home  Finance Finance  books books  Pricing - Erukhimovich IL Pricing - Erukhimovich IL |
Pricing - Erukhimovich IL
1.4. Classification production costs in degree depending on the number of products
According to the degree depending on the number of products all the costs of its production and sales are divided into quasi-permanent (non-proportional) and variable (proportional).
Fixed costs do not depend on changes in the volume of production subject to the maximum use of the existing capacities of the enterprise. If the market for products it is possible to study a sharp increase in production in excess of the available production capacity, needed capital investment in the expansion of production, which will determine the increase in fixed costs. In addition, fixed costs can increase (decrease) resulting from any administrative decision (eg, increase or decrease in the costs of protection and so on. N.).
The unit cost of production fixed costs vary inversely proportional to the change in output.
By the fixed costs are depreciation of fixed assets, salary management personnel and working-time-worker, rent for premises and equipment, utilities and others.
The total amount of fixed costs calculated for the whole company and its structural divisions; then for each item of expenditure in the cost calculation is determined by the proportion depending on the technological conditions of production. The rate of fixed costs at each facility shall be determined after a detailed cost-benefit analysis taking into account the technical and organizational conditions for its operation.
Variable costs vary in proportion to the volume of products. The unit cost they remain unchanged (at a constant rate of consumption of raw materials, fuel, certain types of energy and constant prices). These costs can be calculated for each product type based on consumption rates and the price of the resource unit.
The variables include the cost of raw materials, wages of workers, piece workers, transport services for transportation of raw materials, finished products and others.
Some costs are considered as part of the variables representing the amount of variable and fixed costs. These include the cost of replacement equipment, tools, low value items, the cost of maintenance and operation of plant and equipment, wages of production workers with charges, overhead expenses and others.
The amount of variable and fixed costs constitutes the cost of production.
The dependence of the variable and fixed costs of production volume based on the total output per unit of product, and is shown in Fig. 1.
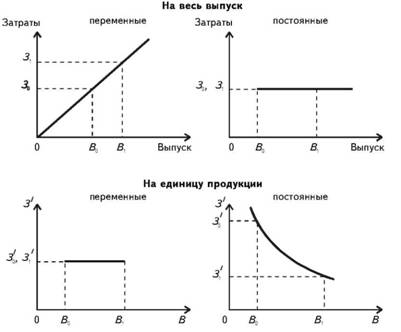
Fig. 1. Dependence of the production costs by the number of products
How calculated fixed costs in the unit cost of production and its annual production? For example, total cost of production of one product is 80 USD, annual output -. 1800 pcs. Product Costing and allocation of cost into fixed and variable is given in Table. 1. From these data it can be seen that the proportion of fixed costs in the shop cost is 17.4% (12.69 / 73.0 * 100%), in the production - 21.7% in the total - 23.5%.
How to change the unit cost of production and its annual output, if as a result of any technical event production output will increase by 10%?
As can be seen from Fig. 1, the fixed costs per unit of output will vary in inverse proportion to the variables - do not change, and based on the annual production of the fixed costs remain constant, the variables will increase in direct proportion.
This dependence is described by the following formulas.
1. Unit costs after the release change
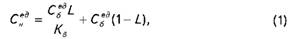
where Sedb - unit cost in the base period;
L - rate (share) of fixed costs (cost);
Apt. - The rate of change in output,
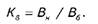
In this example,
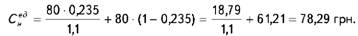
Therefore, an increase in output by 10% the cost of one product to decline by 2.1% (80-78,29) / 80 * 100%
2. Cost of the annual production
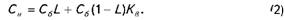
In this example,
CH = 144,02 • 0,235 + 144,02 • 0,765 • 1,1 = 33,77 + 121,28 = 155,05 thousand. UAH.
Table 1
CALCULATION
Product costs and distribution costs into fixed and variable
Rate | The cost of a single product, UAH. | Total expenses, thousand. UAH. | ||||||
p / p | Article expenses | permanent | Total | including | Total | including | ||
cost% | standing | variables | standing | variables | ||||
I | Raw materials | - | 60.0 | - | 60.0 | 108,00 | - | 108,00 |
Waste ( "-") | - | 9.0 | - | 16,20 | 16,20 | - | 16,20 | |
Defined minus waste | - | 51.0 | - | 51.0 | 91.80 | - | 91.80 | |
II | Refining expenses | |||||||
Fuel Processing | 40 | 4.2 | 1.68 | 2.52 | 7.60 | 3.0 | 4.60 | |
Energy costs | thirty | 3.6 | 1.08 | 2.52 | 6.48 | 1.94 | 4.54 | |
Wages of production workers with charges | 60 | 4.5 | 2.70 | 1.80 | 8.10 | 4.86 | 3.24 | |
Depreciation | 100 | 2.4 | 2.40 | 4.30 | 4.30 | - | ||
Replacement equipment, tools, | 10 | 0.8 | 0.08 | 0.72 | 1.44 | 0.14 | 1.30 | |
Maintenance and operation of fixed assets | 65 | 3.0 | 1.95 | 1.05 | 5.40 | 3.51 | 1.89 | |
The guild costs | 80 | 3.5 | 2.80 | 0.70 | 6.30 | 5.04 | 1.26 | |
shop cost | - | 73.0 | 12.69 | 60.31 | 131.42 | 22.79 | 108.63 | |
III | works general expenses | 100 | 4.0 | 4.00 | - | 7.20 | 7.20 | - |
actual manufacturing cost | 77.0 | 16.69 | 60.31 | 138.62 | 29.99 | 108.63 | ||
IV | Non-production costs | 70 | 3.0 | 2.10 | 0.90 | 5.40 | 3.78 | 1.62 |
full cost | 80.0 | 18.79 | 61.21 | 144.02 | 33.77 | 110.25 | ||
Consequently, when a 10% increase in output cost of annual production increase by 7.7% ie (155,05-144,02) / 144.02 * 100%
If the implementation of any technical measures to change the volume of production, but also lead to additional costs ( "+") or save ( "-") of one of the types of material resources, the new cost price will be:
• per unit of production
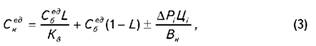
where API - an additional expense ( "+") or savings ( "-") i-th kind of resource to the new production capacity;
Ts - price of i-type resource;
• based on annual production
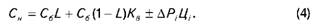
For example, in this example, the fuel consumption for technological needs will be reduced by 1.5%. Then
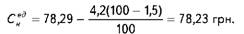
Implementation of technical measures often require additional capital investments in fixed assets, resulting in increased costs under the item "Depreciation".
In this case, the unit cost will be calculated according to the formula
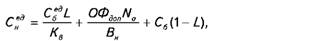
where OFdop - additional cost of fixed assets as a result of technical measures;
Na - depreciation rate. For example, in this example, to increase the output you need to purchase additional equipment in the amount of 10 thousand. UAH. with the annual rate of depreciation of 15%. Then after the event the unit cost will be
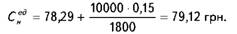
In view of the factors examined (changes in production volume, and fuel-saving technology further depreciation) unit cost reaches 79.06 USD., A decrease compared to the level of 1.2% in the base period.
All this is important to consider, as the cost is the basis of the prices of products.




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.