home
 Management Management
 Management - Vikhanskiy OS Management - Vikhanskiy OS
|
Management - Vikhanskiy OS
1.4. Organization Management Process
Management, although it plays a very definite role in the organization, nevertheless permeates the whole organization, touching and affecting virtually all areas of its activities. However, for all the variety of interaction between management and organization, it is possible to establish quite clearly the boundaries of activities that make up the content of management, and also to define quite clearly the subjects of managerial activity - managers.
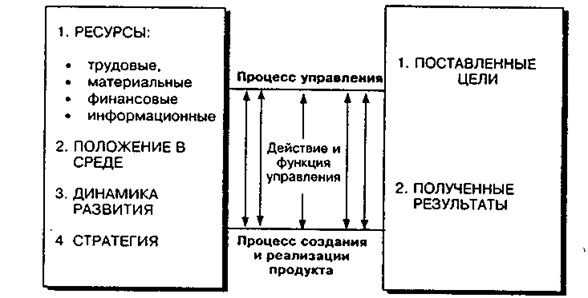
Management of the organization is presented in the form of a process for the implementation of a certain type of interrelated actions for the formation and use of the resources of the organization to achieve its goals. Management is not equivalent to all the activities of the organization to achieve the ultimate goals, but includes only those functions and activities that are related to the coordination and establishment of interaction within the organization, with incentives for the implementation of production and other activities, with the targeted orientation of various activities, P. (Figure 1).
Initial state End state
Fig. 1. Place of the process of managing the organization
The content and set of actions and functions carried out in the management process depend on the type of organization (business, administrative, public, educational, army, etc.), on the size of the organization, on the scope of its activities (production of goods, services), from Level in the management hierarchy (senior management, middle management, lower level of management), from functions within the organization (production, marketing, personnel, finance) and many other factors. However, despite all the diversity, as A. Fayol drew attention to in 1916, for all management processes in the organization, there is the presence, in general, of homogeneous activities. It is possible to group all types of management activities into four main management functions: 1) planning, which consists in selecting goals and an action plan for their achievement; 2) the function of the organization, through which the distribution of tasks between individual units or employees and the establishment of interaction between them; 3) management, consisting in motivating the performers to implement the planned actions and achieve the set goals; 4) control, which consists in comparing the actually achieved results with those that have been planned.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.