home
 Management Management
 Management - Vikhansky OS Management - Vikhansky OS
|
Management - Vikhansky OS
2.2. Analysis of the internal environment
Internal company environment - this is part of an overall environment that is within the organization. It has a constant and most direct impact on the functioning of the organization. The internal environment has several sections, each of which includes a set of key processes and elements of the organization, the state of which collectively define the potential and the opportunities available to the organization. Personnel section of the internal environment includes processes such as the interaction of managers and workers; hiring, training and promotion of staff; evaluation of results and stimulation of labor; creating and maintaining relationships between employees and etc. Organizing section includes: communication processes; organizational structures; rules, regulations, procedures; the allocation of rights and responsibilities; hierarchy of subordination. The production section includes product manufacture, supply and maintenance of storage facilities; Maintenance Technology Park; implementation of research and development. The marketing section of the internal environment of the organization covers all the processes that are associated with product sales. This product strategy, pricing strategy; strategy of product promotion in the market; range of markets and distribution systems. The financial section includes the processes related to ensuring the effective use of operations and cash flows in the organization. In particular, it is to maintain liquidity and to ensure profitability, investment opportunities, etc.
The internal environment as it is fully permeated organizational culture, which is the same as the above sections, shall be subjected to serious study in the analysis of the internal environment of the organization.
Organizational culture can help to ensure that the organization is very strong, stable to survive in the competitive structure. But it may be true that the organizational culture weakens the organization, not allowing it to develop successfully, even if it has a high technical and technological and financial potential. The special importance of the analysis of the organizational structure for the strategic management is that it not only defines the relationship between the people in the organization, but also has a strong influence on how the organization builds its interaction with the external environment, how to treat their customers and what methods chooses conducting competition.
Since the organizational culture does not express symptoms, it is difficult to study. But nevertheless, there are several stable points that are important to clarify in order to try to point out those strengths and weaknesses, organizational culture that gives an organization.
Information about the organizational culture can be obtained from various publications in which the organization presents itself. For organizations with a strong organizational culture is characterized by emphasizing the importance of the people working in it. Such organizations in the publications currently paying great attention to explaining its brand philosophy, the promotion of its values. At the same time, organizations with weak organizational culture characterized by a tendency in publications talk about formal organizational and quantitative aspects of its work.
The notion of organizational culture enables observation of how employees work at their jobs, they communicates with each other, what they prefer in conversations. Also, an understanding of organizational culture can be improved, if acquainted with the way the system is built a career in the organization and what criteria are used for the promotion of workers. If the organization of the workers are moving quickly and the results of individual achievements, we can assume that there is a weak organizational culture. If the career staff is long-term and preference is given to SEO ability to work well in a team, the organization has clear signs of a strong organizational culture.
Understanding organizational culture conducive to study whether there are organizations in sustainable commandments, unwritten norms of behavior, ritual activities, legends, heroes, etc., how about this, all employees are aware of the organization and how serious they are to all of this. If employees are knowledgeable about the history of the organization, seriously and with respect for the rules, rituals and organizational symbols, it can be assumed with a high degree of compliance with the reality that the organization has a strong organizational culture.
In order to successfully survive in the long run, the organization must be able to predict the difficulties which may arise in its path in the future, and what new opportunities may open up for her. Therefore, strategic management, studying the external environment, focuses on finding out what threats and opportunities which conceals the external environment.
To cope with the threats and opportunities to effectively use, does not have enough knowledge of only one of them. You can know about the threat, but not be able to resist it, and thus fail. You can also know about the opening of new opportunities, but did not have the capacity to use them, and therefore not be able to use them. Strengths and weaknesses of the internal environment of the organization to the same extent as the threats and opportunities, define the conditions for the successful existence of the organization. Therefore, the strategic management at the internal environment analysis is interested in revealing what the strengths and weaknesses of the individual components have the organization and the organization as a whole.
In summary, it can be stated that the analysis of the environment, as it is conducted in strategic management, aims to identify the threats and opportunities that may arise in the external environment to the organization, as well as strengths and weaknesses, which have organization. To solve this problem and developed certain environmental analysis techniques that are used in strategic management.
The applied method for the analysis of the environment SWOT (an acronym composed of the first letters of English words: strength, weakness, opportunities and threats) is fairly widely recognized approach that allows to carry out a joint study of the internal and external environment. Applying the method of SWOT, can not establish the link between the strength and the weakness inherent in the organization and external threats and opportunities. SWOT methodology is first to identify the strengths and weaknesses as well as threats and opportunities, and further - to establish chains of connections between them, which later can be used to formulate the organization's strategy.
First, taking into account the specific situation in which the organization compiled a list of its strengths and weaknesses, as well as a list of threats and opportunities. Once compiled a list of the specific strengths and weaknesses of the organization, as well as threats and opportunities, comes the stage of establishing links between them. To establish these connections in a matrix SWOT, which is as follows (Fig. 3.2).
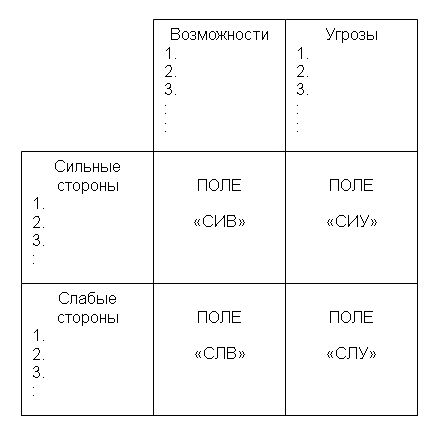
Figure 3 2. SWOT Matrix
On the left are two sections (strengths, weaknesses), in which, respectively, are made all identified in the first stage of the analysis the strengths and weaknesses of the organization. At the top of the matrix are also two sections of stands (opportunities and threats) that are subject to all of the identified opportunities and threats.
