home
 Economy Economy
 Business Economics - Pokropivny SF Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
|
Business Economics - Pokropivny SF
Chapter 15: Performance, motivation and remuneration
Key concepts and terms
Labour productivity; development of products; labor input per unit of output; factor productivity method of forecasting; labor motivation; methods of labor motivation; salary; basic salary; additional remuneration; tariff system; forms of remuneration; wage workers; bonus system personnel; employee participation in the profits of the enterprise (organization).
15.1. Productivity of personnel: the nature, methods and determination of growth factors
Essence and Measurement
Under the labor productivity as an economic category is commonly understood as the effectiveness of (fruitful) labor costs, the ability to easily create a specific unit of time in a certain amount of wealth. Any increase in productivity saves total (living, embodied and future) labor. Specifically, such an increase is that the proportion of living labor decreases and increases materialized, but the total value of the complexity of the production of goods is reduced.
productivity level is determined by the amount of product (volume of work or services), which produces one worker per unit of time (hour, shift, day, month, quarter, year), or the number of working hours consumed per unit of production (performance of work or services ).
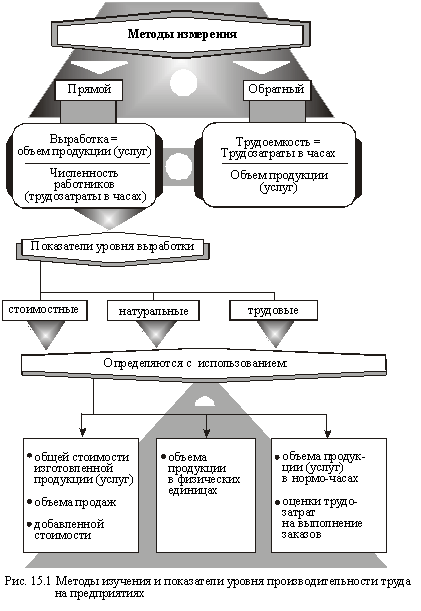
A variety of approaches to the definition of labor productivity levels depend on the specific activity of certain companies or their divisions, and the purpose of the calculations are based on the methodological characteristics, the list of which is shown in Fig. 15.1.
If the figures are developing more generalized, versatile nature, the complexity of indicators can be calculated for certain types of products (services) and used to determine the required number of workers, identification of specific reserves for raising labor productivity. Reliability calculations increases when determining the total labor input (technological, service and production management).
Natural indicators to determine the most accurate reflection of the dynamics of labor productivity, but can be used only in establishments producing homogeneous products. The use of so-called quasi-natural gauges (eg, conditional cans) allows you to expand the applicability of these indicators.
Employment indicators require a well-established work on technical regulation and labor integration. Mainly they are used in the workplace, plots, shops, producing diverse products, the presence of significant amounts of work in progress, which is impossible to measure the natural monetary units.
The most universal and, therefore, are the most common indicators of production cost. They can be applied to determine the level and dynamics of labor productivity in enterprises with a variety of products (services). At the same time to ensure the accuracy of measuring productivity (especially its dynamics) on cost indicators should take into account the impact on the level above all the price factor.
Classification of factors
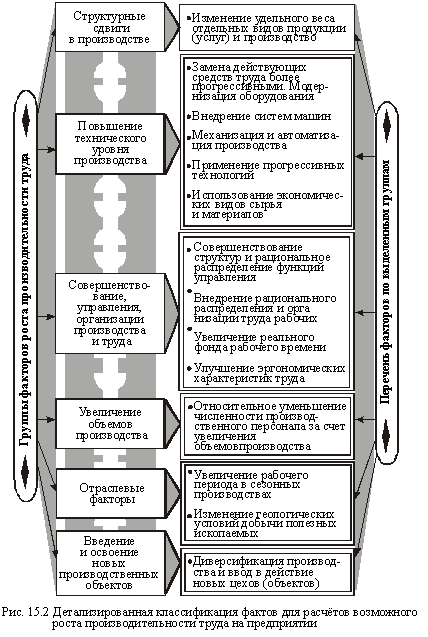
Targeted control of labor productivity, the development of specific measures to ensure more effective and full utilization of the labor potential of the enterprise (organization) require the classification of factors affecting this performance. From this point of view, all the factors that contribute to increased productivity are divided into two groups - external and internal.
