home
 Management Management
 International Management - Rodchenko VV International Management - Rodchenko VV
|
International Management - Rodchenko VV
Training for managerial personnel abroad
Experience in industrialized countries shows that the introduction of flexible automated production requires an additional amount of knowledge for engineers and managers. Such training can be received only in the course of study in higher and secondary specialized educational institutions and training centers.
In this constantly felt an acute shortage of highly qualified specialists, including in the field of management. One of the main reasons is the constant increase of the requirements for their competence.
Experts define competence as a combination of the following factors:
• Knowledge as a result of the formation of the individual;
• skills as a result of experience and training;
• methods of communication as the ability to work with people.
Training managers abroad is carried out continuously, in accordance with the concept of lifelong learning. This concept is defined as a set of measures which gives a person the opportunity to learn throughout their lives by the principle: any valuable education, in any place and any content. They put forward the requirements of the individual on the distribution of educational resources throughout their life, rather than their concentration in certain period according to the traditional logical sequence.
For example, in the United States for training managers involved about 1,500 schools. In 1985, $ 60 billion was spent. for all forms of training management, including 13 billion dollars. - On training managers.
Training and retraining of managers in US firms, Europe and Japan attached great importance.
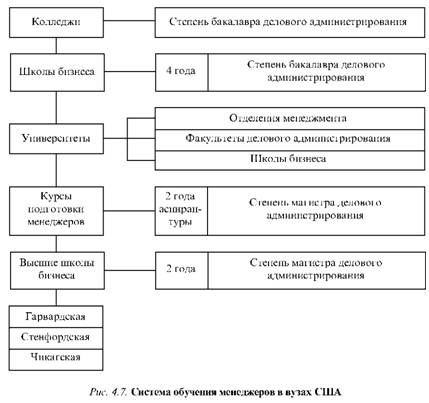
Fig. 4.7 shows the management training scheme in the US universities.
In addition to training in universities abroad widely developed system of training in enterprises. Almost every company has its own system of training and retraining. New employees must be retrained each year, so that the learning process is continuous. Firms use huge amounts on training and retraining. So, 1VM company only in 1986, spent 750 million on employee training dollars.
Japanese firms spend on training per employee in 3-4 times more than the US. In Japan, continuing education is seen as part of the labor process. The basis of Japanese professional training in companies is the concept of "flexible workers", whose purpose - selection and training of the employee for not one, but 2-3 specialties, and then training throughout life.
The transition to new technologies requires significant costs associated with the upgrading of knowledge. It is believed that retrained workers cheaper than replacing them. But here comes the problem of existence of a mechanism for continuous training of all employees in the process of transition from one set of required knowledge and skills to the next.
According to the experts, a great disadvantage training programs is their lack of economic knowledge. The vast majority of workers in American companies do not understand the essence of economic systems. They are not always aware of how to increase productivity, quality and competitiveness of products could have an impact on their own standard of living and job security.
In the US example, consider a system of retraining and improvement of qualification of business managers.
• In the US, there are about 150 short courses at business schools and universities that teach in the year to 10 thousand. People .; They are designed mainly for 2-3 weeks of training, but sometimes - and up to two years. Expenses paid by firms and account for about 16 billion dollars. in year.
• Evening courses are also paid for by companies and aimed at training senior and middle management staff.
• American Association of Managers spends annually more than 2,000 seminars and courses, which are taught to 100 thousand. Managers of the lower and middle management.
• In-house training courses for managers of lower and middle management levels are 200 large and medium-sized firms. For example, in the training center of the company "Xerox" trained 12 thousand. People. in year. Large complexes and their training programs have company "IBM", "Western Electrics", "General Motors".
• training centers at colleges and universities have more than 400 firms which carried out specialized training program, developed by the contracting authority.
• Re-training at the workplace involves the creation of groups of workers who are trained on the basis of specific economic situations. This system is used of "IBM", "General Motors", "Hewllet-Packard", "Boeing" et al.
