemental composition of current assets of the enterprise (organization)
Of definite practical importance is the definition and evaluation of the structure of working capital. They are used more efficiently when most of them are engaged in production. The stay of circulating assets in the sphere of circulation is a necessary condition for the continuity of the reproduction process, however this part of the enterprise's funds does not take a direct part in creating the value of the manufactured products. At industrial enterprises of Ukraine, part of the working capital in the production sector is 72% (including 48% and 20% in production inventories and work in progress), and in the sphere of circulation - 28% (of which approximately 17% is the cost of finished goods, and 6% - cash).
Rationing . The necessary amount of money invested in the minimum inventory of commodity and material assets to ensure a continuous process of production is best determined by their standardization (calculation of standards).
There are three methods for calculating the standards of working capital: analytical , coefficient and direct calculation . Analytical (experimental-statistical) method provides for a thorough analysis of cash inventory with subsequent correction of actual stocks and the exclusion of surplus. Coefficient method is to clarify the current assets at the beginning of the calculation period of current assets in accordance with changes in this period of production indicators affecting the value of these funds. The direct calculation method is a scientifically based calculation of the norms for each regulated element of circulating assets (production reserves, work in progress, future expenses, finished product balances). In business management, it is the main one, other methods of calculation are used in most cases as auxiliary ones.
The standard of working capital in production reserves . In terms of economic content, industrial reserves are divided into elements relating to working capital (raw materials, materials, fuel), and elements that gravitate to fixed assets (spare parts for repairs, tools, tools and other low-value items). The methodology for determining the standard of working capital in the two types of production stocks is not the same.
The standard of circulating assets in production reserves relating to circulating assets is determined by multiplying the average daily consumption of materials in value terms by the rate of their stock in days.
The accuracy of the calculations depends on the correct definition of the necessary reserves of material resources. At the enterprises there are several types of such stocks: transport , preparatory (technological) , current , reserve (insurance) . In the transport stock, which usually does not exceed two days, working capital is invested for the period from the moment of payment of the invoice issued by the supplier before the arrival of the goods to the warehouse of the enterprise. Preparatory stock is created for the time necessary to accept the material resources of their storage and preparation for production use. The largest in terms of volume is the current stock of raw materials (materials) and other elements of circulating assets (labor): it is calculated within half of the average interval between deliveries of certain types of material resources (for example, if the terms of the contract between the supplier and the consumer stipulate the receipt of materials, for example, one Once a month, their current stock should provide 15 days of work). The reserve (insurance) reserve can be determined in two ways: according to the average deviation of the actual delivery dates from those stipulated by the contract or by the period necessary for urgent ordering and delivery of materials from the producer to the consumer.
In general, the norms of working capital in production reserves relating to working capital are determined according to the following scheme (conditional data):
| 1. Quarterly demand for materials | - 2700 t |
2. Average daily consumption of materials |
- 30 t |
3. The price of one ton of material |
- 12000 UAH |
4. Cost of daily consumption of materials (item 3? Item 2) |
- 360000 uah |
5. Stock Rate: |
|
A) transport |
- 2 days |
B) the preparatory (technological) |
- 3 days |
C) The current |
- 15 days |
D) reserve (insurance) |
- 5 days |
E) Total |
- 25 days |
6. The standard of working capital in production reserves (paragraph 4 x 5, d) |
- 9 000000 UAH |
The method of rationing circulating assets in the elements of production reserves that gravitate to fixed assets, but according to the current accounting system are referred to revolving funds, differs significantly from the one described above. In particular, the basis for calculating working capital in spare parts for repairs is the reserve of parts per unit of repair complexity of the respective types of machinery and equipment. General principles of rationing of current assets in low-value and rapidly wearing items are also: 1) separate definition of norms for material values stored in the warehouse of the enterprise and used (operated) in production; 2) the monetary valuation of warehouse stocks at their full procurement cost (cost price), and the used items - at a rate of 50% of their primary cost, 3) the rejection of rationing in days of consumption of exploited items, and the calculation of norms for their individual groups on the basis of coefficients characterizing The dependence of the size of the stock on the number of personnel, the number of jobs, the cost of certain types of equipment, and so on.
