home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
16.4. Cost of individual items
The essence and methods of calculation
The system of technical and economic calculations of the company occupies an important place kalkulirovanie - determining the cost of certain products. The latter is necessary to solve some economic problems:
- justify the price of the product;
- determining the profitability of products;
- cost-benefit analysis for the production of identical products in different enterprises;
- the calculation of the effectiveness of various organizational and technical measures.
In enterprises, as a rule, make up planned and actual costing. The first are calculated at planned cost norms, the second - on their actual level. A variation of the standard cost estimate are the so-called design-estimate calculation that make up one-time orders, new products at the design stage. The peculiarity of these calculations is that the calculations are approximate because of the lack of detailed and reliable regulatory framework.
Regardless of the specific characteristics of production and calculation of the product provides a solution to inherent methodological problems: the definition of the object of calculation and choice of calculation units, a clear allocation of calculation cost items (costs) and the application of a methodology to determine them.
The object of calculation - this is the product or the work (service), the cost of which is calculated. The objects of calculation are: basic and auxiliary products (tools, energy, spare parts); service or work (repair, transportation, and so on. n.). The main object of calculation - finished products that are delivered outside the enterprise (market). Kalkulirovanie other products is of secondary importance.
For each object corresponding to the selected calculation calculation unit - a unit of its quantitative measurement. For example, the calculation of the object - tractors, the calculation unit - one tractor a certain type (purpose); coal, respectively - one ton; electricity - kilowatt-hour, and so on..
There are different methods of calculation of production. Their use depends on the specific production purpose calculations, enterprise traditions, etc. First of all, we must distinguish between the methods of calculation depending on the completeness of cost accounting. On this basis allocate:
- for calculation of total costs;
- According to incomplete calculation of costs.
According to the first method of all the operating expenses of the enterprise as a productive and non-productive (administrative, sales) are fully charged to cost of production. This was the traditional method of calculation in the domestic industry until 2000. It is used to a certain extent and in the world. His dignity is sufficient flexibility so that the cost of products to determine their cost-effectiveness; because the total cost is the price of the base, the last smears be determined using pricing models, "cost plus profit"; sum of the products the cost of certain products in the common object of their release forms the full cost of commodity products, etc.
However, the calculation of the total cost for has disadvantages. The main ones include: the complexity of the calculation and the complexity of its production due to Multicommodity complex indirect cost allocation procedures; inaccurate calculations from the impossibility of accurate distribution of indirect costs; not full compensation of non-production costs in a certain period, if the increase remains of finished products in stock, and so on. n.
Calculating costs for an incomplete theory has been proved in the 20-ies of XX century. Its essence lies in the fact that not all the costs are included in the calculation. This simplifies the calculation of and making it more operational. What costs are included in the calculation, and which are not included, and include the full amount for a certain period - a particular problem. In most cases, are not included in the cost of certain products administrative costs and marketing costs. Such procedures are provided, and national regulations (standards) of accounting in Ukraine, developed in accordance with international standards (IAS). In this case, the calculation is made on the costs of production units, and forms the production cost of the product. All other indirect manufacturing costs do not relate to a specific period and the calculation of profit enterprise just deducted from the proceeds.
One option for the calculation of costs is incomplete method "direkt - cost", where costs are determined only by direct costs and indirect costs related to a specific period.
Significantly affect the method of calculation of the breadth of the range of company's products and specific production. The most accurate and methodologically simplest is the calculation of the production in odnoproduktnom: unit costs are calculated by dividing the total costs for a given period by the number of manufactured products. However Multiproduct production prevails in most manufacturing industries. The calculation of these conditions and becomes much more complicated Me accurate because, as already stated, the problem of correct distribution of indirect costs.
During the calculation of the costs are grouped according to calculation items, the range of which depends on the characteristics of production. Establishing cost items, you must comply with the following requirements:
- the maximum share of the costs included in the cost, you need to calculate the right on certain products;
- Article indirect costs should be formed so that they can be reasonably distributed among products.
The estimated range of calculation cost items shown in Fig. 16.5.
With calculation on the total cost to the listed items are added to items such as administrative costs, other operating costs and marketing costs.
In some sectors of the economy and especially in industry nomenclature of calculation differs from the articles above. In particular, engineering-specific are the articles "purchased products, semi-finished products, production services of outside organizations and enterprises", "Depreciation of tools and accessories for special purposes", "losses from marriage," in some industries stand article "Semi-finished products of own production" (black metallurgy), and others.