The group of external factors are those that objectively exist outside the control of the individual enterprise (ie factors of national and general economic - legislation, policy and strategy, market infrastructure;.. Macrostructural changes in society, natural resources), and internal - those that directly affect at the level of labor productivity (product, technology and equipment, materials, energy, personnel, organization of production and labor, incentives, etc...). However, external factors also have specific enterprise economic interest. Taking into account it, you can motivate deeper appropriate management solutions to strategize dynamics of labor productivity for a long period.
In addition to the reduced global (system) the classification, in the practice of management for analytical purposes and may be aggregated calculations Execu zovany and other groups integrated labor productivity growth factors in the workplace. Thus, in accordance with one of them all factors that significantly affect the productivity can be grouped into the following groups:
- logistics (improvement of techniques and technologies, the use of new types of raw materials, etc...);
- organizational (greater specialization, combination, improve the management system, the organization of labor, etc...);
- economic (improving the methods of planning, system of remuneration, employee participation in company profits, etc...);
- social (creation of proper material and psychological climate, intangible promotion, improving the system of training and retraining of personnel, etc...);
- environmental conditions and the geographical distribution companies (the group of factors is isolated and analyzed mainly in mining enterprises and some processing industries).
Factor forecasting method
In the real business management (organization) practice is always current need for quantifying the effect of individual factors on the level of labor productivity. The calculations are based on the identification of reserves (unused capacity) growth of labor productivity, which is manifested both in space (for all production units) and in time (according to the calendar plan of their possible use).
Quantifying the impact of individual factors is detailed in a conventional circuit (Fig. 15.2).
From the overall effect of a change in the level of productivity is determined in the following order:
- First, the original number is calculated industrial production personnel in the billing period (Chiskh), ie, the number of conditional necessary to ensure the plan (estimated) production in the conditions of maintaining baseline production output per worker..;
- secondly, determined change (decrease "-" increase "+") of the original number of workers under the influence of individual factors and total change in the population (Ech);
- Third, it is calculated in comparison with the base period by the formula possible total labor productivity growth in the billing period (MFR)
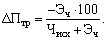 (15.1)
(15.1)
Calculation of changes in the number of initial billing period are carried out, usually by comparison of labor costs for the whole volume of products (services) in the calculation of basic conditions and activities of the relevant categories and groups of workers. The current number of employees savings through the introduction of new techniques, technologies, equipment modernization (Ech.n.t) can be calculated by the formula
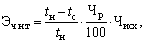 (15.2)
(15.2)
where t c, t n - production labor input respectively the old and new (upgraded) equipment (according to the old and new technologies);
The Czech Republic - the proportion of workers employed in the equipment (when using a particular technology) in the total number of employees in the base period,%.
Changes in population by reducing downtime vnutrismennyh can be determined using the formula
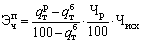 (15.3)
(15.3)
Where  - Vnutrismennyh downtime respectively in the billing and reference periods%.
- Vnutrismennyh downtime respectively in the billing and reference periods%.
Decreasing or increasing the number of employees due to the change in the share of purchased semi-finished products and cooperative deliveries can be expected enlargement formula:
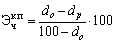 (15.4)
(15.4)
where d a d p - the proportion of purchased semi-finished products and cooperative deliveries total volume of production in the base years and calculated%.
Savings (increase) in the number of employees due to changes in the structure of production is determined by using the formula
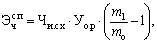 (15.5)
(15.5)
where Uo.r - where the proportion of main workers in the total number of personnel of the base period, U .;
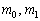 - The complexity of the specific (per 1000 units den products..) In the standard-setting the clock in the base and the settlement period.
- The complexity of the specific (per 1000 units den products..) In the standard-setting the clock in the base and the settlement period.
If it is impossible to settle on a specific formulas (especially the impact of economic and social factors), saving size and the corresponding growth of labor productivity are determined on the basis of expert assessments of the situation analysis, comparison with peers, and so on. N.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.