• Evening of the American Institute of world trade school holds up to 45 courses in its three centers; Classes are held 1-2 times a week, from 3 to 15 sessions, with the cost of training ranges from 80 to 500 dollars. for the course.
In the UK, the retraining of managerial staff involved:
- Academic courses;
- Private centers;
- Small firms, leading training and carrying out counseling;
- Special courses continuing education management at universities.
Many theorists and business practices predicted an increase of difficulties and reduced effectiveness in the training of managers, because in the last 30 years, a set of courses and program content changed slightly. Highly qualified managers need for successful work, but not nearly enough. in psychology training programs to learn skills allow the formation of a cohesive group. Increased competition requires managers to not only quantify the effects of skills as a permanent target to find new non-standard solutions to unprecedented problems. These skills can be described as a business. In recent years, an increasing demand for entrepreneurs. For this new programs needed. Fig. 4.8 shows a model of systematic training in foreign enterprises.
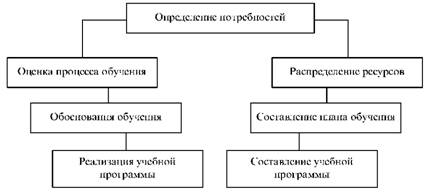
Fig. 4.8. Model systematic study abroad
Of great importance are teaching methods. Among the most promising point such as simulations, role plays, seminars. Traditional methods also gradually lose its significance. Table. 4.7 Brief descriptions used by foreign companies as the methods of training in the workplace and beyond.
Table 4.7
Methods of training
| Training in the workplace | Training outside the workplace |
|
"Copy" - the employee "attached" to a specialist, copying his actions Mentoring - Manager sessions with their staff in the course of daily work Delegating - the transfer of the employees clearly defined task pane with the authority for decision-making stipulated range of issues. At the same time the manager trains his subordinates in the course of work Method of increasing complexity of tasks - a special program operating activities, which was built by order of importance, the volume of tasks and solutions of increasing complexity. The final level - independent quest Rotation - the employee is transferred to a new job or position for more professional development and extension of experience Execution of training manuals, methodologies |
Business game - party games (usually a computer), including analysis of the example, in which participants receive a role in the gaming business situation and consider the consequences of decisions Teaching situations - real or fictional situation with management issues for analysis. This eliminates the rigid framework of time that bind thought in a production environment Simulation - Play real operating conditions Training senzitivnost - participation in the group in order to increase human susceptibility and improve the ability to interact with others. Held in the presence of a psychologist Role-playing game (modeling human behavior) - worker puts himself in someone else's place in order to obtain practical experience (usually in interpersonal communication) and received confirmation of the correctness of his behavior |
Of course, the list does not exhaust the methods of teaching in the table, since virtually every foreign company has its own system of training and its specific methods. For example, the management of the American branch of "Apple" made a decision on his ascent of Mount Kilimanjaro managers (North Africa) in order to strengthen the corporate spirit of its employees and to improve mutual understanding between them.
But, in spite of the existing set of methods, experts agree that it should focus on the assessment of external influences, the main integration activities with adverse events. All this leads to a strengthening of the leading role of managers in all aspects and at all levels. They are required skill to inspire their subordinates, and to mobilize their energies to solve common problems.
Based on this concept focuses on three training and development managers (PPKM):
1) The piecemeal approach that does not require investments not related to the specific objectives of the organizations giving basic training in the training centers; He recognized experts unpromising;
2) The formal approach, considering PPKM as part of a manager's career; it is aligned with the company's resource needs and personal aspirations. The basis is the basic knowledge and special courses on the development of individual skills (using teachers and line managers trainee);
3) targeted approach, viewed as a continuous learning to solve problems.
As already noted, PPKM closely associated with the company's strategy and goals of the individual learner. They are implemented by means of elective courses, strictly linked to the nature of the work.
In addition to learning processes an important role in working with the managers of the company plays a policy with respect to those already working.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.