8 useful regexps with a clear analysis of
About the power and flexibility of regular expressions written much, and their use has long been the standard for various types of operations on a text consisting of letters, numbers and service sivmolov. Perhaps the most regexps operate validation (verification) data entry - they are virtually no alternative, except bulky cyclic analysis functions with a bunch of non-obvious and obscure checks.
1. Part of the CNC (chelovekoponyatny URL)

pattern:
/ ^ [A-z0-9 -] + $ /
In fact, the word with hyphens.
2. The user will
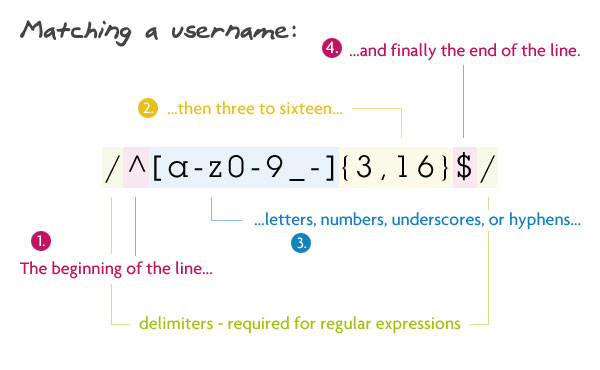
pattern:
/ ^ [A-z0-9 _-] {3,16} $ /
Letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores, from 3 to 16 characters.
3. Password

pattern:
/ ^ [A-z0-9 _-] {6,18} $ /
Same yuzerneym and only 6 to 18.
More succinctly - / ^ [\ w _] {6,18} $ /.
Similarly, for yuzerneym.
4. Hex color

