home
 Economy Economy
 Books Books
 History of the world economy - Polyak GB History of the world economy - Polyak GB
|
History of the world economy - Polyak GB
Trade and finance
The agricultural and handicraft surplus production, created first in subsistence farming, allowed it to begin an exchange between producers, then on a larger scale - within the country, and later exported outside the state. On the level of trade and availability in the country already in the III millennium BC. E. Wide trade links are evidenced by the texts of trade agreements that have reached us, not only for the sale of agricultural and handicraft products, but also for real estate (land, houses). As a result of international trade, the necessary goods were imported into the country. From India they brought cotton, jasper, from Iran - tin, lapis lazuli, obsidian, from Syria - cedar wood.
To ensure developed economic relations, the state fulfills its functions, and, consequently, tax collection, the monetary and tax systems are introduced. First taxes were levied in kind (cattle, grain), then in the XX century. BC. E "began to use weighted metal money in the form of ingots of silver - shekels, whose weight was about 8 g.
Real estate transactions (sale, land, houses), domestic trade, and especially foreign trade, caused the need to create banks that appeared in the II millennium BC. E. Banks gave loans. If the financial position of the borrower was stable, he received a loan at 20-30% per annum. If his position was doubtful, then the bank took control of the borrower's real estate. In Babylon in the VI. BC. E. Already known was the banking dynasty "Egibi and Sons" , in Nippur - the Murash dynasty . Already at that time, the banks of wealth exceeded not only the temples, but in a number of cases the state, concentrating in its possession of land, houses, livestock.
Cities. Building
The rapid separation from agriculture of handicraft production as an independent industry served as the basis for the development of numerous cities, many of which arose already in the IV millennium BC. E. The high density of urban population is evidenced by the close distance between cities. For example, the major cities of Lars and Uruk were 24 km from each other. In the year 3000 BC. E. The population of Uruk was about 50 thousand people.
Cities have become administrative, economic and cultural centers. Urban planning served as the basis for the development of construction equipment. Since ancient times, for construction began to use raw brick, and then fired in ovens. The use of bricks as a building material allowed already at the beginning of the III millennium BC. E. Large amounts of massive stepped temple towers (ziggurats) on the artificial embankments (because of the swampiness of the terrain) .
The largest ziggurat was built in Babylon in honor of the god Marduk . It had a height of about 60 m, eight tiers spiral upward. At the top of the ziggurat was a temple decorated with gold. Apparently, this ziggurat became the basis of the biblical legend of the Tower of Babel.
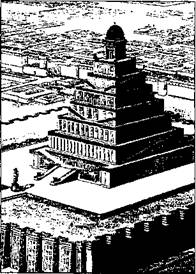
One of the reconstructions of the Tower of Babel
The scale of construction works in Ancient Mesopotamia can be judged by the navigable and irrigation canal, a length of 1600 km, built more than 4000 thousand years ago.
Naturally, not only temple structures were erected, but also palace, administrative and residential buildings. We also built large rooms for archives, as clay tablets with information occupied a very large amount of space.
In the construction of the first began to use faience tiles, which served to decorate the exterior walls of buildings. Wall masonry was strengthened with a substance made on the basis of asphalt. Inside the temples and palaces the walls were decorated with mosaics. Sculptures, reliefs were used to decorate the premises. Such were the temple of the goddess Ishtar in Ash-Shura, palaces and temples in Ur, Babylon. The architecture of Mesopotamia had an impact on the architecture of the entire Middle East.
Urban development has reached an impressive scale. Herodotus, who was an eyewitness, described Babylon "... lies in a wide plain - a huge city in the form of a square, whose sides are more than 22 km long, and the inscribed steep - about 90 km. Not only in size, but also in beauty, it surpasses any city in the known world. " The city was surrounded by a wall. The width of the wall was such that one-room buildings were located on its inner and outer sides, between the buildings there was a road on which a chariot drawn by four horses could turn. At that time in the city lived about 500 thousand people. For comparison: in the heyday of Rome, that is, after 500-600 years, its population was 900 thousand people, and in 1526 after the plague epidemic - only 55 thousand people.
The cities were not only large, but also quite equipped. Houses of townspeople already in the III millennium BC. E. Had plates on which it was possible to put vessels for cooking. In many cities there were water pipes.
The world's first canal-water pipeline was built before 2500 BC. E. In the Sumerian city of Lagash. An example of a high level of construction of water pipes for cities can serve as a water pipeline, built in 690 BC. E. For the city of Nineveh, a length of 57 km. The bottom of the canal was covered with asphalt and lined with limestone, the walls were fortified with limestone blocks. When crossing the river, the water main was raised to an aqueduct 2730 m long and 13 m wide.
In the palaces of kings and rich people already in 2300 BC. E. There were toilets. The sewage in the bitumen-covered gutters fell into the sewerage wells.
Serving the branches of the economy required the development of transport and transport network. For these purposes, the natural waterways of the rivers Tigris, Euphrates, numerous water channels were used. On land, roads were laid along which, from ancient times, goods were transported on carts drawn by mules. The first image of wheeled vehicles, dating back to the 4th millennium BC. E., Found in the territory of the former Sumer.
Mesopotamia gave the world not only the first samples of civil, but also military equipment and equipment. Around 3000 BC. E. Here appeared chariots. In the 1st millennium BC. E. Siege mechanisms were created - battering rams . They were wooden towers on four or six wheels, which had either flat or pointed rams for piercing stone walls and fortress gates. In the III thousand appeared protective armor made of leather. Metal helmets began to be used around 2500 BC. E. Around 1000 BC. E. Here appeared the first scaly armor-mail, made of iron rings.
Thus, already in ancient times, the economy of many countries carried a burden of production of weapons, forcing these countries to seek inwardly or abroad raw materials, to increase its extraction or purchase, diverting material and financial resources.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.