At the intersection of sections formed of four fields: "SIV" field (strength and capabilities); the "CSC" (force and threats); the "SLV" (weakness and opportunities); the "SLN" (weakness and threats). In each of these fields, the researcher must consider all possible pair combinations and highlight those that need to be taken into account in the development of behavioral strategies of the organization. For those couples who were selected from the field "SIV", should develop a strategy on the use of the organization's strengths in order to get the most from the opportunities that emerged in the external environment. For those couples who were on the "SLV" strategy should be built in such a way that at the expense of emerging opportunities to try to overcome the weaknesses in the existing organization. If the couple is on the "CSC", the strategy must involve the use of force the organization to eliminate the threats. Finally, for couples, "SLE" on the field, the organization must develop a strategy that would allow it to get rid of weakness and try to prevent the threat hanging over it.
In formulating a strategy, it should be remembered that the opportunities and threats can be transformed into its opposite. So, untapped opportunities may become a threat if it is used by the competitor. Or on the contrary, successful prevention of threats may create an organization more powerful party in the event that competitors are not eliminated this as a threat.
For the successful application of the methodology of the SWOT-analysis environment organization it is important to be able to not only discover threats and opportunities, but also to try to evaluate them in terms of how important for the company is registered at the strategies for the behavior of each of the identified threats and opportunities.
In order to evaluate the method of positioning each particular opportunities on the matrix features (Fig. 3.3).
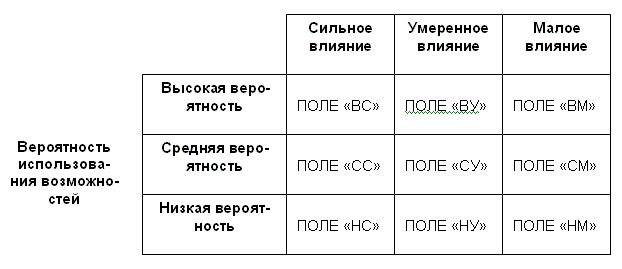
Figure 3. Matrix 3 possibilities
This matrix is constructed as follows: the top postponed the degree of influence on the possibility of the organization (a strong impact, moderate impact, low impact); side postponed the probability that the organization will be able to seize the opportunity (high probability, medium probability and low probability). The resulting matrix of nine possibilities within the fields have a different meaning for the organization. Features that fall on the field, "Sun", "TA" and "CC" are of great importance for the organization, and it is necessary to use. The possibilities of getting on the field "CM", "OU" and "NM", virtually no noteworthy organization. With respect to opportunities that come on the rest of the field, management must take a positive decision on their use, if the organization has enough resources.
A similar matrix is prepared for the threat assessment (Fig. 3.4). Top postponed the possible consequences for the organization, which may result from implementation of the threat (destruction of the critical state in a serious condition, "minor injuries"). Side postponed the likelihood that a threat will be realized (high probability, medium probability and low probability).
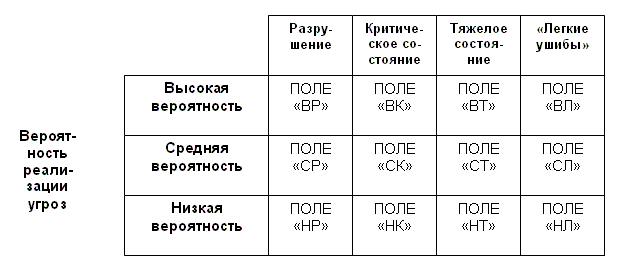
Figure 4 March Matrix threats
Those threats, which fall on the field, "BP", "VK" and "SR", represent a very great danger to the organization and require immediate and compulsory removal. Threats, trapped on the field "BT", "IC" and "the HP", should also be in the field of view of senior management and be eliminated in the paramount consideration. As for the threats that are in the fields of "NC", "ST" and "VL", then it requires careful and responsible approach to eliminate them.
Caught in the remaining fields threat should also not fall out of the field of view of the organization's leadership. In this case, it should be careful monitoring of their development, although it does not attempt to resolve their priority.
In addition to methods for studying the threats, opportunities, strengths and weaknesses of the organization to analyze the environment can be applied a method of drawing up its profile. This method is useful for profiling separately makrookruzheniya, immediate environment and the internal environment. Using the method of preparation of the environment profile is possible to estimate the relative importance to the organization of individual environmental factors.
The method of preparation of the environment profile is as follows. The table Environment Profile (tab. 3.1) are issued separate environmental factors. Each factor is given by the expert way:
• assessment of its importance for the industry on the scale: 3 - strong value, 2 - moderate value, 1 - poor value;
• an assessment of its impact on the organization of the scale: 3 - strong influence, 2 - moderate effect, 1 - weak effect, 0 - no effect;
• Evaluation of the effect of orientation on the scale: 1 - positive trend, -1 - negative direction.
Table 3.1.
profile environment
environmental Factors |
The importance of the industry A |
The impact on the organization in |
The direction of the effect of C |
The importance of D = A? B? C |
Further, all three expert opinions multiplied, and it turns out the integrated assessment, showing the degree of importance of the factor for the organization. For this assessment, management may determine which of the environmental factors are relatively more important to their organization and, therefore, deserve the most serious attention, and what factors deserve less attention.


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.