Guide MIT on the opening of locks picklock
Chapter 3 - The Horizontal Model
For. To learn how to properly open locks, it is necessary to study in detail how locks work and what happens at the autopsy. This manual uses two models to help understand the principle of locks. This chapter describes a model that shows the relationship between the positions of the pins. This model is used in Ch. 4 to explain the principles of autopsy. The same model will be used in Ch. 9 to explain complex mechanical defects.
The "horizontal" lock model is shown in Fig. 3.1 . This is not an incision of a real castle. This is a simplified view of the castle in the section. The purpose of this lock is to hold the two metal plates in a fixed position until a suitable key is inserted. The lock is made in the following way: two plates are placed one above the other and holes are drilled, passing through both plates. The figure shows a lock with two holes. Two pins are placed in each hole in such a way that the gap between the pins is not in line with the gap between the plates. The lower pin is called the key pin, as it touches the key. The upper pin is called the guide pin. Often the guides and key pins are called simply the guide and the pin. The protrusion on the lower surface of the lower plate keeps the pins from falling out, and the spring above the top plate presses the guide pin.
When the key is not inserted in the groove, the plates can not move, since the guide pins pass through both plates. The correct key raises the pin pairs, and the gap between the pins aligns with the gap between the plates. Look at Fig. 3.3 . That is, the key raises the key pin, and the tip of the pin reaches the line of rotation of the cylinder. In this position, the plates can move.
Fig. 3.3 illustrates also one of the important features of these castles. Between any parts moving relative to each other, there must be a gap. The gap between the top and bottom plates allows you to open the lock next to the keys. Note that the right key pin in Fig. 3.3 is not raised as high as the left pin, but the lock, however, opens.
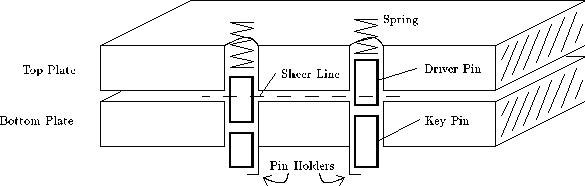
Fig. 3.1 . Horizontal lock model
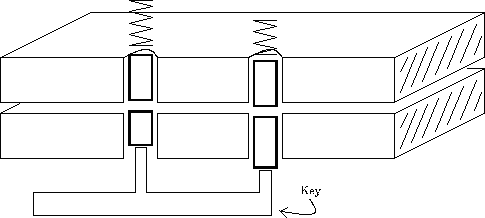
Fig. 3.2 (a) . The key raises the pins
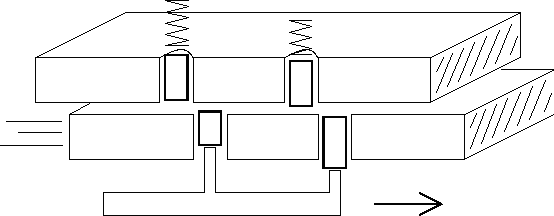
Fig. 3.3 (b) . The right key leads the plate into motion




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.