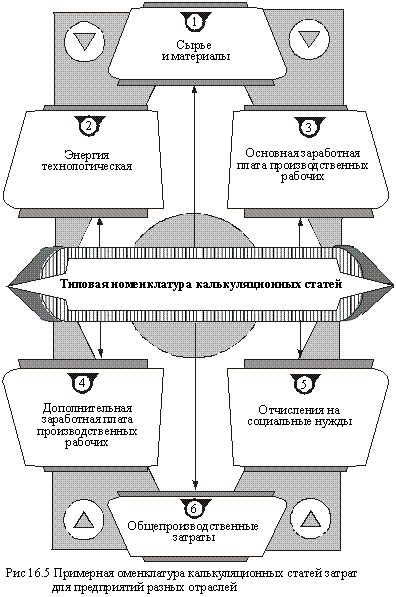
The methodology of calculation of the main items of calculation
In the process of calculation of direct costs are calculated directly on the unit of calculation in accordance with the applicable rules and prices. For indirect costs, first make an estimate for a certain period, after which the costs are allocated between the different products according to the procedure adopted in the enterprise.
The article "Materials" includes costs for raw materials, basic and auxiliary materials, components, specifically for the particular finished product, which manufactures the enterprise. The absolute value of the material substance (physical resources) based on the physical unit is determined on the basis of predetermined shape and consumable costs. It should be borne in mind that transportation and procurement costs can vary significantly, and recyclable waste absent.
The article "Energy technology" includes energy (fuel, electricity, gas, steam, etc.) The costs, which is used directly in the process to change the state of an occupational or objects (melting, heating, welding, drying, etc.) . Calculated according to the norms of costs and energy tariffs
The article "The basic wage of production workers" include labor costs of workers directly involved in production of the main products. Calculated in accordance with the rules of time-consuming to perform technical operations and tariff rates, or piece-rate operations, parts, components.
Additional wages of production workers (paid vacations, runtime state duties, surcharges for additional functions, etc..) Is calculated as a percentage of the basic wage and social spending, including contributions to the Pension Fund of Ukraine as the principal of their kind - in a percentage of the sum of basic and additional wages.
Article "General costs" is complex. These include various overhead costs, which by their functional purpose are divided into two groups: the first - the cost of maintenance and operation of machinery and equipment; the second - the costs of organizing and management of production.
The cost of maintenance and operation of machinery and equipment covering a wide range of costs necessary for the operation of the equipment in the manufacturing process mode, as well as to maintain it in a state of readiness for operation (depreciation, cost of electricity, compressed air, lubricants, tools, services and repair and so on. n.).
The costs for the organization and management of production include: salaries of the administrative staff of production units, in the information management software costs, depreciation and maintenance of buildings, structures, repair, maintenance costs of production and so on..
On the overhead costs are estimated for each production unit (workshop, site) for one year with a quarterly breakdown. In the unit of each type of product they are calculated by the method of distribution in proportion to the selected database.
The most common in domestic enterprises is the allocation of overhead costs in proportion to the basic salary of industrial workers. In this case
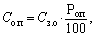 (16.15)
(16.15)
where C OP - overhead costs per unit of output, UAH .;
With z.o - basic wage of production workers per unit of production, UAH;
Rop - the ratio of overhead costs and basic salary,%.
The value of Rop is calculated on the shop floor (production) as the ratio of the annual estimates these costs to the payroll during the same period. The main advantage of this method is its simplicity. However, it has serious shortcomings, particularly with respect to the distribution of costs for maintenance and operation of machinery and equipment. First, the salary is not an exact base distribution of these costs, because under different level of mechanization of labor, it does not adequately reflect the cost of computer time; secondly, when such distribution costs per product is defined as a unit on average no matter what the product is processed on hardware; Third, when the comprehensive mechanization and automation of production in the operating functions begin to dominate the functions of control and regulation of operation of production systems. Under these conditions, wages can not be normalized operation by operation and, therefore, can not be the basis of other distribution costs.
To a large extent, you can fix this problem by distributing overhead costs in proportion to the product processing time, t. E., Based on the average cost per hour of parking equipment. This method is quite common in international practice, but it is also inaccurate. Firstly, the costs of the organization and management of production depends not only on the amount of time the machine park and it works, but also on the number of workers and labor-intensive process. Therefore, the distribution of these costs with the use of a base can be considered reasonable if labor and mashinoemkost different types of products are not very different. Second, this method does not take into account that the operating costs per unit of time on different machines will be different due to the fact that the machines are unequal in value of engine power, require the use of various additional tools and so on. N.
In the context of increasing demands for precision of calculation, particularly in mashinoemkih industries, distribution of general production costs it is advisable to carry out separately for their parts, ie, the cost of maintenance and operation of machinery and equipment to distribute one base, the rest of the -.. On the other.
The most reasonable is costing the maintenance and operation of machines and equipment for one product based on the time it is processed and the cost of one hour of parking your specific hardware. Unlike the previous method, this is used in calculations that the parking cost hours, not all equipment and for each group of similar machines.