The standard of working capital in work in process . The value of this standard depends on the volume of manufactured products, the cost of its individual types and the nature of the distribution of costs throughout the production cycle. Other things being equal, working capital in this functional form varies directly in proportion to the dynamics of the scale of output and the cost of production. At the same time, the ratio of the average cost of work in progress and the cost of finished goods, which is commonly called the coefficient of increase in costs , should also be taken into account.
The norm of circulating assets in work-in-process 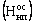 Can be determined using formula
Can be determined using formula
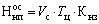 (7.1.)
(7.1.)
Where V с - average daily output of commodity output at its production cost;
Tc is the average duration of the production cycle in days;
Кнз - coefficient of growth of expenses (the cost price of a work in progress).
The determination of the average figures of daily output at its cost and duration of the production cycle does not cause any difficulties. The first of them is calculated by dividing the planned (expected) output by the number of days of the calculation period, and the second - as a weighted average by the specific weight of products (their groups) in the cost of goods.
The coefficient of growth of costs requires special preliminary calculations. Most accurately, it can be determined by allocating costs on the days of the production cycle. For this purpose, according to the estimates of production costs, they are divided into disposable (the cost of raw materials and basic materials, which initially participate in the production process) and those that are gradually increasing (the remaining costs). If the cost of wages and maintenance of production can not be calculated on the days of the production cycle, then they are conditionally distributed in equal parts for each day of the cycle.
The methodology for determining the coefficient of increase in costs is shown in the example. Let's assume that the cost price of some change is 50100 UAH, and the average duration of the production cycle is 6 days. The distribution of costs by the days of the production cycle is shown in Table. 7.1. In these conditions, the average cost of work in progress will be 39100 UAH. (234,600: 6), and the coefficient of increase in costs - 0,78 (39100: 50100).
Table 7.1.
DISTRIBUTION OF COSTS ON MANUFACTURE OF THE PRODUCT ON DAYS OF PRODUCTION CYCLE, UAH.
| The production cycle | Daily Costs |
Sum Expenditure Expenditure |
first |
30000 |
30000 |
second |
3000 |
33,000 |
the third |
3500 |
36500 |
fourth |
4000 |
40500 |
fifth |
4000 |
44500 |
sixth |
5600 |
50100 |
Total |
50100 |
234600 |
However, with a large nomenclature of manufactured products, this method of determining the coefficient of increase in costs can be extremely laborious. Therefore, at enterprises manufacturing material-intensive products and because of this need for significant one-time costs, the coefficient of increase in costs can be calculated by the following simplified formula:
Rn = (Sp.dec + 0.5 s.d.): Sp.i, (7.2)
Where Sp.d. is the initial costs on the first day of the production cycle;
Со.д.Ц - the cost of manufacturing products in the remaining days of the cycle;
Sp.i - the production cost of the product.
So, proceeding from the data of tab. 7.1, the coefficient of increase in costs, calculated by formula (7.2), will be equal to 0.8
[(30000 + 0.5x20100) / 50100]. As you can see, the error in the calculations is small - only 0.02 (0.8 - 0.78) - and is entirely acceptable for this kind of practical calculations.
If we proceed from the assumption that the average daily output is 20,000 UAH, and the duration of the production cycle is 6 days, then the standard of funds in the work in process, calculated according to formula (7.1), will be
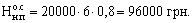
The standard of working capital in other normalized elements . In addition to production stocks and work in progress, the normalized elements of current assets also include future expenses and leftovers of finished goods in the enterprise.
The norm of circulating assets in the expenses of future periods is calculated on the basis of the balance of funds at the beginning of the period and the amount of costs over the estimated (planned) period, minus the amount of subsequent cost recovery due to the cost of production.
For example, at the beginning of the settlement period, the balance of future period funds is 8000 UAH., The need for them during this period is 82,000 UAH., The cost of the products to be manufactured will be charged to the repayment of previously incurred expenses of UAH 36,000. The standard of working capital in the expenses of future periods will be 54000 UAH. (8000 + 82000 - 36000).
The standard of working capital in the remainders of finished goods is defined as the product of the cost of one-day output of finished goods to the norm of their stock in the warehouse in days. In turn, the stock norm consists of the number of days necessary to prepare the products for sale (sale), i.e., its acquisition, packaging and shipping to consumers, with the addition of time for the discharge and delivery of payment documents to the bank.
It is clear that the aggregate standard of the company's current assets for the settlement (planned) period is the sum of the standards calculated for individual elements (production stocks, work in progress, future expenses and finished product balances).


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.