pattern:
/ ^ # ([A-f0-9] {6} | [a-f0-9] {3})? $ /
The # (optional), then the word consisting of the letters a through f or numbers, length 3 or 6.
5. XML tag
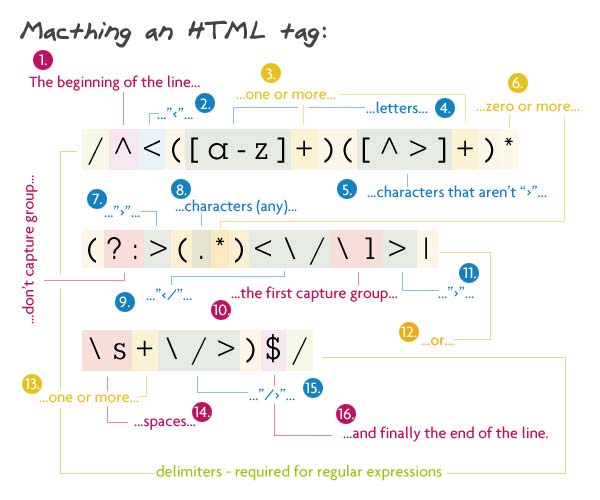
pattern:
/^<([az]+)([^>]+)*(?:>(.*)<\/\1>|\s+\/>)$/
During the opening parenthesis <must be the word of the letters - the element name can then be attributes - any characters except the closing bracket>. Next - any text (content) and the closing tag, ie <Name />, or at least one space, slash and closed bracket (self-closing tag).
6. Email
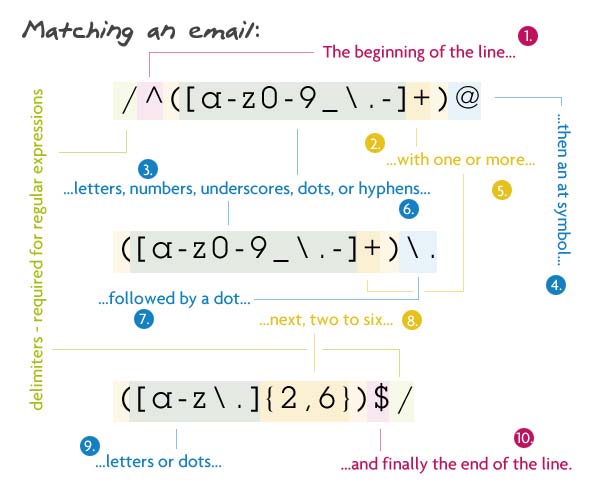
pattern:
/^([a-z0-9_\.-]+)@([a-z0-9_\.-]+)\.([az\.]{2,6})$/
General view - логин@поддомен.домен. Login as a subdomain - words from letters, numbers, underscores, dashes and dots. A domain (meaning 1st level) - is from 2 to 6 letters and dots.
It can be shorter - /^([\w\._]+)@\1\.([az]{2,6}\.?)$/.
It is also a little more correct - a point in the domain of the first level can occur only once and only at the end.
7. URL
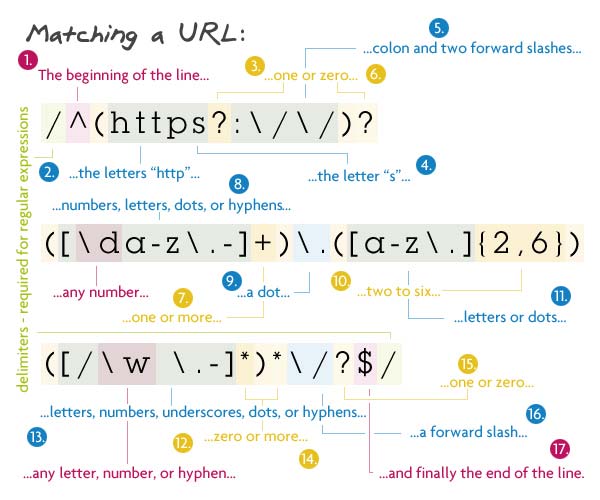
pattern:
/^(https?:\/\/)?([\da-z\.-]+)\.([az\.]{2,6})([\/\w \ .-] *) * \ /? $ /
First of all - the optional protocol (http: // or https: //), then the sequence of letters, numbers, hyphens, underscores and dots (domains level> 1), then the zero-level domain (from 2 to 6 letters and dots) and, finally, the file structure - a set of words from letters, numbers, hyphens, underscores and dots with a slash at the end. All this can be completed again slash.
The best way - /^(https?:\/\/)?([\w\.]+)\.([az]{2,6}\.?)(\/[\w\.]*) * \ /? $ /
8. IP address
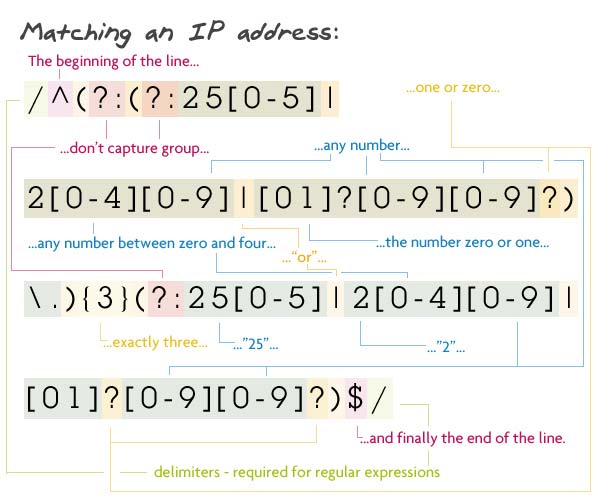
pattern:
/ ^ (?: 25 [0-5] | 2 [0-4] [0-9] | [01] [0-9] [0-9]) \) {3} (25 ?: [0-?. 5] | 2 [0-4] [0-9] |?? [01] [0-9] [0-9]) $ /
4 groups of numbers (1 to 3 digits each) separated by periods. If the group consists of three characters, the first of which - one or two; if 1, then the remaining 0 to 9, and if the two - then a second from 0 to 5; if the second symbol from 0 to 4, the third - from 0 to 9, and when the second 5 - the third from 0 to 5. If the group consists of two characters, the first - from 1 to 9, the second - from 0 to 9 . In the case of single-character group with this symbol can be any number from 1 to 9.
So correct - / ^ (?
 : 25 [0-5] | 2 [0-4] \ d | [01] \ d \ d) \) { 3} (25 ?: [0-5] | 2 [0-4]?. \ d | [01] \ d \ d) $ / ??.
: 25 [0-5] | 2 [0-4] \ d | [01] \ d \ d) \) { 3} (25 ?: [0-5] | 2 [0-4]?. \ d | [01] \ d \ d) $ / ??.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.