If necessary, determine the total cost of administrative expenses are added to the production cost of production, other operating costs and expenses for the sale of goods. These costs are estimates, similar estimates of overhead costs. With calculation on full costs are allocated between the products in proportion to the installed base.
The administrative costs are associated with the management of the enterprise as a whole and the organization of its activities: maintenance of management, information technology companies, depreciation and maintenance of fixed assets general economic purpose, post and telegraph, office expenses, the costs of settlement of economic relations in the destinies of the organs, and so on. n. in most cases, the calculation of these costs are allocated in proportion to the wages of industrial workers and the labor intensity of production in man-hours. In the medium and large n redpriyatiyah more reasonable distribution of a two-stage administrative costs. First, they are allocated between the production units in proportion to the selected database, and after that - between departments products.
Other operating expenses include expenses for the preparation and development of new products, the amount of uncollectible receivables Provision for doubtful debts, losses from devaluation of stocks and other. They can be distributed in proportion to the cost of production or distribution on the basis of the administrative costs.
Costs of sales include expenses for market research, advertising and sale of products. Some of these costs are direct and can be directly calculated for the individual products (in packaging, packaging costs, advertising, transportation in a particular area of the market). Indirect costs (in the market analysis, sales commission payments to organizations, fairs and so on. N.) Are allocated between the products in proportion to production costs.
Forecasting cost during the design and development of new products
On the stages of development of new products when there is no set of technical documentation and the necessary regulatory framework, its cost is defined only as the likely magnitude of the forecast. It uses various methods of forecast evaluation, among which are the main parameter. Parametric they are called, therefore, that are based on production costs, depending on its parameters - technical and operational parameters.
Parametric method of calculating the cost of production owned by the methods: unit costs, ranking point, correlation and aggregation.
The method of unit costs is the simplest, but least accurate. In accordance with these new product cost (CH) is determined by the formula
CH = Ca • Mon (16.16)
where Ca - unit cost of development of production of goods- analogue;
Mo - the main parameters of the new products (engine power, vehicle load or crane, the volume of the refrigerator).
A more accurate are the methods that take into account not one but several options. These include tenths and correlation techniques.
Scoring method is based on expert evaluation of the influence of the main parameters of the product at its cost. Each parameter product is evaluated certain number of points. Cost of the basic product divided by the sum of points of all parameters and in a manner determined by the cost of one score (Sat). After that, the cost of a new product is calculated by the formula
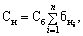 (16.17)
(16.17)
where n - number of parameters that affect the cost of the product;
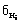 - The number of points on the i-th parameter of the new products.
- The number of points on the i-th parameter of the new products.
Корреляционный метод позволяет установить зависимость себестоимости изделия от его параметров в виде эмпирических формул, выведенных на основе анализа фактических данных для группы аналогичных изделий. В процессе анализа выясняется форма связи (линейная, степенная) себестоимости и основных параметров изделия, а также ее плотность. Корреляционный метод прогнозирования себестоимости новых изделий является наиболее точным и распространенным.
Агрегатный метод не является самостоятельным параметрическим методом. В соответствии с ним себестоимость изделия определяется как сумма себестоимости конструктивных его частей — агрегатов. Стоимость унифицированных агрегатов учитывается по существующим ценам, оригинальных — определяется по одному из рассмотренных выше методов или экспертным путем.
Себестоимость новой продукции — динамический показатель, который существенно зависит от уровня освоения производства, а последний — от количества изделий, изготовленных с момента начала производства. С учетом этого эмпирически установлена зависимость себестоимости новых изделий от их количества, иначе говоря, от порядкового номера изделия с начала освоения. Эта зависимость имеет форму степенной функции:
С i = С1 • N–в i , (16.18)
где С i — себестоимость i-го изделия с начала выпуска;
С1 — себестоимость первого изделия;
N i — порядковый номер изделия с начала освоения;
в — показатель степени, который характеризует темп снижения себестоимости в период освоения (определяется эмпирически из анализа кривых освоения).
Условный пример . Осваивается производство новой сложной машины. Период освоения — 2 года. Себестоимость машины на начальном этапе освоения (первого образца) — 320 тыс. грн. За первый год освоения предусматривается изготовить две машины, за второй — четыре. Коэффициент освоения, характеризующий темп снижения себестоимости изделия к концу второго года — 0,8, а показатель степени соответственно — 0,322 (loq2• кос = — в). Необходимо определить прогнозную себестоимость изделия на конец второго года освоения производства, то есть себестоимость шестой машины. По формуле (16.18) она будет составлять
С6 = 320 • 6–0,322 = 179,8 тыс. грн.
Знание закономерностей изменения себестоимости продукции, особенно сложных машин, в процессе освоения производства позволяет обоснованно управлять формированием затрат, прогнозировать их уровень на разных этапах освоения.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.