home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
16.3. Total costs and production costs
The total cost of the enterprise, depending on their purpose expressed by several indicators. The main estimates include the cost of production and product and sales of products sold.
Estimated production
Estimated production - is the cost of the enterprise associated with the primary (operating) of its activities for a certain period. Overall estimates of the enterprise is made on economic elements. An exemplary form is shown in Table. 16.1 and below briefly reviewed the content of individual elements of cost and procedure for the development budget.
Table 16.1
ESTIMATED PRODUCTION TO ______________________ year
| cost elements | Sum, thousand. UAH |
|
Fakticheskayaza last year |
plan for the next year |
|
|
5210 |
5400 |
|
2050 |
2300 |
|
720 |
805 |
|
800 |
800 |
|
450 |
500 |
|
9230 |
9805 |
|
1630 |
1805 |
|
- |
+200 |
|
10 |
- |
|
50 |
-300 |
|
7560 |
8100 |
|
-140 |
+100 |
7700 |
8000 | |
Material costs as an element of the estimates consist of the costs of:
- raw materials and basic materials, which are the material substance of products;
- products that need to be purchased for the staffing of products (engines, appliances, etc...);
- purchased semi-finished products (stampings, castings, forgings, etc...);
- production services of foreign companies and organizations, necessary for the manufacture of the product;
- auxiliary materials used in the process (hardware, paint, hardware and so on. p.) or required for maintenance (repair, maintenance equipment, etc..), for economic needs and administrative requirements (maintenance of premises, office supplies and so on. P.);
- fuel and energy on the part of (electricity, gas, steam, etc...); costs of own energy production are included in the estimates for the individual items;
- search and the use of natural raw materials (deductions for exploration, land reclamation, etc..).
material costs are determined on the basis of norms of consumption and prices, taking into account transportation and procurement costs, which are not components of other budget items (payment for transportation, handling, commissions procurement organizations and others.). Because the cost of materials is subtracted the cost of waste and costs of use or sale.
Salary includes all forms of labor staff and freelance production staff of the enterprise payment, t. E. The personnel engaged in the production of products, services and manufacturing process control. It does not include an estimate of employee benefits, which are financed from profits or other sources of special purpose.
Social contributions include social security contributions to the Pension Fund and other similar events. The magnitude of these allocations is determined by the established norms on the basis of labor costs, regardless of the sources of its financing.
Depreciation of fixed assets in the form of depreciation on the full their reproduction (renovation) is determined by the established norms of their book value. Amortization of intangible assets is carried out on linear uniform method based on the period of their operation.
The other costs include those that the content can not be attributed to the mentioned above. This wide range of costs for different purposes, namely: payment services, security, travel expenses, property insurance, compensation for inventions and rationalization proposals, payment of works on certification of products, warranty repair costs, rent and others.
Estimated production costs generalizing elementwise companies shows their resource structure (the cost of materials, personnel, fixed assets), which is very important to analyze the factors reducing production costs.
The order of development of production estimates may be different depending on the stage of planning, the state of the information base and the size of the enterprise. At the stage of the forecast estimates of the cost of production estimates can be correcting the actual costs for the previous period.
Elements of the actual costs are adjusted with the help of predictive factors changes in production volume, number of staff and the cost of fixed assets, taking into account the laws of dynamics of cost, probability of changing norms and of prices (tariffs). A more reasonable estimate of production is determined for each economic element based on planned volumes of production (services), standards and prices (tariffs). For small businesses this calculus is generalizing. In the medium and large enterprises estimate production is summing cost estimate places (shops, services, administrative costs to sell).
product cost
At the enterprises calculated cost of production and sales of commodity.
The cost price of a commodity output of the enterprise is calculated in two ways. First, a synthetic, based on production estimates. As can be seen from Table. 16.1, in this case, the estimate is corrected as follows:
- deducted from the estimate of the costs, which are not considered manufacturing and production costs are not included. This is primarily administrative costs, distribution costs, and some other;
- subtracted gains added declining balance of deferred costs;
- added growth, subtracted reduction in balances of future payments (vacation pay, compensation for length of service, for the preparatory work in seasonal industries, and others.);
- subtracted growth, added the decrease in work in progress of production.
The resulting amount is the cost of production of marketable products.
Another way to calculate the cost of commodity products is the summation of the pre-counted the cost of separate products, ie
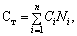 (16.10)
(16.10)
where C - the cost of marketable products;
n - number of different products (services);
Ci - i-th unit of production (services) prime cost;
Ni - i-th production of goods (services) in physical measurement.
There is another method of calculation of marketable production costs - pofaktorny. He methodically worked well and is mainly used as an auxiliary. In accordance with this method
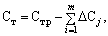 (16.11)
(16.11)
where St.r - the cost of the planned production volume at the level of the base cost (past) period (estimated cost);
m - number of factors influence the cost of production in the planning period;
? C j - the cost of a change in the planned (forecast) period under the influence of j-th factor.
? Changing the cost under the influence of organizational and technical factors So.t determined on the planned volume of production costs as the difference before and after the implementation of measures:
? So.t = (C2 - C1) of N 2 (16.12)
where C1, C2 - the cost per unit of output before and after the implementation of measures;
N 2 - the volume of production of these products after the introduction of measures in the plan period.
Because the estimated cost St.r conditionally fixed costs are taken at the level of the base period, and in the planning period the volume of production may change, which consequently will affect the cost of production, it must be considered as a single factor:
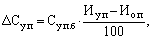 (16.13)
(16.13)
? Where Su.p.b - conditionally fixed costs in the base period;
Iu.p, Io.p - a change in the planning period, respectively conditionally fixed costs and output,%.
Conventional example. The volume of commodity production in the reporting year amounted to 10,200 thousand UAH, while the cost of 1 USD to this product -. 0.75. The planned year is planned to increase the production volume by 10%. Due to the introduction of new technology will be saved 256 thousand. UAH Fixed costs have reached 2500 thousand. UAH, and due to rising production volume, they increase in planned year by 4% in the reporting year.
Against this baseline, the estimated figures will be:
- Planned production volume:
Fr = 10200 = 11220 • 1,1 thousand. UAH
- the cost of commodity production on the level of the reporting year costs:
St.r = 11 220 • 0,75 = 8415 thousand. UAH
- the relative savings of fixed costs due to increased production volume:
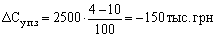
- the cost of commodity products:
CT = 8415 - (265 + 150) = 800 thousand. UAH.
In economic practice also define and regulate the overall level of cost per unit of production volume. In this example, the planned costs of USD 1 commodity output amounted to UAH 0.713 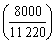 and decreased in comparison with the previous year by 4.9%
and decreased in comparison with the previous year by 4.9% 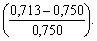
Cost of sales is calculated by adjusting the cost of commodity production on changes in the balance of unsold goods:
Cp = Cm + (Ss.n - Ss.k), (16.14)
where Cpn - cost of goods sold;
Ss.n., Ss.k - the cost of the remnants of commercial products in stock, respectively, at the beginning and end of the year.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.