home
 Marketing Marketing
 Principles of Marketing - Philip Kotler Principles of Marketing - Philip Kotler
|
Principles of Marketing - Philip Kotler
Competitors
Any company faces many different competitors. Suppose, vice president of marketing, wants to reveal all the competitors of the company "Schwinn". The best way to do this? to conduct a study of how people make the decision to buy a bicycle. The investigator may interview the student of the first year of college, John Adams, who was going to spend some money (see. Fig. 25). John is considering several options, including vehicle purchase, purchase a stereo system or a trip to Europe. This desire to competitors, ie, desires that the consumer may wish to meet. Suppose that John Adams decides that he most needs to improve its transport capacity. In front of him a few options: buying a car, buying a motorcycle or bicycle purchase. This commodity-generic competitors, ie other basic ways to meet any particular wishes. If the most attractive option would be the purchase of a bicycle, John will think, what kind of bike to buy. You receive a number of commodity-species competition, ie other varieties of the same product that can satisfy a particular desire of the buyer. In this case, the varieties of goods will be three-, five- and desyatiskorostnye bikes. John may stop at desyatiskorostnom bike, then he'll want to meet with several brands of competitors. These are different brands of the same product to satisfy his desire. In this case, "Schwinn" "Raleigh", "Sears", "Asuka" and "Gitay".
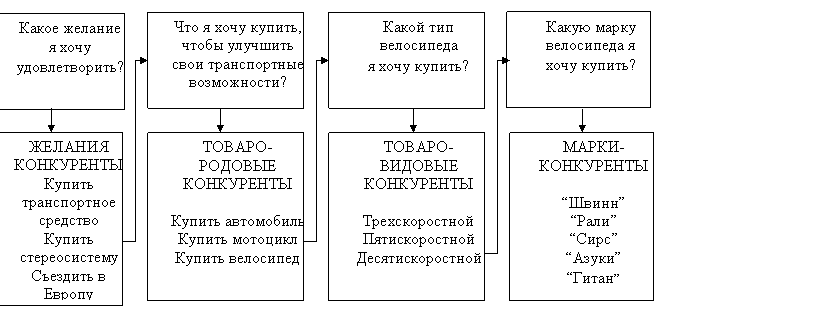
Fig. 25. Four main types of competitors
Understanding how consumers make decisions, can ease the vice-president of marketing for the identification of all competitors hindering the company "Schwinn" to sell more of their bikes. Manager wants to look at all four competitors species, paying particular attention to the brand - the competitors, because they actively discourage sales of the firm "Schwinn".


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.